Vehicle cathodic protection
Content
- The essence of cathodic protection
- What is iron corrosion
- Ability to prevent corrosion
- How to choose an anode
- metal garage
- Ground loop
- Metallic rubber tail with ground effect
- Protective electrodes-protectors
- How to mount protection
- What devices are used
- How to make a cathodic protection device yourself
- Feedback on the effectiveness of cathodic protection
- Other ways to protect
Despite the widespread use of the method of cathodic protection of metal structures in serious industries (energy, pipelines, shipbuilding), there are few devices intended for cars in the Russian-speaking sector of the network.
The cathodic protection of a car against corrosion in the conversations of experienced drivers has long turned into something mysterious and overgrown with rumors. It has both fierce adherents and skeptics. Let's find out what we're talking about.
The essence of cathodic protection
The main enemy of the car, limiting its service life, is not mechanical breakdowns at all, but the general rusting of the metal case. The process of corrosion of the iron from which the machine is made cannot be reduced to a single chemical reaction.

Sprayed soundproofing corrosion
The destruction of the metal, turning it into ugly red spots of rust, occurs as a result of a combination of various factors:
- features of the climate in which the car is operated;
- the chemical composition of air, water vapor and even soils in the area (affect the properties of road dirt);
- the quality of the body material, the presence of bumps and damage, the repairs carried out, the protective coatings used, and dozens of other reasons.
In the most general terms, the essence of the processes of corrosion of a machine can be explained in this way.
What is iron corrosion
Any metal in structure is a crystal lattice of positively charged atoms and a common electron cloud surrounding them. In the boundary layer, electrons, which have the energy of thermal motion, fly out of the lattice, but are immediately attracted back by the positive potential of the surface they left.
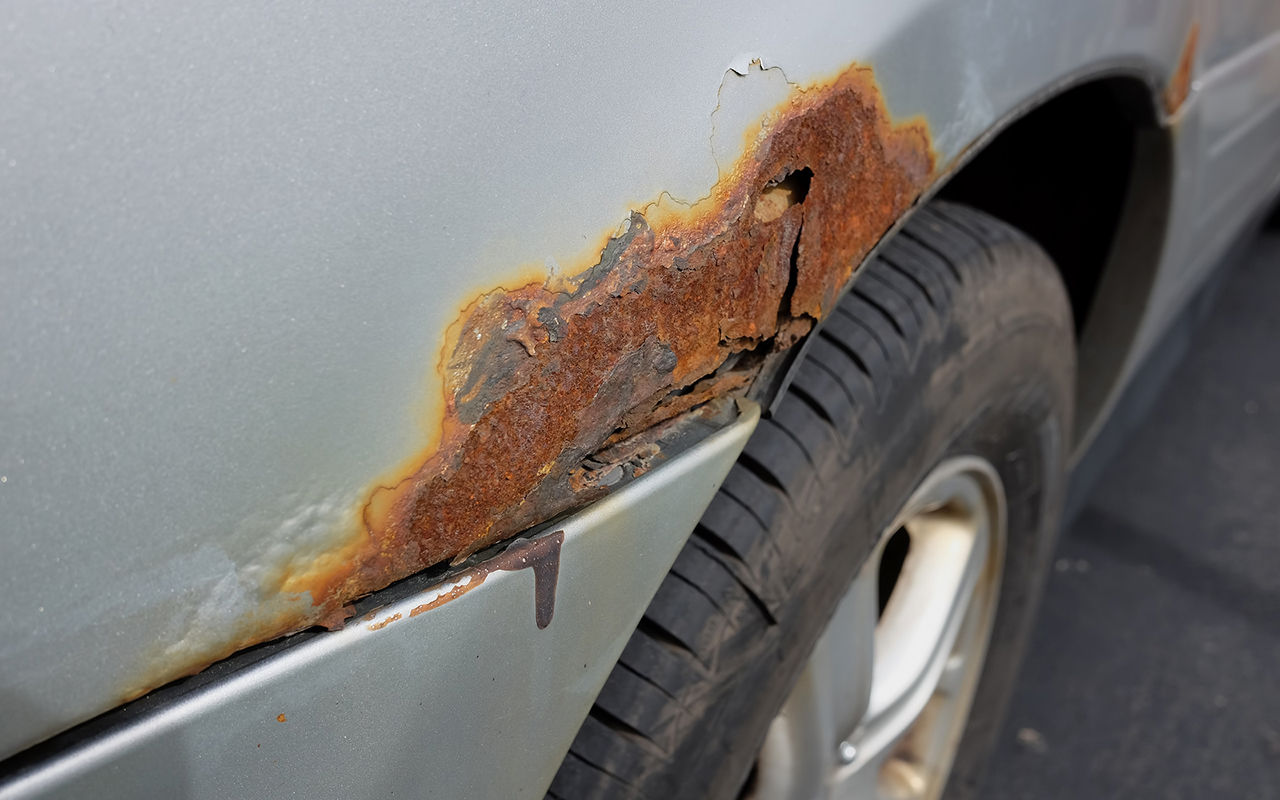

Car body corrosion
The picture changes if the metal surface comes into contact with a medium capable of transporting electrons - an electrolyte. In this case, the electron that left the crystal lattice continues to move in the external environment and does not return any more. To do this, a certain force must act on it - a potential difference that appears if the electrolyte connects two different metals with different properties by conductivity. It depends on its value which of the two metals will lose electrons, being a positive electrode (anode), and which one will receive (cathode).
Ability to prevent corrosion
There are a lot of folk myths around how to protect your car from rust in the driving community. In reality, there are two ways:
- Protect the metal surface of the body from contact with electrolytes - water, air.
- With an external energy source, change the surface potential so that the iron body from the anode turns into a cathode.
The first group of methods is a variety of protective anti-corrosion coatings, primers and varnishes. Car owners spend serious money, but you should understand that corrosion cannot be stopped in this way. It only hinders the access of the active reagent to the body iron.
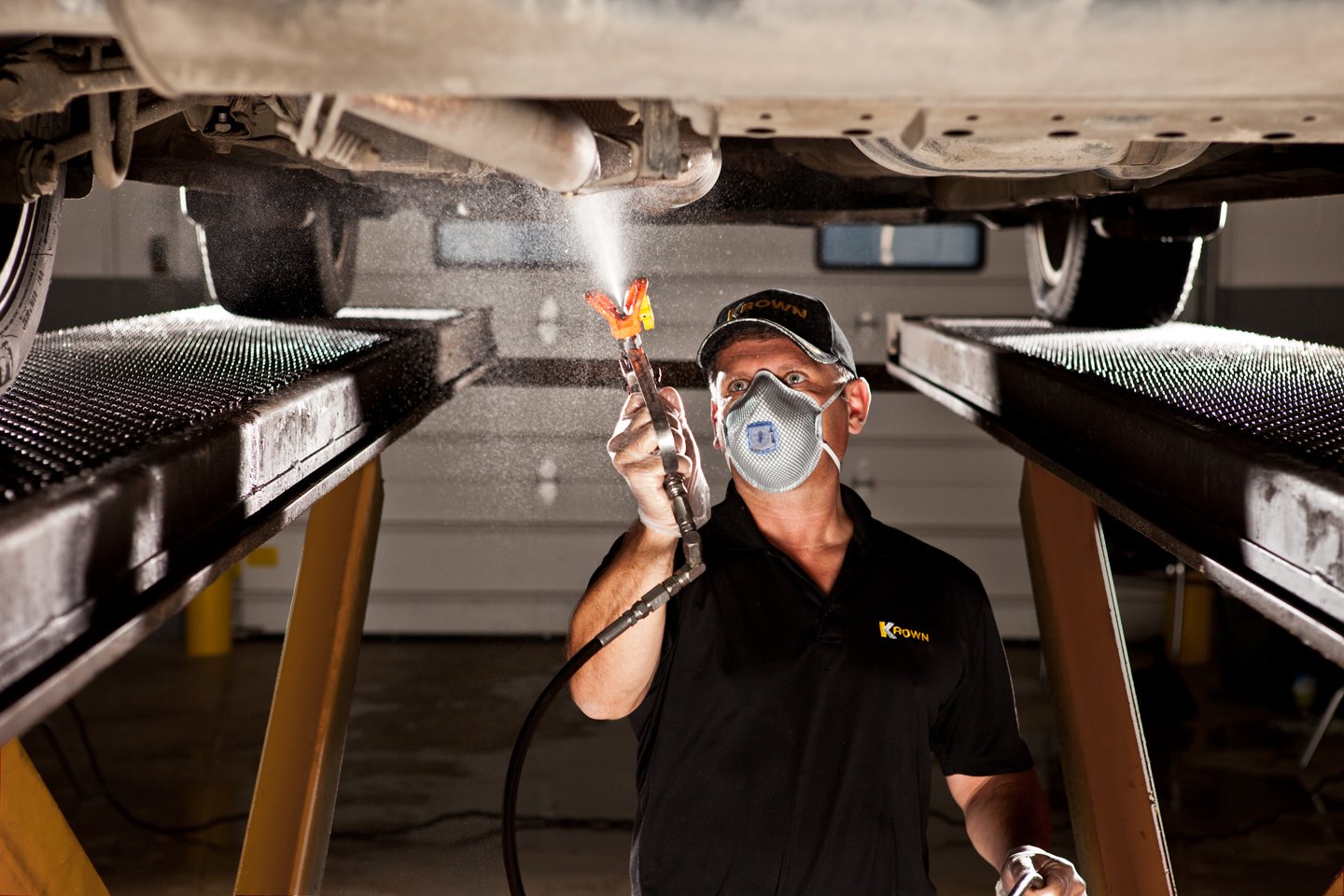

Anti-corrosion treatment of the car
Electrochemical protection technologies can be divided into two technologies:
- Using an external source of electricity (car battery), using a special circuit, create an excess of positive potential on the body so that the electrons do not leave the metal, but are attracted to it. This is the cathodic protection of the car.
- Place elements of a more active metal on the body to create a galvanic pair in which it will become the anode, and the car body will become the cathode. This method does not need to be connected to a battery at all and is called tread or anode protection.
Let's consider each of the methods.
How to choose an anode
In the role of an external circuit, you can successfully use the metal surfaces of the garage, the ground loop in the parking lot and other means.
metal garage
Through a wire with a connector, the board of the cathodic protection device is connected to it and the necessary potential difference is created. This method has repeatedly proven to be highly effective.
Ground loop
If the car is parked in an open area, an external loop for galvanic protection can be created around the perimeter of its parking lot. Metal pins are driven into the ground in the same way as conventional grounding and connected into a single closed loop by wiring. The car is placed inside this circuit and connected to it through a connector in the same way as in the garage method.
Metallic rubber tail with ground effect
This method implements the idea of creating the necessary electropositive potential of the body relative to the road surface. The method is good because it works not only when parked, but also in motion, protecting the car just when it is especially vulnerable to moisture and road chemicals.
Protective electrodes-protectors
As electrodes that create a protective potential, steel plates are used, the composition of which is close to the metal of the body itself. This is necessary in case the device breaks down, so that the placed plates themselves do not become a source of corrosion, creating a new galvanic pair. The area of each plate is optimal in size from 4 to 10 cm2, the shape is rectangular or oval.
How to mount protection
One separate electrode creates a protective potential area around itself within a radius of 0,3-0,4 meters. Therefore, the full equipment of a medium-sized car will need from 15 to 20 such plates.
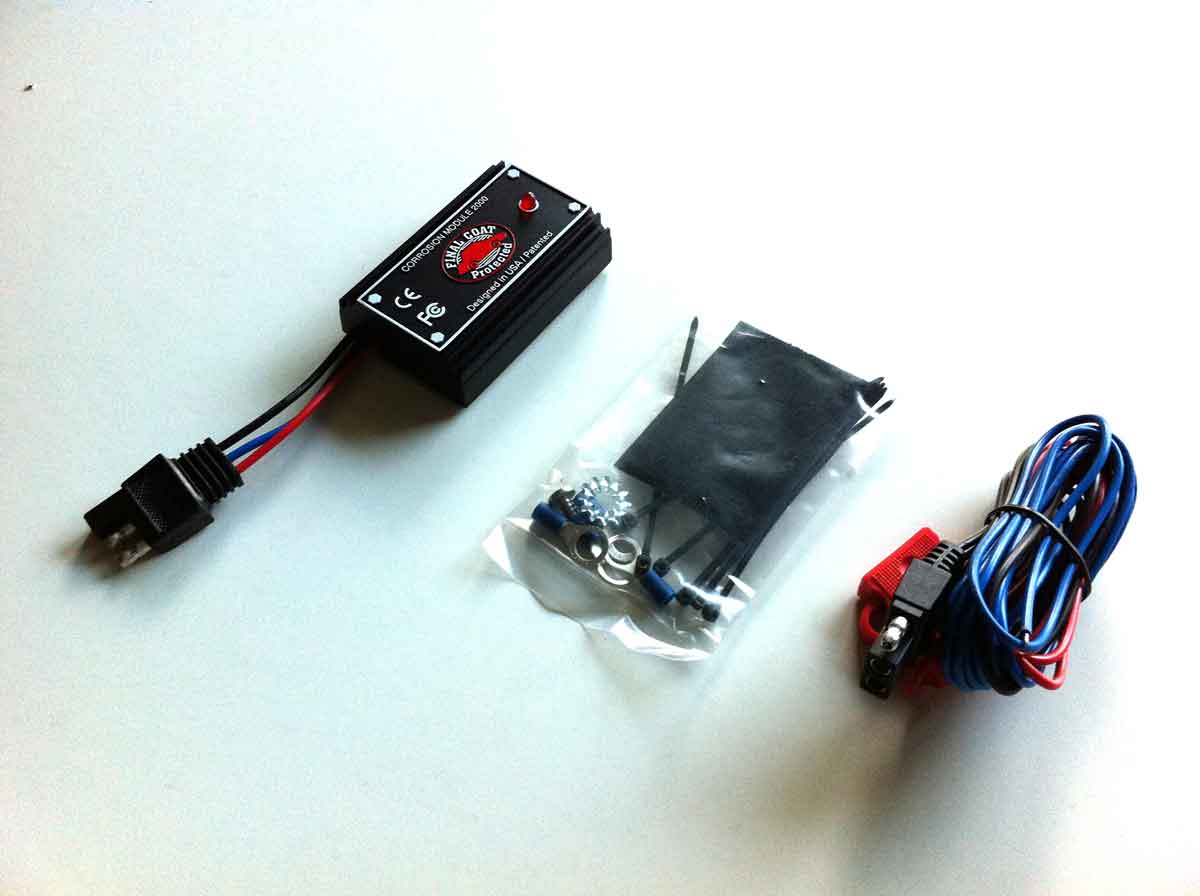
Electronic anti-corrosion protection for cars
The electrodes are placed in the places most vulnerable to atmospheric corrosion:
- on the bottom of the car;
- in the arches of the front and rear wheels;
- on the floor of the cabin under the rugs;
- on the inside of the doors below.
It is necessary to exclude the possibility of contact of the electrode plates connected to the plus of the battery with the minus of the car body. To do this, they are mounted on epoxy glue on top of the existing paintwork or anti-corrosion coating on the body.
What devices are used
Despite the widespread use of the method of cathodic protection of metal structures in serious industries (energy, pipelines, shipbuilding), there are few devices intended for cars in the Russian-speaking sector of the network. The few that can be found are difficult to verify from tests and reviews, since sellers do not provide a sufficient set of data. The car cathodic protection device is represented by the RustStop-5, BOR-1, AKS-3, UZK-A models.
Patented in the US and Canada, FINAL COAT operates on the principle of pulsed current and is accompanied by research data. According to tests, this device showed the real efficiency of protecting the steel surfaces of the body at a potential difference of 100-200 mV by more than 400% than the control sample. Stops only the price of the device, which can now be bought for 25 thousand rubles.
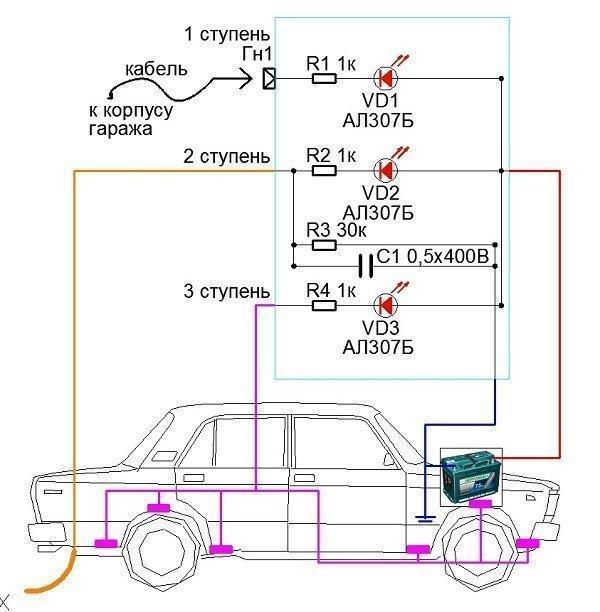
How to make a cathodic protection device yourself
If you do not set yourself the goal of manufacturing a system with complex short-circuit locks, monitoring battery consumption, LED indication, then the device itself can be simply made by yourself.
Body cathodic protection (diagram)
The simplest option includes only a discharge resistor of a certain value (500-1000 ohms), through which the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the protective electrodes. The consumed current should be in the range of 1-10 mA. The protective potential is theoretically sufficient in the amount of 0,44 V (the value of the electronegative potential of pure iron). But taking into account the complex composition of steel, the presence of defects in the crystal structure and other acting factors, it is taken in the region of 1,0 V.
Feedback on the effectiveness of cathodic protection
Reports from instrument users give different estimates.
Oleg:
“Having read about the cathodic protection of the car body from corrosion with my own hands, I decided to try it. I found the ratings of radio components on the Internet, picked up suitable plates for the anodes, connected everything as written. Result: I have been using it for more than five years, my car is not new, but there is no through rust yet.
Anton:
“Electrochemical protection went with the car when I bought it from my hands. The body really holds like a stainless steel, but the plates themselves on the bottom are very rotten. It will be necessary to figure out how and what to change them for.
Other ways to protect
In addition to cathodic protection of cars from corrosion, various alternative methods are popular among the people. Not all of them are equally good, but they help to extend the life of the machine by several years.
Anode technique
Parts specially made of a special shape made of metals with a higher electrode potential than iron are used. As a result, when a galvanic couple occurs, it is this part that dissolves - the consumable electrode. The metal of the body itself is practically not affected. This method is anodic protection of a car from corrosion.
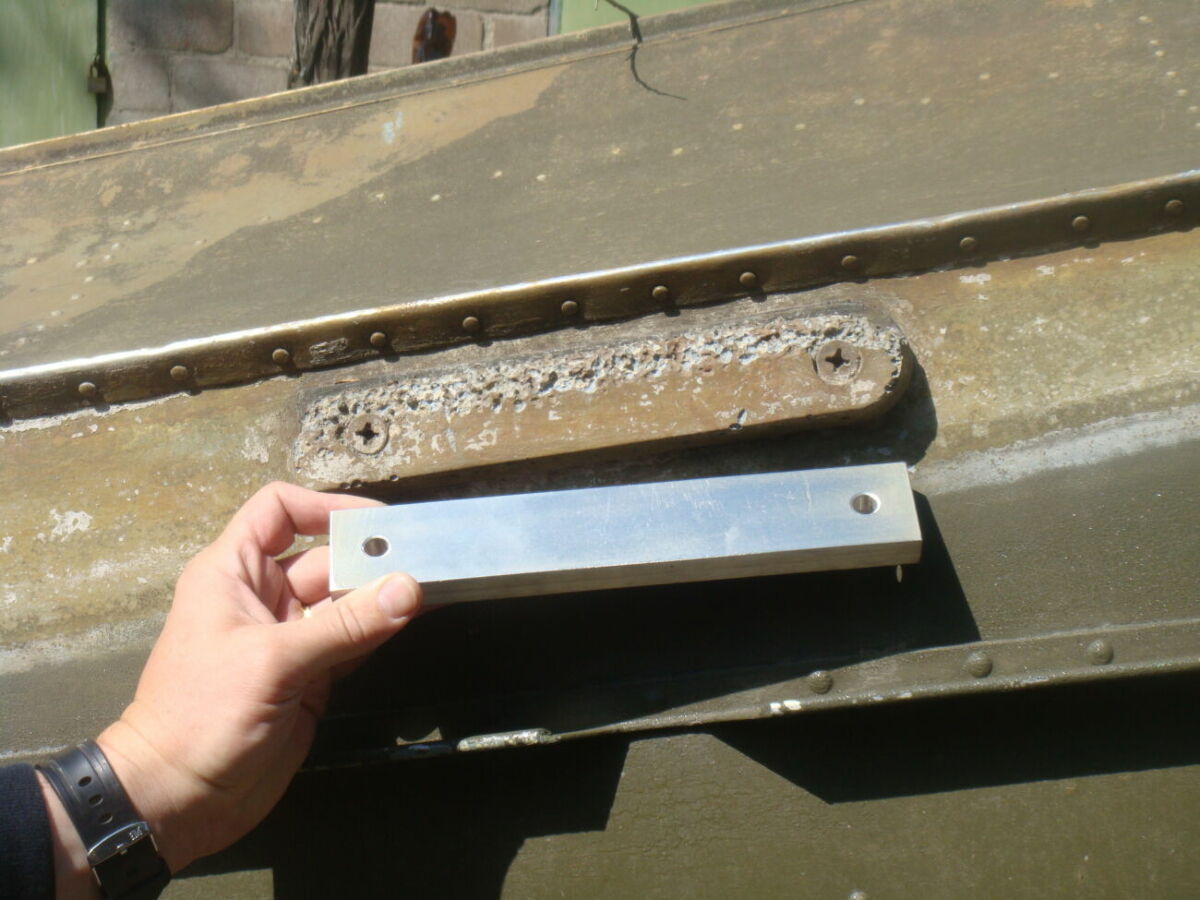

Anode corrosion protection for cars
The most commonly used overlays are made of zinc or magnesium alloys. Numerous reviews of drivers who put pieces of zinc in wheel arches confirm the effectiveness of this protection method for 3-5 years. The disadvantage of this method is the need to monitor the sacrificial electrodes, updating them if necessary.
Galvanized body
Zinc coating of the body metal is another common technique to protect the car from rust for the entire period of its service (often for 15-20 years). The largest Western manufacturers have gone this way, releasing premium brands of their cars with factory hot-dip galvanized bodies.

Galvanized body
The undisputed leader in this direction is Audi, which has developed many patents on the topic of protective coating technologies. It is the Audi 80 model that is the first production model with such processing, and since 1986 all cars produced under this brand have it. Other members of the VW Group also use hot-dip galvanizing: Volkswagen, Skoda, Porsche, Seat.
In addition to German, some Japanese models received real galvanized bodies: Honda Accord, Pilot, Legends.
Primers and paintwork materials
With regard to the topic of electrochemical protection, tread compositions of paints and varnishes containing zinc particles deserve mention. These are phosphating and cataphoretic primers.
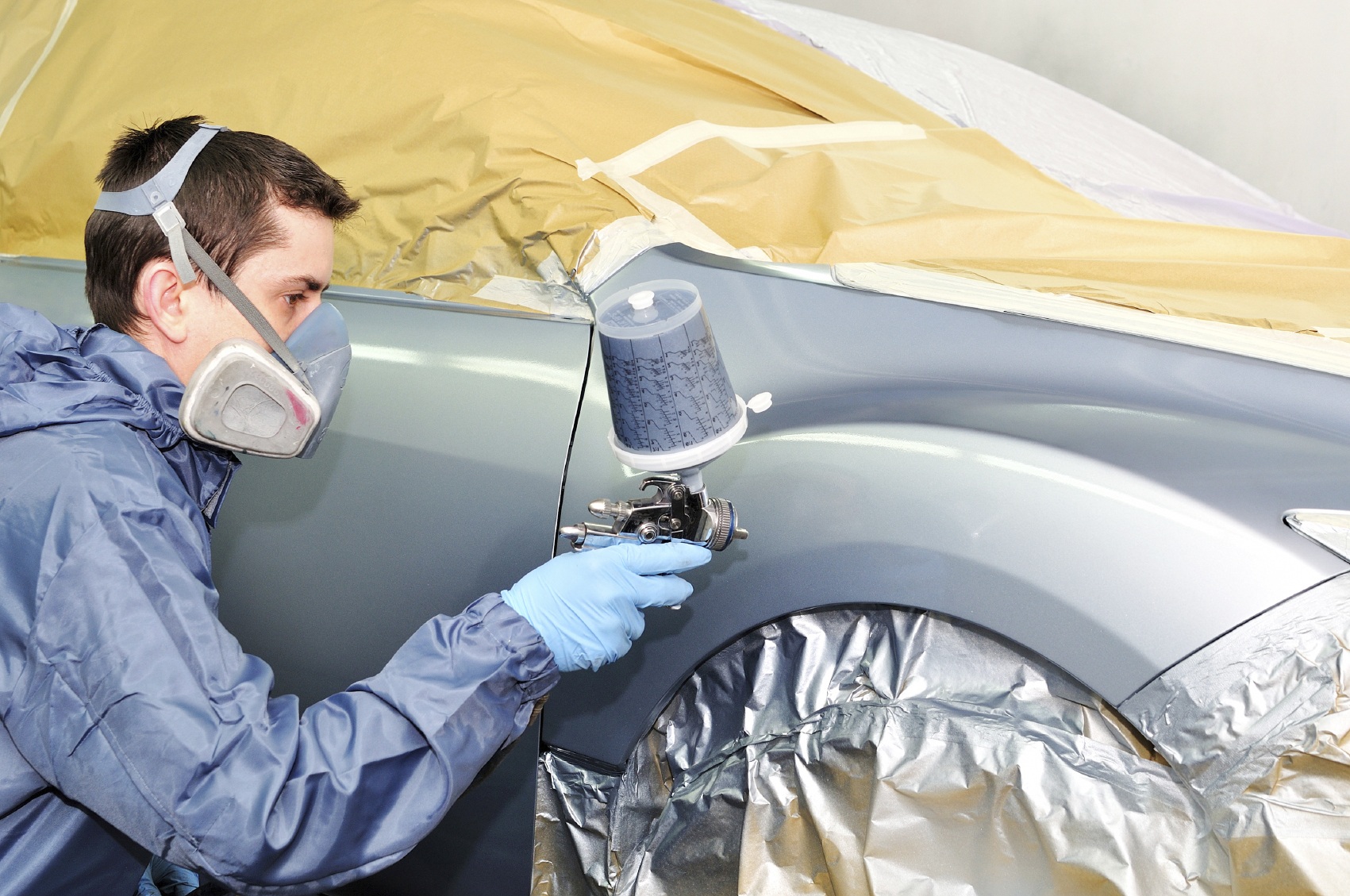

Application of paints and varnishes
The principle of their operation is the same: iron is brought into contact with a layer of a more active metal, which is consumed in galvanic reactions in the first place.
Lamination
A method of protecting the body surface from rust and abrasion by pasting with a special durable transparent film. Well-performed processing is practically invisible to the eye, withstands significant temperature changes and is not afraid of vibration.
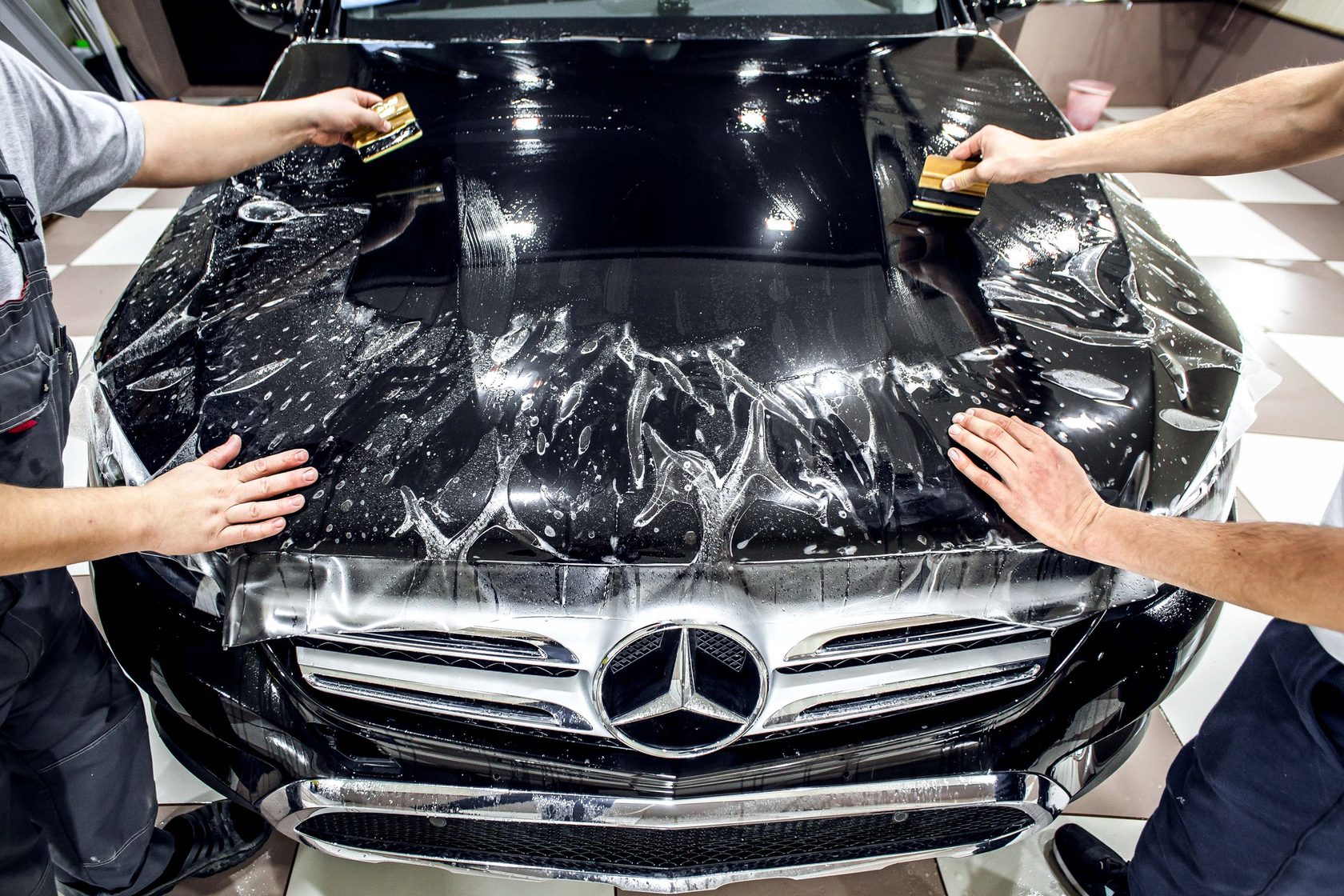

Car lamination
Liquid glass
An additional hardening coating layer is created on top of the base paintwork, which has increased strength. It is applied to a degreased and washed car body, which is preheated with hot air. The polymer base of the material spreads and after hardening is polished. In this way, it is possible to protect the factory paint layer from the penetration of atmospheric moisture through it and thus restrain corrosion for a short time.
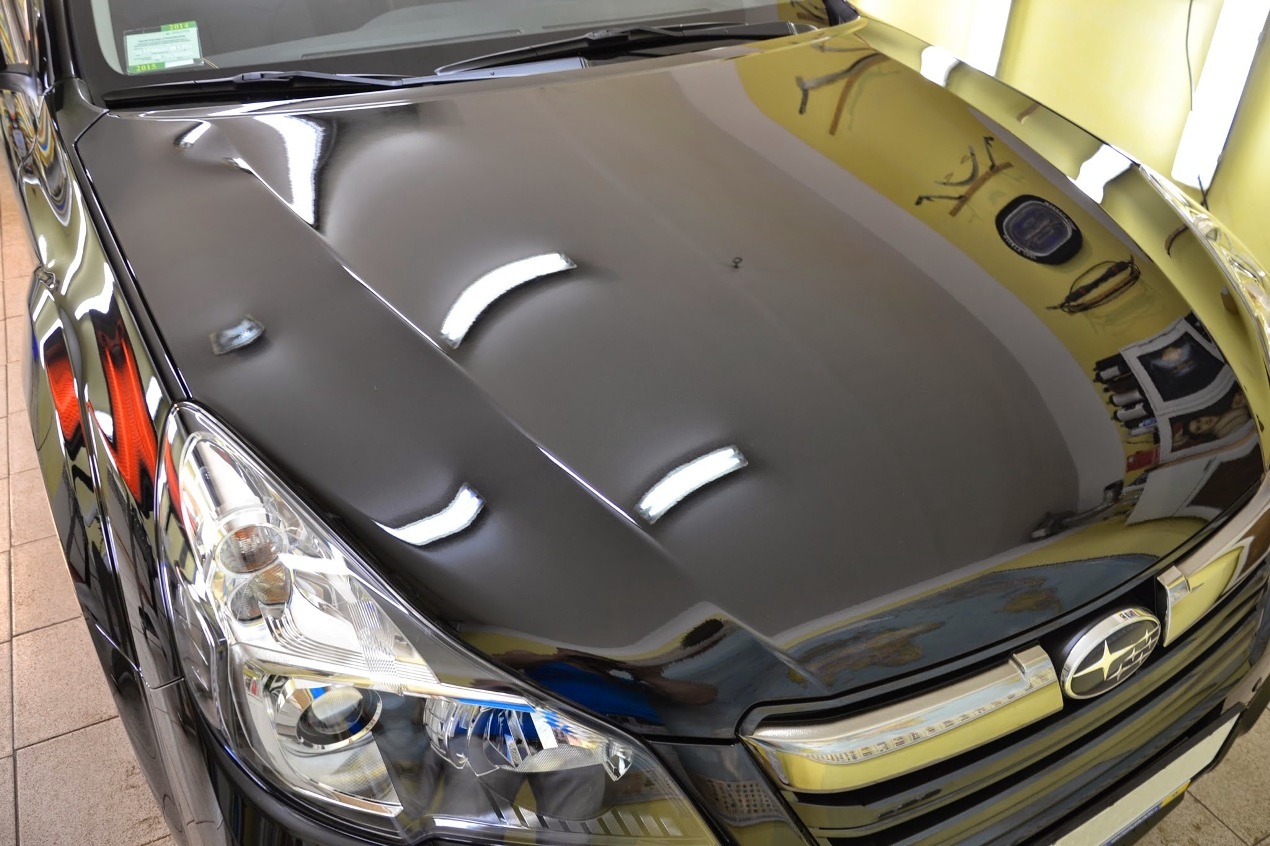

Ceramic liquid glass for cars
The method does not provide complete protection against rust. Protects mainly the appearance of the car from visible manifestations, but leaving unattended hidden foci.
Working with the bottom
To protect the bottom and wheel arches from electrolytes (road dirt, water with salt), coatings with various mastics on a bitumen, rubber and polymer base are used.
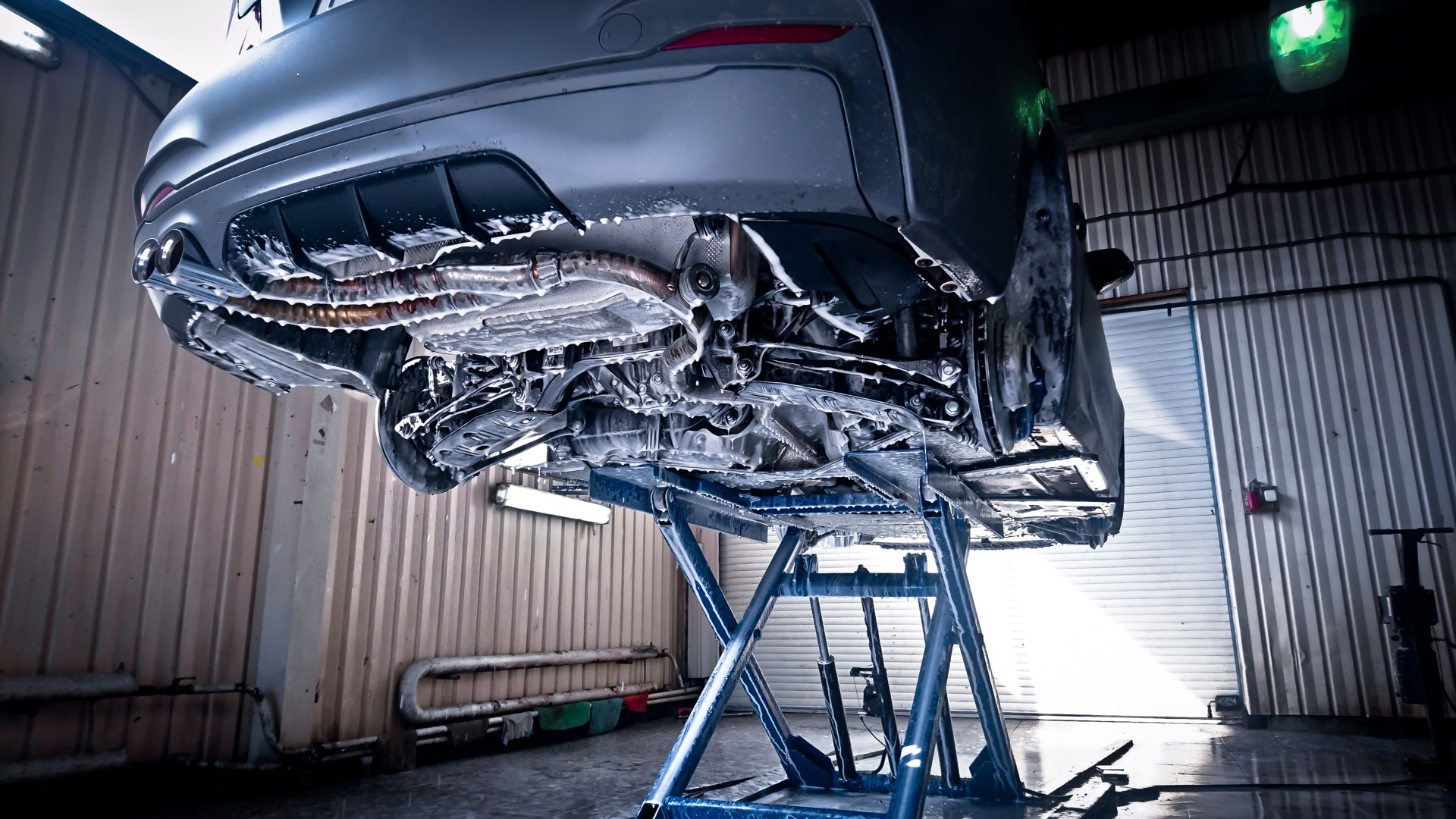

Work with the bottom of the car
Polyethylene lockers are used. All these types of treatment lose in terms of efficiency of the electrochemical protection of the car body, but they allow to delay through rust for a while.