Power steering pump - design, types, principle of operation
Content
Power steering continues to firmly occupy its place in a number of categories of vehicles and individual models of passenger cars. Their key node is the pump, which converts the engine power into the executive pressure of the working fluid. The design is well-established and proven, which allows us to consider it in detail in the general case.

Tasks performed and application
By its nature, the hydraulic pump provides energy to the actuator in the form of circulation of the working fluid of the system - special oil, under high pressure. The work done is determined by the magnitude of this pressure and the flow rate. Therefore, the pump rotor must rotate fast enough, while moving significant volumes per unit time.
The failure of the pump should not lead to the cessation of the steering, the wheels can still be turned, but the force on the steering wheel will increase dramatically, which may come as a surprise to the driver. Hence the high requirements for reliability and durability, which are met thanks to a proven design, the chosen injection method and good lubricating properties of the working fluid.
Versions
There are not so many varieties of hydraulic pumps; as a result of evolution, only the plate and gear types remained. The first one is predominantly used. Pressure adjustment is rarely provided, there is no particular need for this, the presence of a limiting pressure reducing valve is quite sufficient.

In the classic power steering, a mechanical drive of the pump rotor is used from the engine crankshaft pulley using a belt drive. Only more advanced electro-hydraulic systems use an electric motor drive, which gives advantages in control accuracy, but deprives the main advantage of hydraulics - high power amplification.
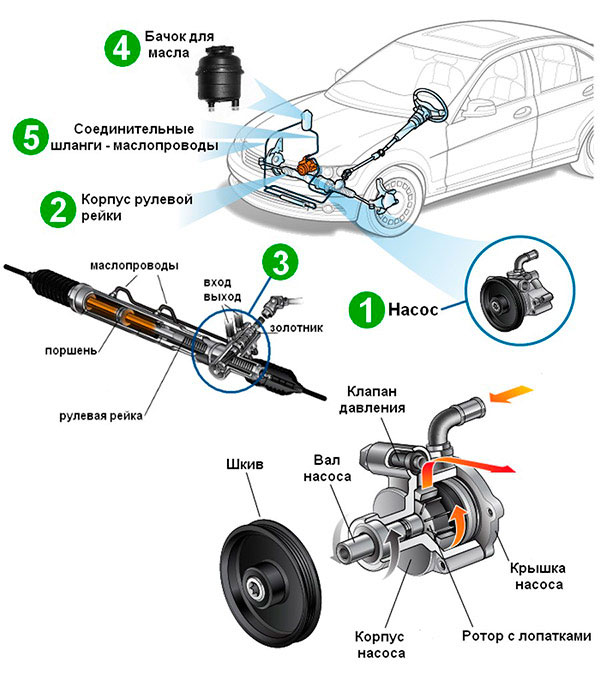
The design of the most common pump
The vane type mechanism works by moving liquid in small volumes with their decrease in the process of turning the rotor and squeezing oil onto the outlet pipe. The pump consists of the following parts:
- drive pulley on the rotor shaft;
- rotor with lamellar blades in grooves along the circumference;
- bearings and stuffing box seals of the shaft in the housing;
- stator with elliptical cavities in the housing volume;
- regulating restrictive valve;
- housing with engine mounts.
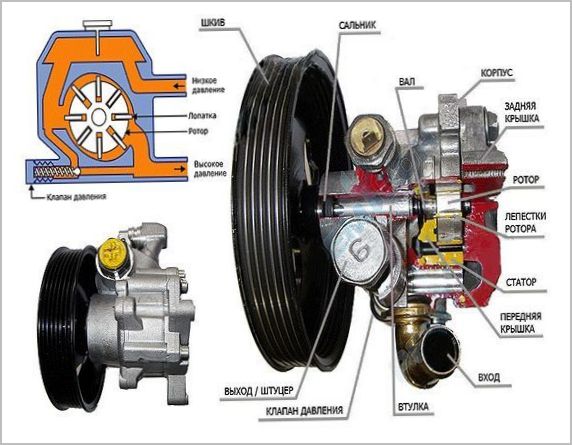
Typically, the rotor serves two working cavities, which gives an increase in productivity while maintaining a compact design. Both of them are absolutely identical and are located diametrically opposite relative to the axis of rotation.
The order of work and the interaction of components
A V-belt or multi-ribbed drive belt rotates the rotor shaft pulley. The rotor planted on it is equipped with slots in which metal plates move freely. By the action of centrifugal forces, they are constantly pressed against the elliptical inner surface of the stator cavity.
The liquid enters the cavities between the plates, after which it moves towards the outlet, where it is displaced due to the variable volume of the cavities. Running on the curved walls of the stator, the blades are recessed into the rotor, after which they are put forward again, taking the next portions of the liquid.
Due to the high speed of rotation, the pump has sufficient performance, while developing a pressure of about 100 bar when working "to a standstill".
The dead-end pressure mode would exist at high engine speeds and the wheels turned all the way, when the piston of the slave cylinder could no longer move further. But in these cases, a spring-loaded restrictive valve is activated, which opens and starts the backflow of fluid, preventing the pressure from increasing excessively.
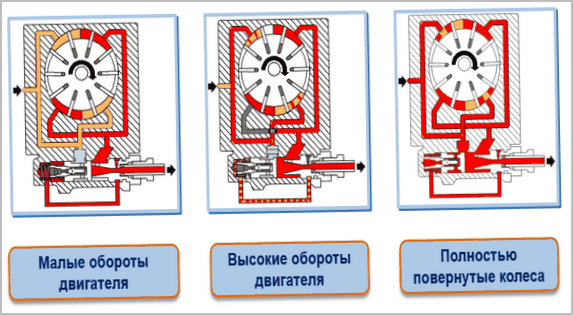
The pump modes are designed in such a way that it can deliver its maximum pressure at a minimum rotation speed. This is necessary when maneuvering with almost idle speed, but with the most light steering. Despite a lot of resistance in the case of turning the steered wheels on the spot. Everyone knows how heavy the steering wheel without power is in this case. It turns out that the pump can be fully loaded at the minimum rotor speed, and after an increase in speed, it simply dumps part of the liquid in the opposite direction through the control valve.
Despite the fact that such modes of operation with excess performance are regular and provided, the operation of the power steering with the wheels completely turned out at close range is very undesirable. The reason for this is overheating of the working fluid, due to which it loses its properties. There is a threat of increased wear and even pump breakdowns.
Reliability, failures and repairs
Power steering pumps are highly reliable and do not belong to consumables. But they are not eternal either. Malfunctions appear in the form of increased effort on the steering wheel, especially during fast rotation, when the pump clearly does not give the required performance. There are vibrations and a loud hum that disappears after removing the drive belt.
Repair of the pump is theoretically possible, but usually it is simply replaced with an original one or a spare part from an aftermarket. There is also a market for remanufactured units in the factory, they are much cheaper, but have almost the same reliability.