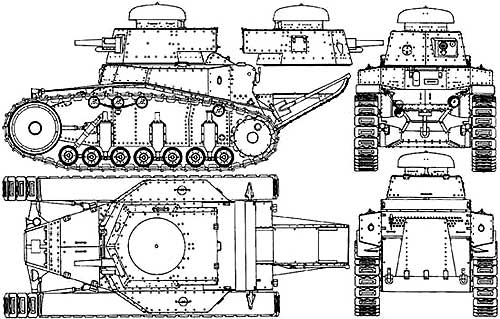
Light tank T-18m
Light tank T-18m
The turning mechanism ensured the turning of the tank with a minimum radius equal to the width of its track (1,41 m). The 37-mm Hotchkiss caliber gun and the 18-mm machine gun were placed in a circular rotation turret. To increase the patency of the tank through ditches and trenches, the tank was equipped with the so-called "tail". During the modernization, a more powerful engine was installed on the tank, the tail was dismantled, the tank was armed with a 45-mm cannon of the 1932 model with a large ammunition capacity. In the first months of the war, T-18m tanks were used as fixed firing points in the system of Soviet border fortifications.
The history of the creation of the tank Light tank T-18 (MS-1 or “Russian Renault”).
During the Civil War in Russia, Renault tanks fought in the interventionist troops, and among the Whites, and in the Red Army. In the autumn of 1918, the 3rd Renault Company of the 303rd Assault Artillery Regiment was sent to help Romania. She unloaded on October 4 in the Greek port of Thessaloniki, but did not have time to take part in the hostilities. Already on December 12, the company ended up in Odessa along with the French and Greek troops. For the first time, these tanks entered the battle on February 7, 1919, supporting, together with the White armored train, the attack of the Polish infantry near Tiraspol. Later, in the battle near Berezovka, one Renault FT-17 tank was damaged and captured by the fighters of the Second Ukrainian Red Army in March 1919 after a battle with Denikin's units.
The car was sent to Moscow as a gift to V.I. Lenin, who gave instructions to organize the production of similar Soviet equipment on its basis.
In the fall of 1918, the captured Renault FT-17 was sent to the Sormovo plant. The team of designers of the technical bureau in a relatively short time from September to December 1919 developed drawings of the new machine. In the manufacture of the tank, the Sormovichi cooperated with other enterprises in the country. So the Izhora plant supplied rolled armor plates, and the Moscow AMO plant (now ZIL) supplied engines. Despite many difficulties, eight months after the start of production (August 31, 1920), the first Soviet tank left the assembly shop. He received the name "Freedom Fighter Comrade Lenin". From 13 to 21 November, the tank completed the official test program. The tank was equipped with a four-cylinder, single-row, liquid-cooled car engine with a capacity of 34 hp, allowing it to move at a speed of 8,5 km / h. In the hull, it was located longitudinally and was directed by the flywheel towards the bow. Mechanical transmission from a conical main clutch of dry friction (steel on the skin), a four-speed gearbox, side clutches with band brakes (rotation mechanisms) and two-stage final drives. The rotation mechanisms ensured this maneuver with a minimum radius equal to the track width cars (1,41 meters). The caterpillar mover (as applied to each side) consisted of a large-sized caterpillar track with a lantern gear. Nine support and seven supporting rollers of the idler wheel with a screw mechanism for tensioning the caterpillar, the drive wheel of the rear location. The supporting rollers (except for the rear one) are sprung with a helical coil spring. Balance suspension. As its elastic elements, semi-eliptic leaf springs covered with armor plates were used. The tank had good support and profile patency. To increase the profile cross-country ability when overcoming ditches and scarps, a removable bracket (“tail”) was installed in its aft part. The vehicle crossed a ditch 1,8 m wide and an escarpment 0,6 m high, could ford water obstacles up to 0,7 m deep, and fell trees up to 0,2-0,25 m thick, without tipping over on slopes up to 38 degrees, and with rolls up to 28 degrees. The electrical equipment is single-wire, the voltage of the on-board network is 6V. The ignition system is from a magneto. The engine is started from the fighting compartment using a special handle and chain drive or from the outside using the starting handle. In terms of its performance characteristics, the T-18 tank was not inferior to the prototype, and surpassed it in maximum speed and roof armor. Subsequently, 14 more such tanks were made, some of them received the names: “Paris Commune”, “Proletariat”, “Storm”, “Victory”, “Red Fighter”, “Ilya Muromets”. The first Soviet tanks took part in the battles on the fronts of the civil war. At its very end, the production of cars was discontinued due to economic and technical difficulties.
After deep modernization in 1938, it received the T-18m index. Performance characteristics
Sources:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


 The tank is the result of the modernization of the first tank of the Soviet design MS-1938 (Small Escort - the first) carried out in 1. The tank was adopted by the Red Army in 1927 and was mass-produced for almost four years. A total of 950 cars were produced. The hull and turret were assembled by riveting from rolled armor plates. The mechanical transmission was located in the same block with the engine and consisted of a multi-plate main clutch, a three-speed gearbox, a bevel differential with band brakes (turning mechanism) and single-stage final drives.
The tank is the result of the modernization of the first tank of the Soviet design MS-1938 (Small Escort - the first) carried out in 1. The tank was adopted by the Red Army in 1927 and was mass-produced for almost four years. A total of 950 cars were produced. The hull and turret were assembled by riveting from rolled armor plates. The mechanical transmission was located in the same block with the engine and consisted of a multi-plate main clutch, a three-speed gearbox, a bevel differential with band brakes (turning mechanism) and single-stage final drives.