Mechanical transmission of a car. Complete guide to manual transmission
The gearbox is one of the most important components of the car, which allows you to change the torque transmitted from the internal combustion engine to the wheels. The presence of a gearbox makes it possible to change the speed of the vehicle over a wide range when using a relatively narrow range of engine speeds. Low gears reduce the load on the internal combustion engine during initial acceleration, uphill driving, and cargo transportation. High ones allow you to develop significant speed at medium speeds of the internal combustion engine. Transferring power to the wheels directly, without a gearbox, would force the ICE to operate in a very heavy duty, which would make it something of a consumable.
Despite the growing popularity of automatic transmissions, manual transmission vehicles are still in demand.
The mechanics has a number of advantages, thanks to which the owners of cars with manual transmission are in no hurry to switch to cars equipped with automatic gearboxes.
So, what can be attributed to the advantages of mechanics?
1. Of course, an important, and often decisive factor, is the price of the car. Typically, manual transmissions cost the automaker less than automatics, and therefore the same model with a manual transmission costs less than a complete set with automatic transmission.
2. If we talk about fuel consumption, then manual transmission is noticeably more economical and allows you to spend less money on fuel. This can be seen by comparing the performance characteristics of any model in different configurations. It is probably for this reason that most Europeans, who are known to be very good at counting money, prefer to buy cars with a manual transmission.
3. Mechanical transmissions are structurally not as complex as automatic ones, and therefore easier and cheaper to repair. However, some modern manual transmissions are quite comparable with automatic transmissions in terms of the complexity of the device and the cost of maintenance.
4. Mechanics are considered more reliable and durable than automatic. This is probably due to the fact that the evolution of mechanical transmissions is relatively slow, the technologies and design solutions in them are usually run-in and time-tested. And in machines, some new technical solutions are not very successful and reduce the quality of this unit.
5. If your battery is dead, you can start a car with a manual transmission from the pusher by turning on the 2nd or 3rd gear. For a car with an automatic transmission in such a situation, you will have to call a tow truck.
6. Mechanics can withstand the towing mode without any problems. But the automatic transmission can overheat and fail, so cars with automatic transmission can only be towed at a speed of no higher than 30 km / h and for a limited distance (up to 30 km), after which you need to let the box cool down. Some automatic transmissions generally exclude the towing mode.
7. Manual transmission allows you to better handle some extreme driving situations on ice, mud, etc.
The main drawbacks of the mechanics are as follows.
1. Driving a car with a manual transmission is less comfortable than driving an automatic. This is undoubtedly the main reason why people choose cars with automatic transmission.
2. The need to constantly move the gear lever can be quite tiring, especially in traffic jams or with a lot of traffic lights along the way.
3. A manual transmission assumes a presence that is not durable and requires periodic repairs. Unlike previous years, in modern cars, clutch replacement is a rather laborious procedure, often requiring the dismantling of the box. For automatic transmissions, no clutch is required at all.
The gears in the manual transmission are switched in steps, and therefore mechanical boxes are distinguished primarily by the number of steps (gears). To put it simply, each stage has its own pair of gears, which provides a certain gear ratio.
The previously common 4-speed gearboxes are now almost never used, since they are inefficient for speeds over 120 km / h. Now the standard is 5 steps, less often 6. There are boxes in which there are more than six steps, but few people like the need to constantly manipulate the gear shift knob in the city start-stop mode, so such options are rarely used in passenger vehicles.
By design features, two main types of mechanical gearboxes can be distinguished - two-shaft, which are installed on front-wheel drive vehicles and three-shaft, used mainly with rear-wheel drive.
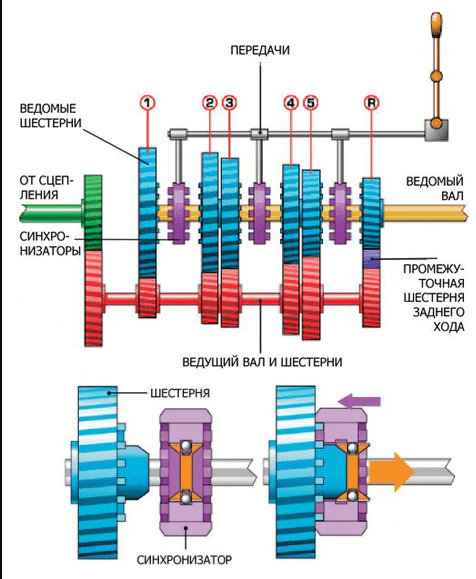
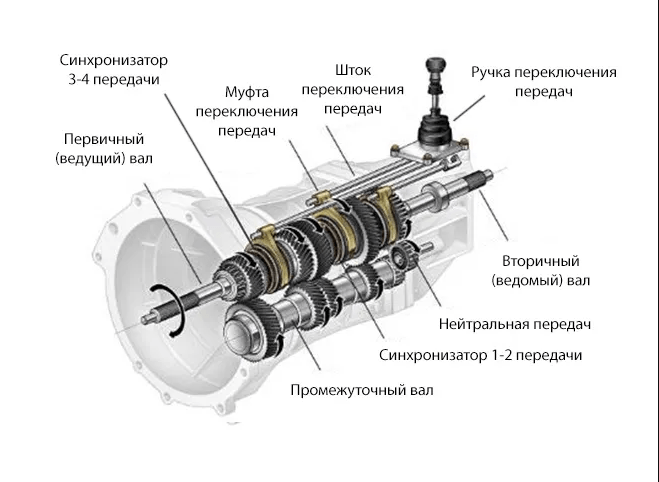
In a classic manual transmission, there are two shafts arranged in parallel. The primary, which is also the leading one, receives rotation from the internal combustion engine through the clutch mechanism. The driven one transmits the converted torque further through the transmission to the drive wheels.
The gears mounted on both shafts are in pairs meshing. At the same time, the gears are not fixed on the secondary shaft and can rotate freely, while they are rigidly fixed on the drive shaft.
The synchronizer clutches installed between the gears of the driven shaft rotate with the shaft, but can move along the splines along it. the purpose of the synchronizer is to block the free rotation of one particular gear and thus engage a specific gear.
Pressing the clutch pedal interrupts the connection between the gearbox input shaft and the internal combustion engine crankshaft. Now you can turn on the transfer. By moving the lever, the driver acts on one of the forks through the drive mechanism, and it shifts the corresponding clutch and presses the synchronizer against the gear through the blocking ring.
Synchronizer ring gears and gears engage. The gear is now locked on the output shaft and can transfer rotation to it from the input shaft with the appropriate gear ratio. Everything, the desired gear is engaged, it remains only to release the clutch pedal, and the torque will be transmitted to the wheels.
The drive mechanism for shifting gears in a two-shaft gearbox is usually remote. To connect the switch lever with the box, rods or a cable are used.
In many designs, instead of one secondary shaft, two shortened ones are used, and the gears are distributed between them. This allows you to significantly reduce the size of the box.
In a three-shaft design, the transmission of rotation from the drive shaft to the driven shaft does not occur directly, but through an intermediate shaft. In this case, the driven shaft is located on the same axis as the primary, and the intermediate shaft is parallel.
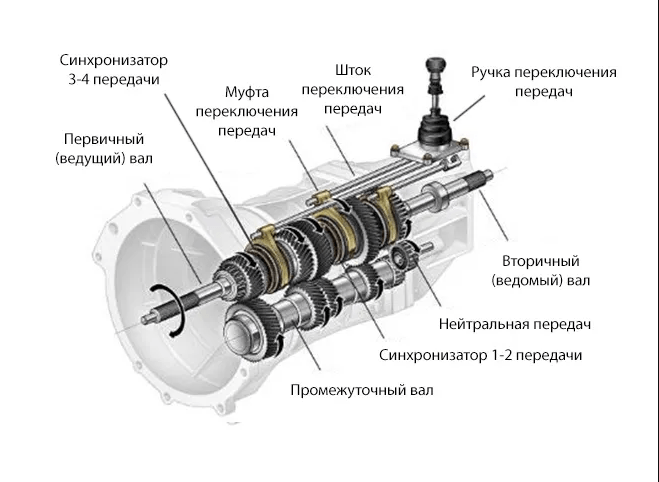
As in the two-shaft design, the gears of the driven shaft are not rigidly fixed to it. But at the same time, they have constant engagement with the gears of the intermediate shaft. Otherwise, the principle of operation is similar to a two-shaft manual transmission.
To enable reverse gear, there is an intermediate gear mounted on a separate shaft. Due to the inclusion of the intermediate gear, the rotation of the output shaft is reversed.
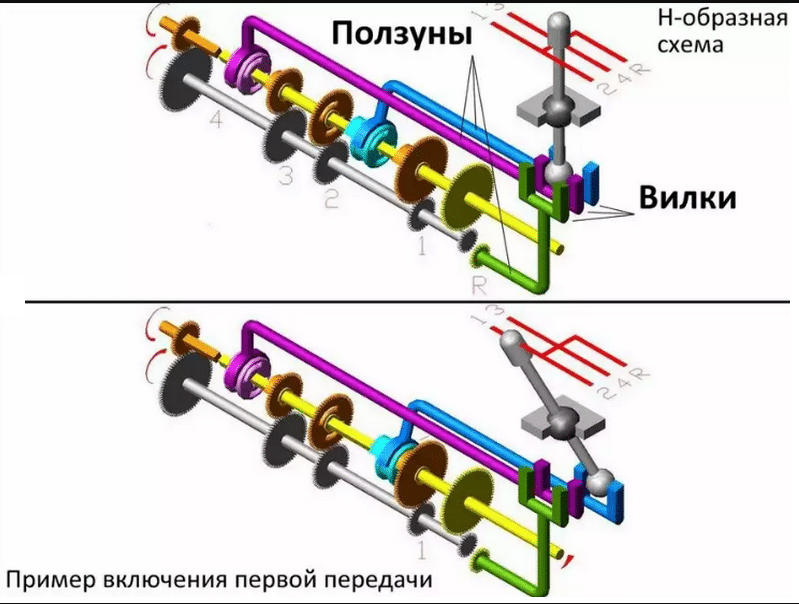
The gearshift mechanism in a three-shaft design is mounted directly inside the box. It includes a lever and sliders with forks.
The best way to avoid premature breakdowns in the gearbox is to operate it correctly.
Gear shifting must be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. It is about the minimum and maximum speed allowed for a particular transmission. You can navigate by the speedometer, tachometer or the sound of the internal combustion engine.
At low speeds and low engine speeds, do not use gears higher than second.
Proper work with the clutch will not only protect it from accelerated wear, but also avoid defects in gearbox parts. Depress the clutch quickly and release it slowly, but not too slowly. Press the pedal to the end, otherwise, during the inclusion of a particular gear, you will hear a crunch coming from the checkpoint. This should not be allowed. And in no case do not throw the clutch pedal sharply.
When moving forward even at low speed, do not allow excessive haste when shifting into reverse gear. The car must come to a complete stop, and only then can reverse gear be turned on. Ignoring this simple rule will disable the reverse gear after a while, and then you will have to repair the box.
Avoid shifting gears while passing a sharp turn.
Get rid of the habit of keeping your hand on the gear lever. Even such a seemingly meager pressure on the drive mechanism contributes to the accelerated wear of the fork and couplings in the box.
Try to restrain yourself if you prefer a sharp driving style. “Schumacher” behind the wheel is the worst enemy of every gearbox.
Check the level and condition of the lubricant in the gearbox. Do not forget to change in time.
Some indirect signs will tell the owner of the car that something may be wrong with the box.
Some problems can be caused by not too serious reasons and are relatively easy to fix.
Noise or vibration. First of all, diagnose the fastening of the box - perhaps you just need to tighten the bolts. Lack or poor quality of lubricant will also cause the box to make noise, so diagnose the level and, if necessary, top up or replace it with flushing.
Oil leaks. They are usually eliminated by replacing the glands and seals. Less common is a crankcase defect or improper installation of the box and associated components.
Gear shifting is difficult. First, diagnose the switching drive mechanism, which is often called. It may have defects or simply requires adjustment and tightening of the fasteners.
Other symptoms may indicate breakdowns that require gearbox repair, especially in cases where the problem occurs in some gears and is absent in other gears.
Difficulty shifting gears, accompanied by a rattle. This is possible with incomplete shutdown, so first diagnose its operation. If everything is in order with the clutch, then the problem is probably in worn synchronizers that require replacement.
Spontaneous reset of the included transmission. The culprits can be a set - a gear shift fork, a retainer, a synchronizer clutch or a blocking ring. In any case, no repairs can be done.
Constant hum, squeal or crunch. The cause may be broken bearings, worn or broken gear teeth. It also needs renovation.
Enthusiasts with sufficient experience, tools and working conditions can try to repair the gearbox themselves. But most drivers would rather entrust this difficult task to car service specialists.
In many cases it may be easier, cheaper and faster to purchase and install a so-called contract gearbox.
If you decide to repair your gearbox, take a look at the online store. Here you can select the necessary ones or purchase a complete box.
