Efficiency of an internal combustion engine - we know the efficiency in comparison
Content
Among the many characteristics of various mechanisms in the car, the decisive factor is Efficiency of an internal combustion engine. In order to find out the essence of this concept, you need to know exactly what a classic internal combustion engine is.
The efficiency of an internal combustion engine - what is it?
First of all, the motor converts the thermal energy that occurs during the combustion of fuel into a certain amount of mechanical work. Unlike steam engines, these engines are lighter and more compact. They are much more economical and consume strictly defined liquid and gaseous fuels. Thus, the efficiency of modern engines is calculated based on their technical characteristics and other indicators.
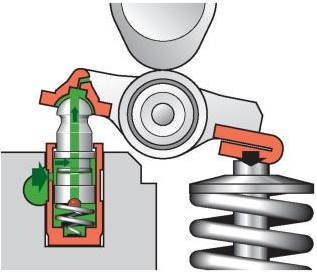
Efficiency (coefficient of performance) is the ratio of the power actually transmitted to the engine shaft to the power received by the piston due to the action of gases. If we compare the efficiency of engines of different power, we can establish that this value for each of them has its own characteristics.

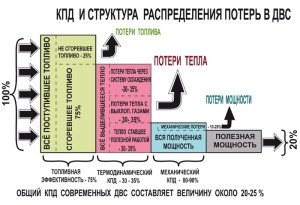
The effective efficiency of the engine depends on various mechanical losses at different stages of operation. The losses are influenced by the movement of individual parts of the motor and the resulting friction. These are pistons, piston rings and various bearings. These parts cause the largest amount of losses, accounting for approximately 65% of their total. In addition, losses arise from the operation of mechanisms such as pumps, magnetos and others, which can reach up to 18%. A small part of the losses are the resistances that occur in the fuel system during the intake and exhaust process.
Most of all, the efficiency decreases due to heat losses. The power plant warms up all elements of the system, including the coolant, cooling radiator and heater, along with this, heat is lost. Part is lost along with the exhaust gases. On average, heat losses account for up to 35% of efficiency, and fuel efficiency for another 25%. Another 20% is occupied by mechanical losses, i.e. on elements that create friction (pistons, rings, etc.). High-quality engine oils help reduce friction, but this factor cannot be completely eliminated.
Given the low efficiency of the engine, it is possible to present losses more clearly, for example, on the amount of fuel. With an average fuel consumption of 10 liters per hundred kilometers, it takes only 2-3 liters of fuel to pass this section, the rest is a loss. A diesel engine has less losses, as well as an internal combustion engine with gas-balloon equipment. If the issue of high engine efficiency is fundamental, then there are options with a coefficient of 90%, but these are electric vehicles and cars with a hybrid engine. As a rule, their cost is somewhat higher and due to the specifics of operation (regular recharging is needed and the smell of running is limited), such machines are still rare in our country.
Comparison of engine efficiency - gasoline and diesel
If we compare the efficiency of a gasoline and diesel engine, it should be noted that the first of them is not efficient enough and converts only 25-30% of the generated energy into useful action. For example, the efficiency of a standard diesel engine reaches 40%, and the use of turbocharging and intercooling increases this figure to 50%.


Both engines, despite the similarity of design, have different types of mixture formation. Therefore, the pistons of a carburetor engine operate at higher temperatures that require high-quality cooling. Because of this, thermal energy that could turn into mechanical energy is dissipated to no avail, lowering the overall efficiency value.


However, in order to increase the efficiency of a gasoline engine, certain measures are taken. For example, two intake and exhaust valves can be installed per cylinder, instead of one intake and one exhaust valve. In addition, some engines have a separate ignition coil for each spark plug. Throttle control in many cases is carried out with the help of an electric drive, and not with an ordinary cable.


Watch this video on YouTube
Diesel engine efficiency – noticeable efficiency
Diesel is one of the varieties of internal combustion engines, in which the ignition of the working mixture is carried out as a result of compression. Therefore, the air pressure in the cylinder is much higher than that of a gasoline engine. Comparing the efficiency of a diesel engine with the efficiency of other designs, one can note its highest efficiency.
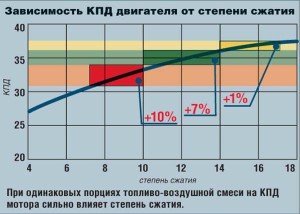

In the presence of low speeds and a large displacement, the efficiency index can exceed 50%.
Attention should be paid to the relatively low consumption of diesel fuel and the low content of harmful substances in the exhaust gases. Thus, the value of the efficiency of an internal combustion engine depends entirely on its type and design. In many vehicles, low efficiency is offset by various improvements to improve overall performance.




Watch this video on YouTube