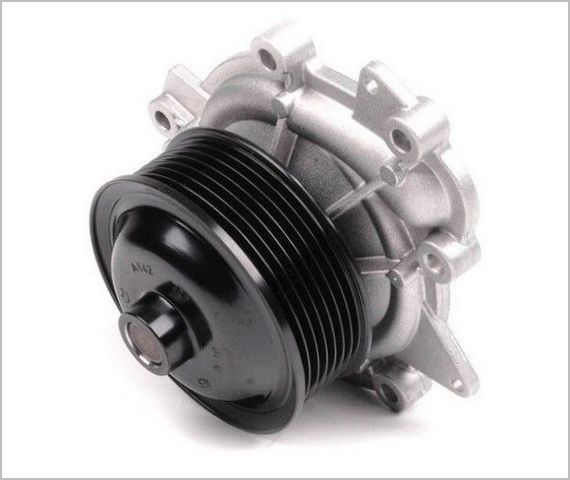
The design and operation of a water pump (pump) in an automobile engine
Content
The heat exchange in the engine is carried out by the transfer of energy from a source in the cylinder area to the air blown through the cooling radiator. A centrifugal vane pump, commonly called a pump, is responsible for giving movement to the coolant in a liquid-type system. Often by inertia, water, although clean water has not been used in cars for a long time.
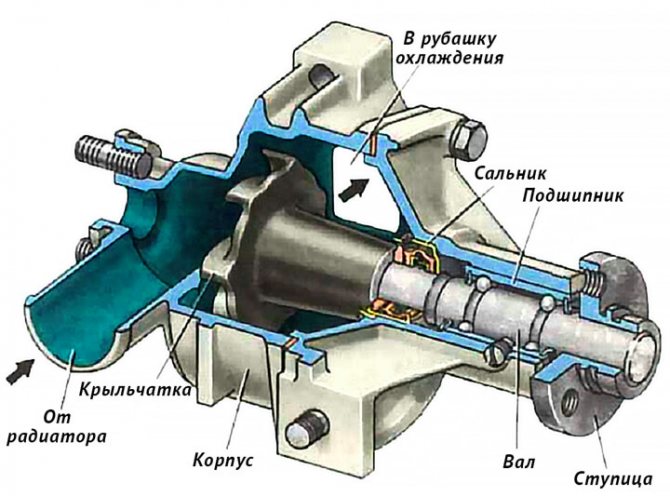
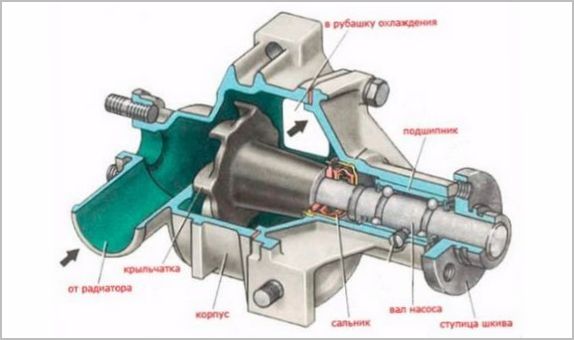
Components of a pump
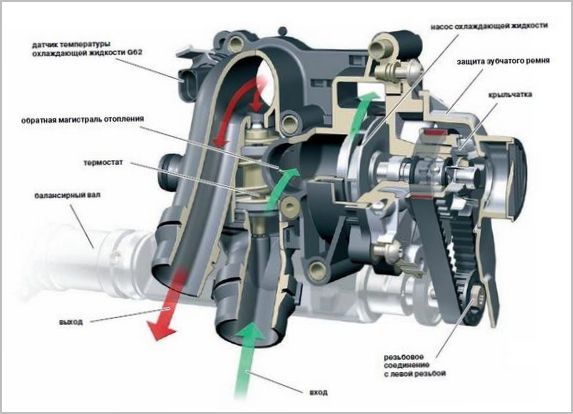
The antifreeze circulation pump is theoretically made rather unpretentious, its work is based on the liquid being thrown by centrifugal forces to the edges of the blades, from where it is injected into the cooling jackets. The composition includes:
- a shaft, at one end of which there is an injection impeller made of metal or plastic, and at the other - a drive pulley for a V-belt or other transmission;
- housing with a flange for mounting on the engine and accommodating internal parts;
- bearing on which the shaft rotates;
- an oil seal that prevents leakage of antifreeze and its penetration to the bearing;
- a cavity in the body, which is not a separate part, but provides the necessary hydrodynamic properties.
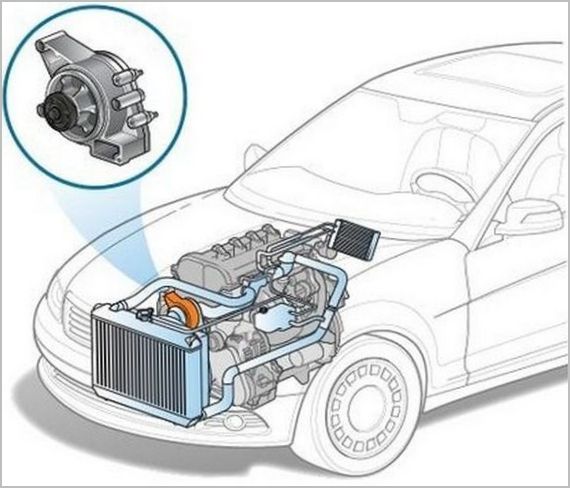
The pump is usually located on the engine from the part where the accessory drive system is located using belts or chains.
The physics of a water pump
To make the liquid heat agent move in a circle, it is necessary to create a pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the pump. If such a pressure is obtained, then the antifreeze will move from the zone where the pressure is higher, through the entire engine to the inlet of the pump with a relative vacuum.
The movement of water masses will require energy costs. Liquid friction of antifreeze on the walls of all channels and pipes will prevent circulation, the larger the volume of the system, the higher the flow rate. To transmit significant power, as well as maximum reliability, a mechanical drive from the crankshaft drive pulley is almost always used. There are pumps with an electric motor, but their use is limited to the most economical engines, where the main thing is the minimum fuel costs, and equipment costs are not considered. Or in engines with additional pumps, for example, with preheaters or dual cabin heaters.
There is no single approach from which belt to drive the pump. Most engines use a toothed timing belt, but some designers felt that it was not worth tying the reliability of the timing to the cooling system, and the pump is driven there from the outer alternator belt or one of the additional ones. Similar to the A/C compressor or power steering pump.
When the shaft with the impeller rotates, the antifreeze supplied to its central part begins to follow the profile of the blades, while experiencing centrifugal forces. As a result, it creates an excess pressure on the outlet pipe, and the center is replenished with new portions coming from the block or radiator, depending on the current position of the thermostat valves.
Malfunctions and their consequences for the engine
Pump failures can be categorized as mandatory or catastrophic. There can be no others here, the importance of cooling is extremely high.
With natural wear or manufacturing defects in the pump, the bearing, stuffing box or impeller may begin to collapse. If in the latter case this is probably a consequence of a factory defect or criminal savings on the quality of materials, then the bearing and stuffing box will inevitably grow old, the only question is timing. A dying bearing usually announces its problems with a hum or crunch, sometimes a high-pitched whistle.
Most often, pump problems begin with the appearance of play in the bearings. Despite the apparent simplicity of the design, they are loaded here significantly. This is due to the following factors:
- the bearing is filled with grease once at the factory and cannot be renewed during operation.
- no matter what the seals of the internal cavity of the bearing, where its rolling elements, balls or rollers are located, atmospheric oxygen penetrates there, which at a high temperature of the assembly causes rapid aging of the lubricant;
- the bearing experiences a double load, partly due to the need to transfer significant power through the shaft to the impeller rotating in a liquid medium at high speed, and mainly due to the high tension force of the drive belt, which, moreover, is often overtightened during repairs if an automatic tensioner is not provided ;
- extremely rarely, a separate belt is used to rotate the pump, usually several fairly powerful auxiliary units with massive rotors and variable resistance to rotation hang on the common drive, these can be a generator, camshafts, a power steering pump and even an air conditioning compressor;
- there are designs in which a huge fan for forced cooling of the radiator is attached to the pump pulley, although at present almost everyone has left such a solution;
- antifreeze vapors can enter the bearing through a leaking stuffing box.
Even if a high-quality bearing does not fail, then play may form in it as a result of wear. In some nodes it is safe enough, but not in the case of a pump. Its shaft is sealed with an oil seal of complex design, which is pressed by excess pressure from inside the system. It will not be able to work in conditions of high-frequency vibration due to the bearing play for a long time. Hot antifreeze penetrating through it drop by drop will begin to enter the bearing, wash out the lubricant or cause its degradation, and everything will end with an avalanche of wear.

The danger of this phenomenon is also that the pump is often driven by the timing belt, on which the safety of the engine as a whole depends. The belt is not designed to work in conditions where it is poured with hot antifreeze, it will quickly wear out and break. On most engines, this will not only lead to a stop, but to a violation of the valve opening phases on a still rotating engine, which will end with a meeting of the valve plates with the piston bottoms. The valve stems will bend, you will have to disassemble the engine and change parts.
In this regard, it is always recommended to replace the pump prophylactically at each scheduled installation of a new timing kit, the frequency of which is clearly indicated in the instructions. Even if the pump looks quite well. Reliability is more important, besides, you don’t have to spend money on unscheduled disassembly of the front of the engine.
There are exceptions to every rule. In the case of a pump replacement, this is due to the use of products that obviously have a longer resource than even the factory equipment. But they are also much more expensive. What to prefer, frequent replacement or an amazing resource - everyone can decide for himself. Although any of the most wonderful pumps can be unwittingly killed by low-quality antifreeze, its untimely replacement, or violations in the belt drive tensioning mechanism or technology.