Four-wheel drive from Audi - Quattro
Content
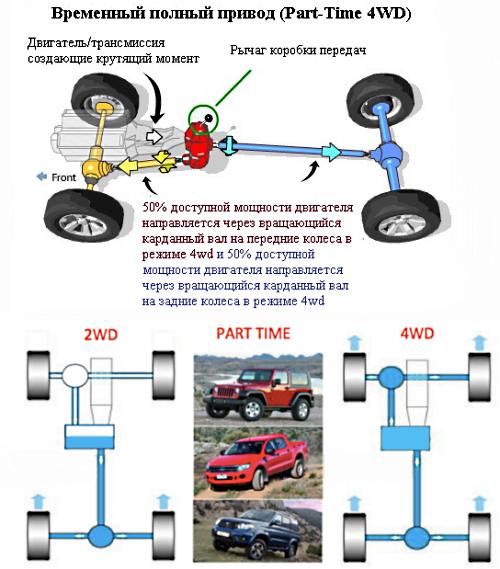
Quattro is a branded all-wheel drive system used in Audi cars. The design is made in the classic layout, borrowed from SUVs - the engine and gearbox are located longitudinally. The intelligent system provides the best dynamic performance depending on road conditions and wheel grip. The machines have excellent handling and grip on any type of road surface.
How did the Quattro come about?
For the first time, a car with a similar all-wheel drive design was presented at the Geneva Motor Show in 1980. The prototype was the army jeep Volkswagen Iltis. Tests during its development in the late 1970s demonstrated good handling and predictable behavior on slippery snowy roads. The idea to introduce the concept of an all-wheel drive jeep into the design of the car was based on the Audi 80 series coupe.

The constant victories of the first Audi Quattro in rally racing proved the correctness of the all-wheel drive concept. Contrary to the doubts of critics, whose main argument was the volume of the transmission, ingenious engineering solutions turned this disadvantage into an advantage.
The new Audi Quattro was characterized by excellent stability. Thus, thanks to the layout of the transmission, an almost perfect distribution of weight along the axles became possible. The all-wheel drive Audi of 1980 became a rally legend and an exclusive serial coupe.
Development of the Quattro all-wheel drive system
XNUMXst generation

The first generation quattro system was equipped with inter-axle and inter-wheel differentials with the possibility of forced locking by a mechanical drive. In 1981, the system was modified, the locks began to be activated by pneumatics.
Models: Quattro, 80, Quattro Cupe, 100.
XNUMXnd generation

In 1987, the place of the free center axle was taken by the self-locking limited slip differential Torsen Type 1. The model was distinguished by the transverse arrangement of satellite gears in relation to the drive shaft. Torque transmission varied 50/50 under normal conditions, with up to 80% of the power being transferred to the axle with the best grip in slippage. The rear differential was equipped with an automatic unlocking function at speeds above 25 km / h.
Models: 100, Quattro, 80/90 quattro NG, S2, RS2 Avant, S4, A6, S6.
III generation

In 1988, an electronic differential lock was introduced. The torque was distributed along the axles, taking into account the strength of their adhesion to the road. The control was carried out by the EDS system, which slowed down the towing wheel. The electronics automatically connected the blocking of the multi-plate clutch of the center and free front differentials. Torsen limited slip differential moved to the rear axle.
IV generation
1995 - an electronic locking system for front and rear free-type differentials was installed. Center differential - Torsen Type 1 or Type 2. Normal torque distribution - 50/50 with the ability to transfer up to 75% of the power to one axle.
Models: A4, S4, RS4, A6, S6, RS6, allroad, A8, S8.
V generation
In 2006, the Torsen Type3 asymmetrical center differential was introduced. A distinctive feature from previous generations is that the satellites are located parallel to the drive shaft. Center differentials - free, with electronic lock. The torque distribution under normal conditions occurs in a proportion of 40/60. When slipping, power increases to 70% in the front and 80% in the rear. Thanks to the use of the ESP system, it became possible to transfer up to 100% of the torque to the axle.
Models: S4, RS4, Q7.
VI generation
In 2010, the design elements of the all-wheel drive of the new Audi RS5 have undergone significant changes. A center differential of our own design was installed based on the technology of interaction of flat gears. Compared to Torsen, this is a more efficient solution for stable torque distribution in various driving conditions.
In normal operation, the power ratio of the front and rear axles is 40:60. If necessary, the differential transfers up to 75% of the power to the front axle and up to 85% to the rear axle. It is easier to integrate into the control electronics. As a result of the application of the new differential, the dynamic characteristics of the car change flexibly depending on any conditions: the strength of the grip of the tires on the road, the nature of the movement and the driving style.
Design of a modern system
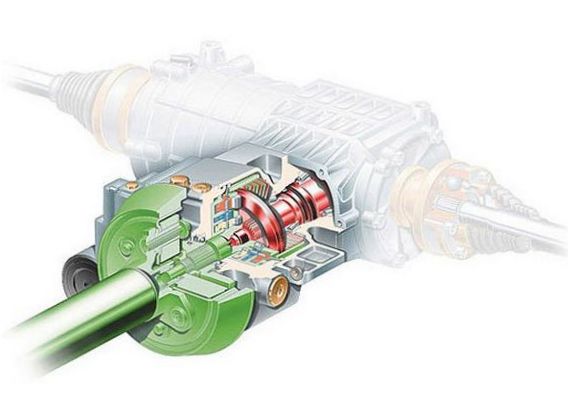
The modern Quattro transmission consists of the following main elements:
- Transmission.
- Transfer case and center differential in one housing.
- Main gear structurally integrated into the rear differential housing.
- Cardan assembly that transmits torque from the central differential to the driven axles.
- Center differential that distributes power between the front and rear axles.
- Free type front differential with electronic locking.
- Electronic freewheel rear differential.

The Quattro system is characterized by increased reliability and durability of the elements. This fact is confirmed by three decades of operation of production and rally Audi cars. The failures that have occurred have mostly been the result of improper or overuse.
Job Description Quattro
The operation of the Quattro system is based on the most efficient distribution of forces during wheel slip. The electronics reads the readings of the sensors of the anti-lock braking system and compares the angular speeds of all wheels. If one of the wheels exceeds a critical limit, it brakes. At the same moment, the differential lock is activated, and the torque is distributed in the correct proportion to the wheel with the best grip.
Electronics distributes energy according to a proven algorithm. The working algorithm, created as a result of countless tests and analyzes of the vehicle's behavior in various driving conditions and road surfaces, ensures high active safety. This makes driving predictable in difficult conditions.
The effectiveness of the interlocks used and the electronic control system allow Audi vehicles with all-wheel drive to move off without slipping on any type of road surface. This property provides excellent dynamic properties and cross-country driving capabilities.
pros
- Excellent stability and dynamics.
- Good handling and maneuverability.
- High reliability.
Cons
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Strict requirements for the rules and operating conditions.
- The high cost of repair in case of failure of the element.
Quattro is the ultimate intelligent all-wheel drive system that has stood the test of time and the tough conditions of rally racing. Recent developments and best innovative solutions have improved the overall system efficiency for decades. The excellent driving characteristics of Audi all-wheel drive vehicles have proven this in practice for more than 30 years.