Why do hydraulic lifters knock
Content
Many drivers, starting a cold engine, hear a characteristic "clatter" in it. To determine why hydraulic lifters knock, you need to familiarize yourself with their design and principle of operation.
Content
- 1 Hydrocompensator: what is it
- 1.1 Устройство
- 1.2 Principle of operation
- 1.2.1 Phase 1
- 1.2.2 Phase 2
- 1.2.3 Phase 3
- 1.2.4 Phase 4
- 2 How hydraulic lifters knock
- 3 Why do hydraulic lifters knock
- 3.1 To the cold
- 3.2 Hot
- 3.2.1 Video: device, principle of operation, causes of knocking
- 3.3 Knocking new knots
- 4 How to identify a faulty hydraulic lifter
- 4.1 Video: how to find out which hydrik is knocking
- 5 What is the danger of knocking
- 6 How to remove a knock
- 6.1 Video: disassembly, repair, inspection
Hydrocompensator: what is it
Parts and assemblies of a running engine, when heated, increase in size. This also applies to the gas distribution mechanism (timing).
In order to avoid breakdowns and reduce the efficiency of the valve drive mechanism, thermal gaps are structurally provided between its individual parts. In the process of warming up the motor, the parts increase in size. Clearances disappear and the engine runs optimally. However, over time, parts wear out, and the thermal gap also changes.
The hydraulic compensator (hydraulic pusher, "gidric") is a device that absorbs the gap formed between the camshaft cams and rocker arms, rods, valves, despite the temperature in the engine and their level of wear.
Installed on all types of timing in engines with upper and lower camshaft placement.
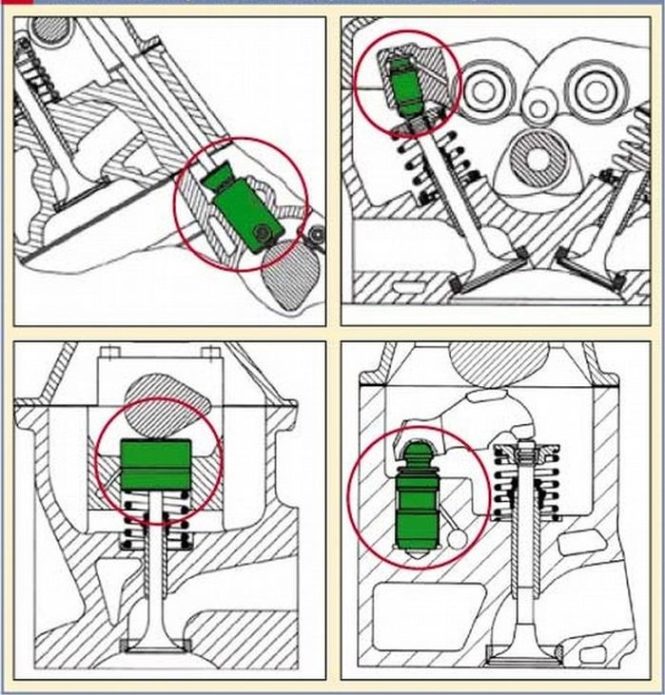
Locations of hydraulic lifters
For different types of timing, 4 main types of expansion joints have been developed:
- Hydraulic pusher;
- Roller hydraulic pusher;
- Hydro support;
- Hydraulic support for rocker arms and levers.

Types of hydraulic compensators
Устройство
Although all types of hydraulic lifters differ structurally, the main action and principle of the device are identical.
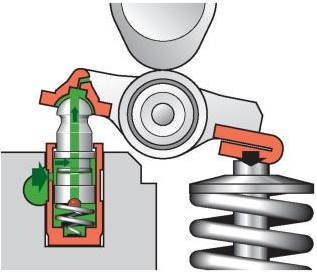
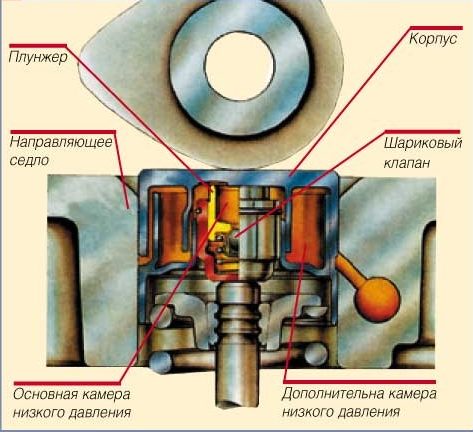
The main unit of the hydraulic pusher is a movable plunger pair with a ball valve located inside. All this is housed in a case. A gap of 5–7 µm, provided between the surfaces of the plunger and the movable piston, ensures their tightness.
The compensator housing moves freely along the guide seat located in the cylinder head (BC).
The design of the labyrinth pusher
It is important! In compensators rigidly fixed in the rocker arms, a plunger with a working part protruding beyond the body serves as a maneuverable element.
At the bottom of the plunger there is an opening for the working fluid, which is closed by a check valve with a ball. A rigid return spring is located in the piston body and tries to push it away from the plunger.
The liquid active ingredient is engine oil, which enters the hydraulic pusher through a hole in the housing from the BC oil channel.
Principle of operation
Using a hydraulic pusher as an example, the basics of operation of all hydraulic lifters are shown.
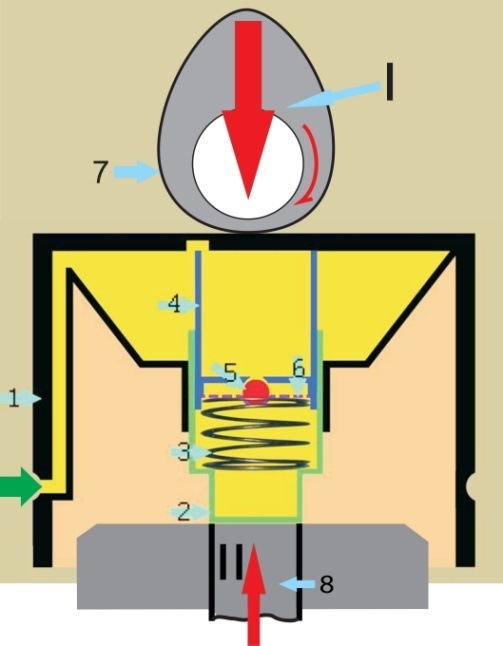
1. Housing. 2. Piston. 3. The spring is returnable. 4. Plunger. 5. Ball check valve. 6. Valve retainer. 7. Cam of a camshaft. 8. Valve spring.
The forces (red arrows I and II) coming from the camshaft cam 7 and the valve spring 8 cause the hydraulic tappet to constantly move in a reciprocating direction.
Phase 1
When the hydraulic pusher is located at the highest mark, the hole in the body 1 is flush with the BC oil channel. Oil (yellow) freely penetrates into the housing (additional low pressure chamber). Further, through the bypass channel located at the base of the body, the oil flows into the cavity of the plunger 4 (the main low pressure chamber). Then, through the open valve 5, the oil penetrates into the piston cavity 2 (high pressure chamber).
The piston moves freely along the guides formed by the plunger 4 and the baffle of the body 1. The pressure of the spring 3 excludes the occurrence of a gap between the piston 2 of the hydraulic pusher and the timing valve 8.
Phase 2
As soon as the cam 7 of the camshaft begins to press on the housing 1, it is displaced. The working fluid ceases to be supplied to the additional low pressure chamber. The spring of the valve 8 is more powerful than the return spring 3 of the hydraulic pusher, therefore it keeps the valve in place. Piston 2, despite the resistance of the return spring, begins to move inside the housing 1, pushing oil into the plunger cavity.
The oil pressure in the piston 2 due to the small volume of the high-pressure chamber increases, eventually closing the check valve 5. The hydraulic compensator, as a single solid body, begins to transfer the force from the cam 7 of the camshaft to the timing valve 8. The valve moves, its spring is compressed.
Phase 3
The cam 7 of the camshaft, having passed the highest point, gradually reduces the force on the body of the hydraulic pusher. The valve spring 8, straightening, returns it to the highest point. The valve, through the piston, pushes the hydraulic compensator towards the cam. The return spring 3 begins to straighten. The pressure in the piston 2 drops. The oil, which had time to flow into the cavity of the plunger 4 at the beginning of the second phase, now presses on the valve ball 5, eventually opening it.
Phase 4
Cam 7 of the camshaft stops pressing on the hydraulic lifter. The valve spring 8 is fully extended. The return spring 3 of the hydraulic pusher is released. Check valve 5 is open. The oil pressure in all chambers is the same. The holes in the body 1 of the hydraulic pusher, which has returned to its original position in the highest position, again coincide with the BC oil channels. Partial oil change in progress.
The return spring inside the "hydra" tries to straighten out, removing the gap between the cam and the hydraulic pusher, even with the inevitable wear of the timing parts.
It is important! The dimensions of the elements of the hydraulic pusher change when heated, but are compensated by the device itself.
How hydraulic lifters knock
Having started the engine, sometimes you can immediately hear a distinct ringing metallic knock, clatter. It resembles the sound of impact of small iron parts, with force thrown on a metal surface. Opening the hood, you can find that the sounds are coming from under the valve cover. The knocking frequency varies with the engine speed.
The noise level from the expansion joints is independent of the motor load. This can be checked by turning on all energy consumers (heater fan, air conditioner, high beam).
It is important! Often the knock of a faulty hydraulic compensator is confused with the noise of the valves. The latter are knocking loudly. The knock of the compensator is more clear and loud.
If the sound did not appear immediately after starting the engine, constant when changing its speed and changing depending on the load on the unit, the source of the knock is different.
Why do hydraulic lifters knock
The characteristic metallic knock that appears, first of all, indicates the appearance of a gap in the timing, which the hydraulic support is not able to compensate.
Depending on the temperature of the motor, possible malfunctions and problems are classified, which are the reason for the knock of the hydraulic lifters.
To the cold
Frequent causes of the clatter of hydraulic mounts in a freshly started engine can be:
- Ingress of dirt into the expansion joint. For this reason, both the plunger pair and the ball of the check valve can jam. In both cases, the hydraulic pusher will not perform its function.
- Dirty oil. Over time, friction products and soot accumulate in the oil. All this can clog the oil channels supplying the hydraulic fluid with the working fluid. After the engine has warmed up, the fluidity of the oil increases and the channels are gradually flushed out.
- Wear of hydraulic pusher assemblies. The working resource of the compensator is 50–70 thousand km. During this period, damage can be observed on the working surfaces that violate their tightness. As a result, there is no required oil pressure in the piston cavity of the compensator.
- Too viscous oil. In this situation, until the engine is fully warmed up, the oil in full volume does not penetrate into the hydraulic pushers, which cannot perform their function.
- Clogged oil filter. In this situation, cold viscous oil in the required volume is not able to pass through the filter and enter the engine head. Sometimes the problem disappears after the engine warms up.
- Coking of the oil channels. It can occur both in the cylinder block and in the compensator. In this situation, it is recommended not to use cleaning additives. Only mechanical cleaning after disassembly will help.
Hot
The reasons for the knock of hydraulic lifters on a cold engine are also relevant for the unit warmed up to operating temperature. But there are problems that appear only on hot:
- The oil has lost its quality. After 5-7 thousand km, the oil develops a working resource. Its viscosity decreases. The hydraulic pushers do not knock on a cold one. When the engine warms up, a knock is heard, caused by the lack of oil in the "hydrics" due to the low pressure in the lubrication system.
- Defective oil pump. Does not give out working pressure. Oil does not reach the hydraulic lifters.
- Oil level is critically low or too high. Both situations are fraught with foaming of the heated product and airing of the hydraulic pushers. The air trapped in the compensator does not form the required pressure during compression, a knock appears.
Video: device, principle of operation, causes of knocking
Knocking new knots
After installation, the new hydraulic pusher begins to knock within 100–150 km of run. This is due to the grinding in of the parts, after which the knocking disappears.
If during installation the compensator is not fully seated in the well, the oil channel of the block head will not coincide with the hole in the hydra casing. Oil will not flow into the expansion joint, which will immediately knock.
Sometimes, when installing the pusher, dirt gets inside the well, clogging the oil channel. In this case, the compensator is taken out, the channel is mechanically cleaned.
How to identify a faulty hydraulic lifter
For self-detection of a defective hydraulic compensator, a phonendoscope with a metal tip is alternately applied to the valve cover at the locations of the "hydraulics". A strong knocking is heard in the area of the faulty pushers.
In the absence of a phonendoscope, the tester can be made from available tools. A resonator (beer or deep tin can) is attached to one end of the metal rod. Pressing the ear to the resonator, the free end of the rod is applied to the valve cover. The search sequence is similar to that of a phonendoscope.


An experienced driver can find a faulty hydraulic lifter by himself
As a last resort, you can use a regular wooden stick.
With the valve cover removed, they try to push through each hydraulic compensator with a screwdriver. The easily recessed pusher is defective.
Video: how to find out which hydrik is knocking


Watch this video on YouTube
It is important! At a car service, non-working hydraulic lifters are determined using acoustic diagnostics.
What is the danger of knocking
The clatter of hydraulic pushers signals a problem that has arisen, affecting the quality of the timing. Often the problem is in the lubrication system, which is fraught with increased wear of all components and mechanisms of the engine.
Car operation with knocking hydraulic pushers provides:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Decrease in accelerating dynamics;
- I will lose up to 30% of power;
- Possible motor overheating.
How to remove a knock
A not always knocking hydraulic compensator needs to be replaced with a new one. When a characteristic knock appears, first of all, you need to change the oil with an oil filter. Sometimes this procedure is enough, the noise disappears.
You can use special flushes of the lubrication system. With the help of modern developments of leading brands, it is possible to wash not only dirty, but also coked oil channels.


Oil channels must be periodically flushed with special fluids.
The most effective is the mechanical cleaning of hydraulic lifters. The wetsuit is removed, disassembled, cleaned and washed.
Video: disassembly, repair, inspection
It is important! If mechanical damage is found, the expansion joint must be replaced.
The emerging knock of hydraulic lifters signals the car owner about problems in the lubrication system or timing. Timely diagnostics and elimination of the causes of knocking can be carried out independently without contacting specialists.