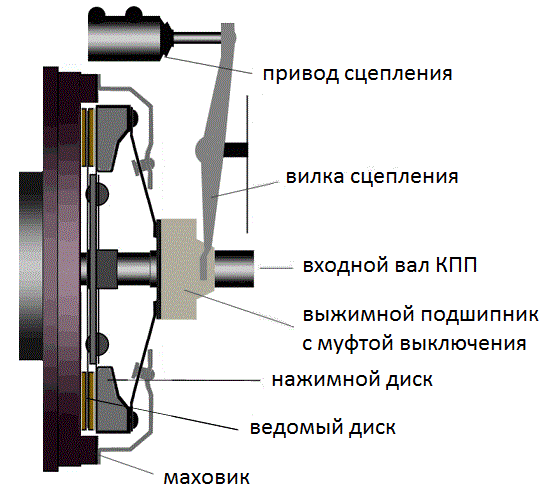
Car clutch design, main elements
Content
The clutch is the mechanism that transmits torque from the engine to the gearbox through friction. It also allows the engine to be quickly disconnected from the transmission and the connection re-established without difficulty. There are many types of clutches. They differ in the number of drives they manage (single, dual or multi-drive), the type of operating environment (dry or wet), and the type of drive. Different types of clutch have respective advantages and disadvantages, but mechanically or hydraulically actuated single plate dry clutch is most commonly used in modern vehicles.
Purpose of the clutch
The clutch is installed between the engine and gearbox and is one of the most stressed parts of the gearbox. It performs the following main functions:
- Soft disconnection and connection of the engine and gearbox.
- Torque transmission without slipping (lossless).
- Compensation for vibration and loads resulting from uneven engine operation.
- Reduce stress on engine and transmission parts.
Clutch components
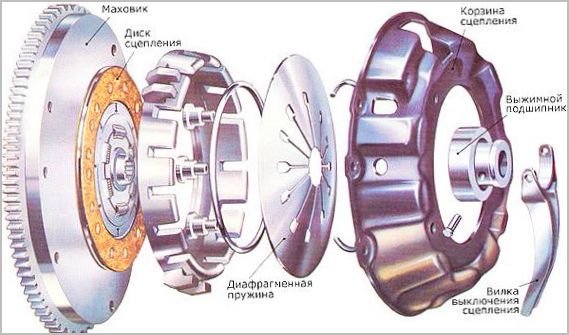
The standard clutch on most manual transmission vehicles includes the following main components:
- Engine flywheel - Drive disc.
- Clutch disc.
- Clutch basket - pressure plate.
- Clutch release bearing.
- pull-out clutch.
- Clutch fork.
- Clutch drive.
Friction linings are installed on both sides of the clutch disc. Its function is to transmit torque through friction. A spring-loaded vibration damper built into the disc body softens the connection to the flywheel and dampens vibrations and stresses resulting from uneven engine operation.
The pressure plate and the diaphragm spring acting on the clutch disc are combined into one unit, called the "clutch basket". The clutch disc is located between the basket and the flywheel and is connected by splines to the input shaft of the gearbox, on which it can move.
The basket spring (diaphragm) can be push or exhaust. The difference lies in the direction of application of force from the clutch actuator: either to the flywheel or away from the flywheel. The draw spring design allows the use of a basket that is much thinner. This makes the assembly as compact as possible.
How the clutch works
The principle of operation of the clutch is based on the rigid connection of the clutch disc and the engine flywheel due to the friction force generated by the force generated by the diaphragm spring. The clutch has two modes: "on" and "off". In most cases, the driven disk is pressed against the flywheel. The torque from the flywheel is transmitted to the driven disk, and then through the spline connection to the input shaft of the gearbox.
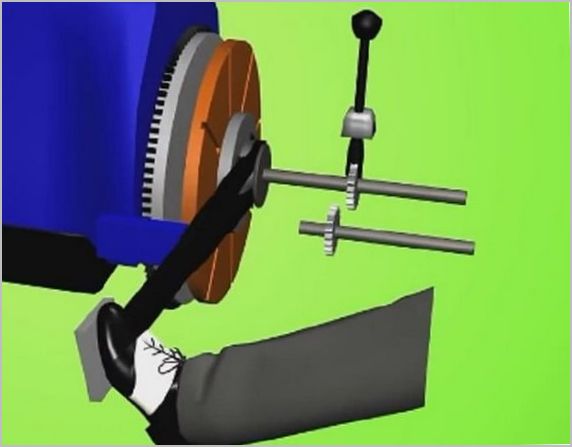
To disengage the clutch, the driver depresses a pedal that is mechanically or hydraulically connected to the fork. The fork moves the release bearing, which, by pressing on the ends of the petals of the diaphragm spring, stops its effect on the pressure plate, which, in turn, releases the driven disk. At this stage, the engine is disconnected from the gearbox.
When the appropriate gear is selected in the gearbox, the driver releases the clutch pedal, the fork ceases to act on the release bearing and spring. The pressure plate presses the driven disc against the flywheel. The engine is connected to the gearbox.
Clutch varieties

Dry clutch
The principle of operation of this type of clutch is based on the friction force created by the interaction of dry surfaces: driving, driven and pressure plates. This provides a rigid connection between the engine and transmission. Dry single plate clutch is the most common type on most manual transmission vehicles.
Wet grip
Couplings of this type operate in an oil bath on rubbing surfaces. Compared to dry, this scheme provides a smoother disc contact; the unit is cooled more efficiently due to fluid circulation and can transmit more torque to the gearbox.
Wet design is widely used in modern dual clutch automatic transmissions. The peculiarity of the operation of such a clutch is that the even and odd gears of the gearbox are supplied with torque from separate driven disks. Clutch drive - hydraulic, electronically controlled. The gears are shifted with a constant transfer of torque to the transmission without interruption in the flow of power. This design is more expensive and more difficult to manufacture.
Dual disc dry clutch

A dual disc dry clutch has two driven discs and an intermediate spacer between them. This design is capable of transmitting more torque with the same clutch size. By itself, it is easier to make than the wet look. Typically used in trucks and cars with particularly powerful engines.
Clutch with dual mass flywheel
The dual mass flywheel consists of two parts. One of them is connected to the engine, the other - to the driven disk. Both elements of the flywheel have a small play in relation to each other in the plane of rotation and are interconnected by springs.
A feature of the dual-mass flywheel clutch is the absence of a torsional vibration damper in the driven disk. The flywheel design uses a vibration damping function. In addition to transmitting torque, it effectively reduces vibrations and loads resulting from uneven engine operation.
Clutch service life
The service life of the clutch depends mainly on the operating conditions of the vehicle, as well as on the driving style of the driver. On average, the clutch life can reach 100-150 thousand kilometers. As a result of the natural wear that occurs when the discs make contact, the friction surfaces are subject to wear and need to be replaced. The main reason is disk slippage.
Double disc clutch has a long service life due to the increased number of working surfaces. The clutch release bearing engages every time the engine/gearbox connection is broken. Over time, all the grease is produced in the bearing and loses its properties, as a result of which it overheats and fails.
Characteristics of ceramic coupling
The service life of the clutch and its maximum performance are determined by the properties of the material of the engagement. The standard composition of clutch discs on most vehicles is a compressed mixture of glass and metal fibres, resin and rubber. Since the principle of operation of the clutch is based on the force of friction, the friction linings of the driven disk are adapted to work at high temperatures, up to 300-400 degrees Celsius.
In powerful sports cars, the clutch is under more stress than usual. Some gears can use a ceramic or sintered clutch. The material of these overlays includes ceramic and Kevlar. Ceramic-metal friction material is less subject to wear and can withstand heating up to 600 degrees without losing its properties.
Manufacturers use different clutch designs that are optimal for a particular vehicle, depending on its intended use and cost. The dry single plate clutch remains a fairly efficient and inexpensive design. This scheme is widely used on budget and medium-sized cars, as well as SUVs and trucks.

