The purpose of the engine mount in a car and its principle of operation
Content
A complex combination of loads acts on a working power unit of any car:
- Reactions from the transmission of torque to the drive wheels;
- Horizontal forces during starting, hard braking and clutch operation;
- Vertical loads when driving over bumps;
- Vibration vibrations, the strength and frequency of which change in proportion to the change in the speed of the crankshaft;
- Own weight of the engine assembled with the gearbox.
The main part of the load is taken by the frame (body) of the car.
High-frequency vibrations of audible frequencies penetrate the cabin, disturbing the comfort of the driver and passengers. Low-frequency vibrations are felt by the skin and body, which also does not add convenience to the trip.
Car owners struggle with sound frequency fluctuations by installing additional noise insulation.
Only serviceable engine mounts can soften and suppress low-frequency vibrations.
The main functions of the engine mount
Supports (pillows) are the nodes on which the engine and gearbox are fixed to the frame, subframe or car body.
The power unit supports are designed for long-term operation with high reliability and minimal wear.
Structurally, most of the supports consist of a prefabricated steel body with elastic elements placed inside that absorb vibrations and dampen shocks. The transverse and longitudinal forces acting on the power unit are perceived by the pillow design.
Main functions of engine mounts:
- Reduce or completely extinguish shock and other loads on the power unit that occur when the vehicle is moving;
- Effectively reduce vibration and sounds generated by a running engine and penetrating into the car interior;
- Eliminate the movement of the power unit and, thereby, reduce the wear of the drive units (cardan drive) and the motor itself.
Number and location of engine mounts
The torque generated by the motor, according to the laws of kinematics, tends to turn the motor in the opposite direction to the rotation of the crankshaft and flywheel. Therefore, on one side of the engine, its supports additionally work in compression, on the other hand, in tension. The reactions of the supports when the machine is moving in reverse do not change.
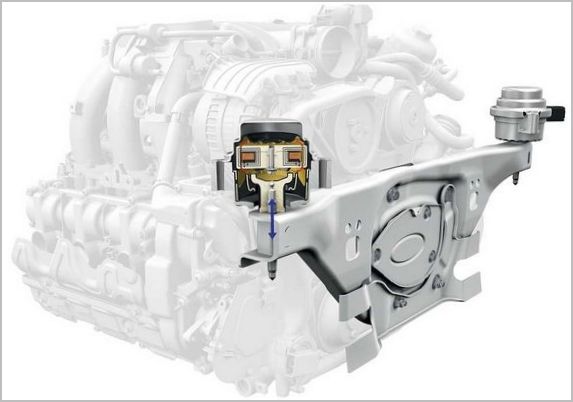

- In cars with a longitudinal arrangement of the power unit, four lower supports (pillows) are used. Engine brackets are attached to the front pair of supports, and the gearbox rests on the rear pair. All four supports of frame cars are of the same design.
On models with a monocoque body, the engine with gearbox is mounted on a subframe, so the gearbox cushions may differ from the engine mounts.
- In the vast majority of front-wheel drive cars, the engine with the gearbox is mounted on three supports, of which the two lower ones rest on the subframe and the third, upper one, is suspended.
The upper cushion is structurally different from the lower ones.
In all designs, between the subframe and the side members of the body, elastic rubber elements are installed that absorb vibration.
You can check the condition and diagnose the supports of the power unit by lifting the car onto a lift or using a viewing hole. In this case, it is necessary to dismantle the engine protection.
The top support is accessible for inspection from under the hood. Often, to inspect the upper support, you need to remove the plastic casing of the engine and some of its components and even assemblies, such as an air duct or generator.
Type of power unit supports
For each model, automakers select powertrain mounts with the best performance properties. All samples are tested on the stands and during real sea trials. The accumulated experience of large-scale production allows for years to use pillows of the same design in machines manufactured on common platforms.
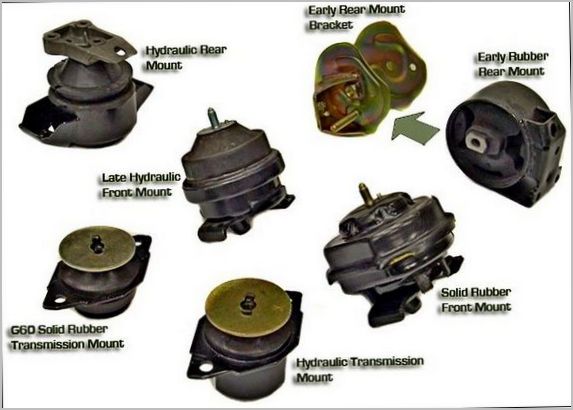

All pillows (supports) of modern cars can be divided into two groups by design:
- Rubber-metal. They are equipped with almost all mass and budget cars.
- Hydraulic. They are used in cars of higher and premium classes. In turn, they are divided into:
- passive, with constant performance;
- active, or managed, with changeable properties.
How the engine mount is arranged and works
All supports (pillows), regardless of their design, are designed to securely fix the power unit relative to the frame (body) of the vehicle, absorb or reduce variable loads and vibrations to acceptable values.
Rubber-metal supports are simple in design. Between the two steel clips are two elastic inserts made of rubber (synthetic rubber). A bolt (stud) passes along the axis of the support, fastening the engine to the subframe and creating a primary force in the support.

In rubber-metal bearings, there can be several rubber elements of different elasticity, separated by steel washers-spacers. Sometimes, in addition to elastic liners, a spring is installed in the support, which reduces high-frequency vibrations.
In sports racing cars, where the requirements for comfort and sound insulation are lowered, polyurethane pillow inserts are used, which are more rigid and wear-resistant.
Almost all rubber-metal bearings are collapsible, any worn part can be replaced.
The wide distribution of collapsible supports with elastic liners is explained by their simple device, maintainability and low cost.
Hydraulic bearings dampen almost all types of loads and vibrations in the engine-body system.
A spring-loaded piston is mounted in the cylindrical body of the hydraulic support filled with the working fluid. The piston rod is fixed on the power unit, the working cylinder of the support is mounted on the body subframe. When the piston moves, the working fluid flows from one cylinder cavity to another through the valves and holes in the piston. The stiffness of the springs and the calculated viscosity of the working fluid allow the support to smoothly dampen compressive and tensile forces.
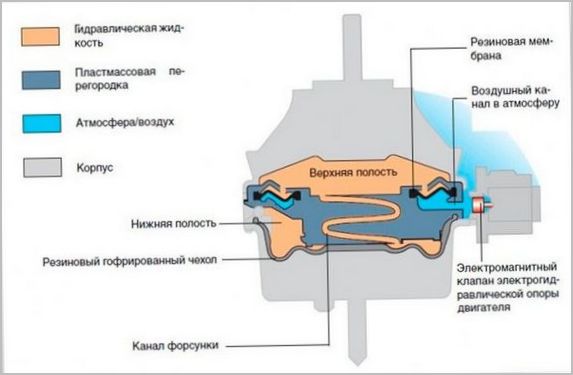
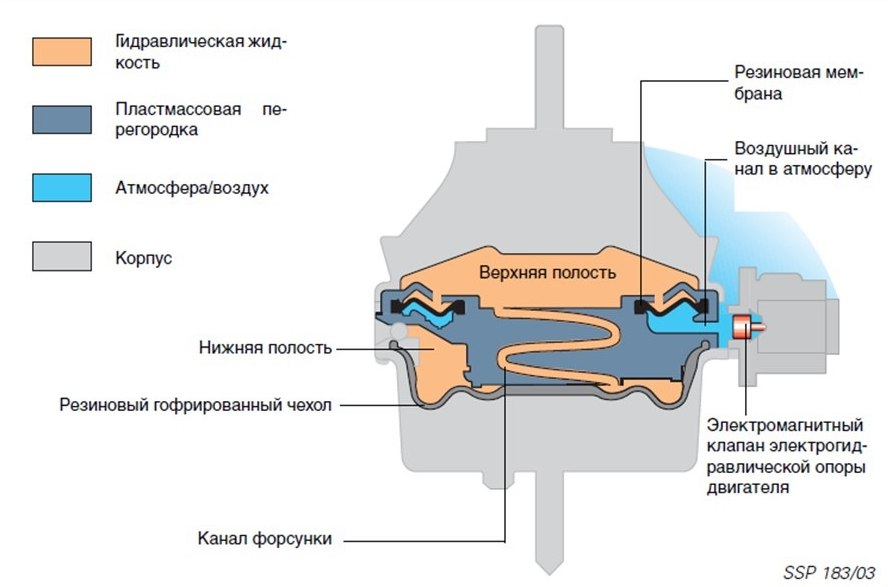
In the active (controlled) hydromount, a diaphragm is installed that changes the volume of liquid in the lower cavity of the cylinder and, accordingly, the time and speed of its flow, on which the elastic properties of the hydromount depend.
Active hydraulic supports differ in the way they are controlled:
- Mechanical. With a switch on the panel, the driver manually controls the position of the diaphragms in the supports, depending on driving conditions and loads on the power unit.
- Electronic. The volume of the working fluid and the movement of the diaphragms in the working cavities, i.e. the rigidity of the hydraulic bearings is controlled by the onboard processor, receiving a signal from the speed sensor.
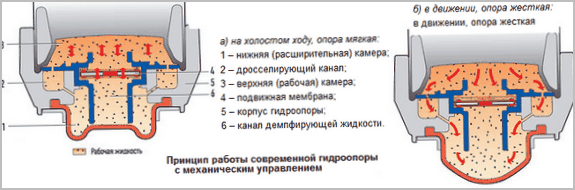
Hydrosupports are complex in design. Their reliability and durability depend on the invariance of the properties of the working fluid, the quality of the parts, valves, seals and rings.
The development of modern technologies has caused the emergence of a new type of hydraulic bearings - with dynamic control.
The working fluid in dynamic hydromounts is a dispersion of microparticles of magnetic metals. The viscosity of the magnetic working fluid changes under the influence of an electromagnetic field created by special windings. The on-board processor, controlling the driving conditions of the car, controls the viscosity of the magnetic fluid, changing the elastic properties of the engine's dynamic hydraulic mounts from maximum to zero.
Dynamically controlled hydraulic mounts are complex and expensive products to manufacture. They are equipped with premium cars, the comfort and reliability of which the buyer makes high demands.
All modern automakers strive to ensure the reliability of the car during the warranty period with possible repairs only at the official service center. The desire to justify rising prices by improving products has led to the displacement of rubber-metal engine mounts by hydraulic ones of all types, which are already being replaced by hydrodynamic ones.
The owner of a brand new car, who expects to ride the entire warranty period without problems and repairs, is simply obliged to drive the car carefully and carefully.
All drivers who want to drive a serviceable car are not recommended to follow sayings like “From the third place - asphalt into an accordion”, “More speed - fewer holes”.