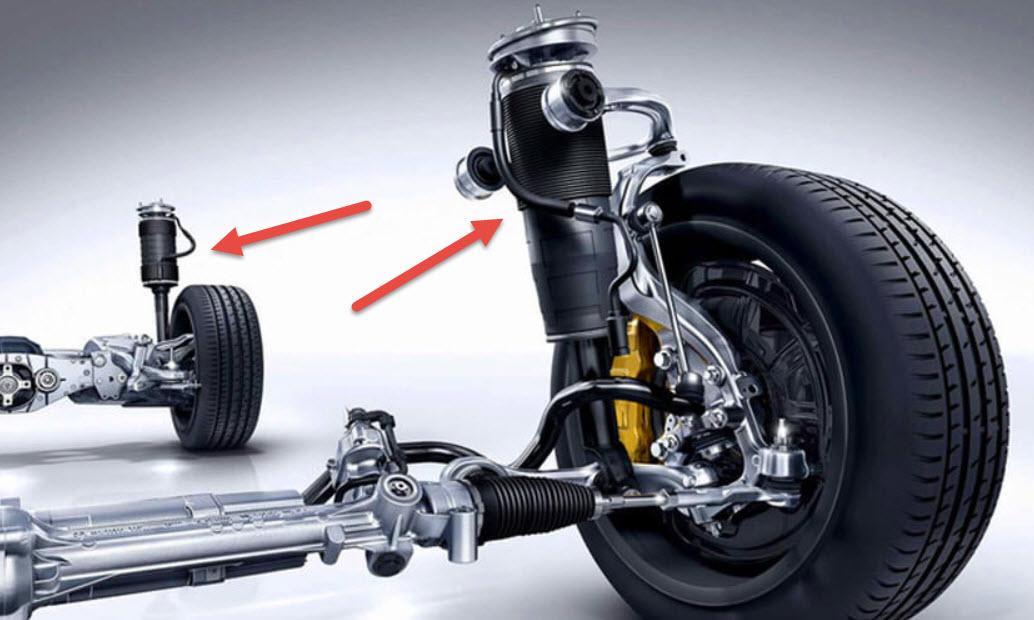
Features and principle of operation of the car's adaptive suspension
Content
In the case of sensors, the rigidity of the elastic parts and the degree of damping are adjusted automatically. But when a signal enters the electronic unit from the driver, the settings are forced to change (at the command of the person behind the wheel).
The suspension device of the machine is a movably connected layer between the body and the wheels. The mechanism that ensures the comfort and safety of the movement of the car crew is constantly being improved. Modern vehicles are equipped with adjustable structures - these are adaptive car suspensions. Consider the components, advantages and disadvantages, as well as types of progressive suspension equipment.
What is adaptive car suspension
There are discrepancies in understanding what an active car suspension is, and how it differs from an adaptive design. Meanwhile, there is no clear division of concepts.
All hydraulic or pneumatic suspensions controlled by a button or an adjusting knob from the passenger compartment are called active - this is a general definition. The only difference with the adaptive device is that the parameters in the latter change automatically on the move. That is, the suspension “by itself” changes the settings. This means that it is a subspecies, a variation of the flexible active chassis.
The vehicle's adaptive suspension collects information about changing environmental conditions, driving style and mode using various sensors every second. And transmits the data to the control unit. The ECU instantly changes the characteristics of the suspension, adjusts it to the type of road surface: increases or shortens the clearance, adjusts the geometry of the structure and the degree of vibration damping (damping).
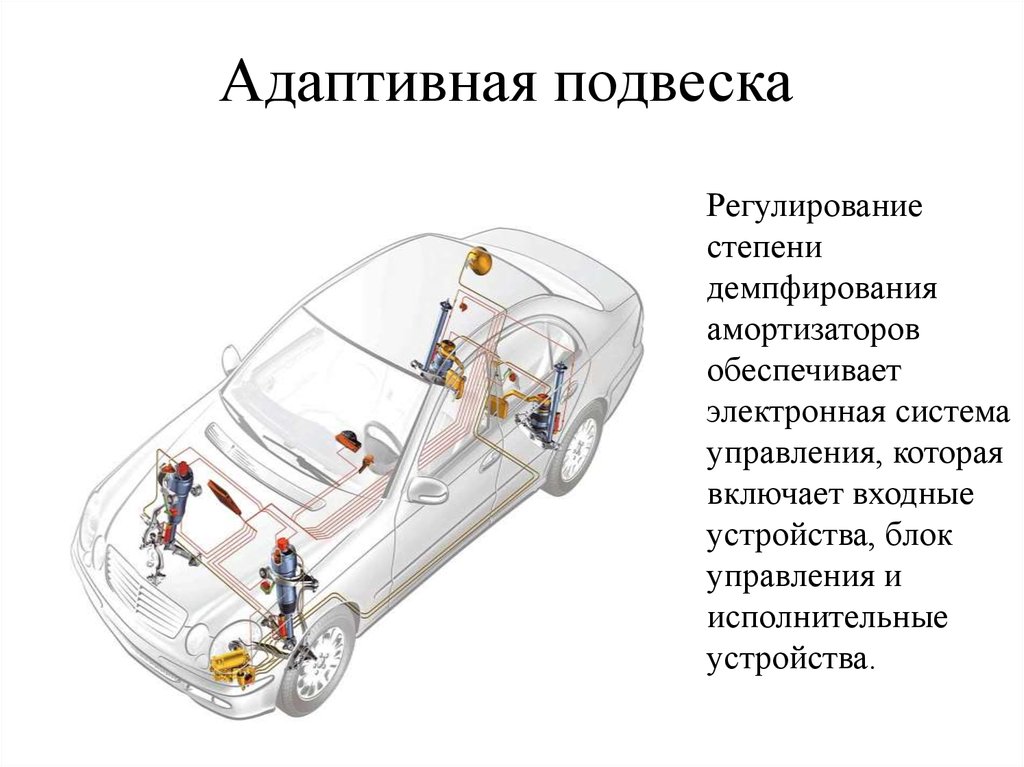
What is adaptive car suspension
Adaptive suspension elements
For different manufacturers, the components of adaptive systems can be modified. At the same time, there remains a standard set of elements inherent in all types of controlled suspensions.
Electronic control unit
Information from sensors or signals from a manual unit - a selector controlled by the driver - flows into the electronic "brain" of the mechanism. The ECU analyzes the data and selects the mode and setting of the individual functional parts of the suspension.
In the case of sensors, the rigidity of the elastic parts and the degree of damping are adjusted automatically. But when a signal enters the electronic unit from the driver, the settings are forced to change (at the command of the person behind the wheel).
Adjustable anti-roll bar
A mandatory component of the adaptive suspension consists of a rod, stabilizer struts and fasteners.
The anti-roll bar is activated by the ECU command. The response time is milliseconds.
SENSORS
Sensors of adaptive suspended equipment collect, measure and send information about changes in external circumstances to the electronic unit.
Main system controllers:
- acceleration of the body - prevent the buildup of the body part;
- rough roads - limit the vertical vibrations of the car;
- body positions - are triggered when the rear of the car sags or rises above the front.
Sensors are the most loaded elements of the car suspension, so they fail more often than others.
Active (adjustable) shock absorber struts
According to the design of the shock absorber strut, they are divided into two types:
- Solenoid valve systems. Such EM valves are based on changing the variable cross section under the influence of the voltage supplied by the ECU.
- Devices with a magnetic rheological fluid that changes viscosity under the influence of an electromagnetic field.
The shock absorber struts quickly change the chassis settings when they receive a command from the control unit.
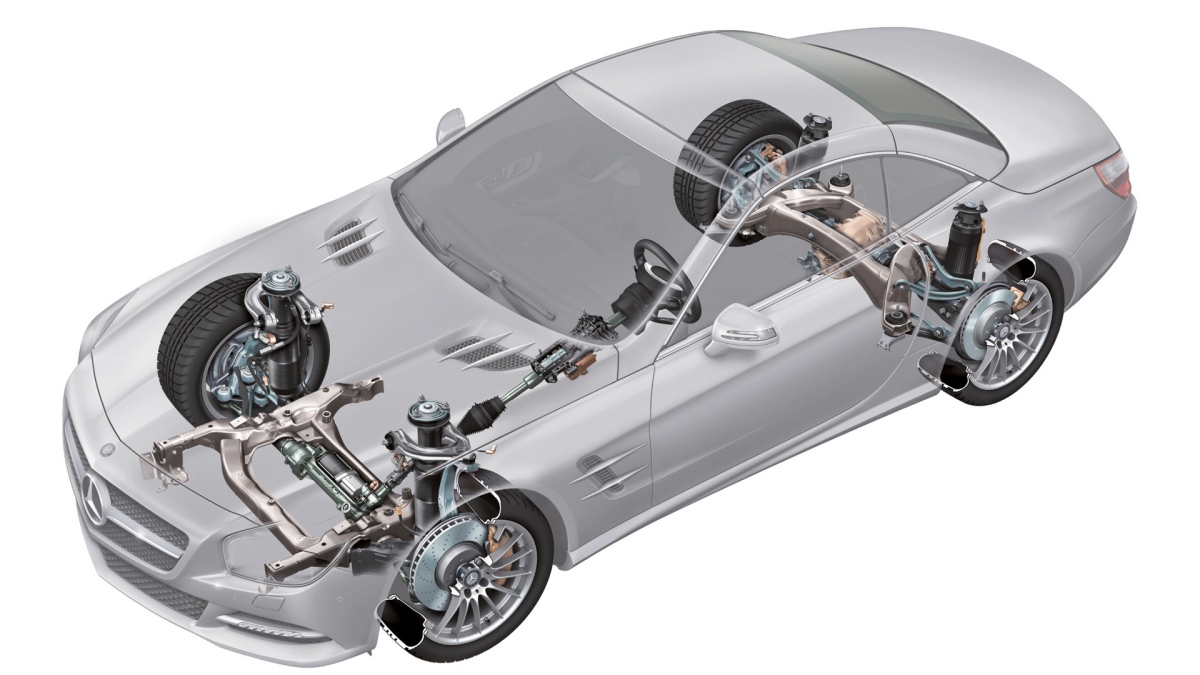
Features of adaptive car suspension
Principle of operation
The adaptive suspension option is the most complex unit, the principle of operation of which is as follows:
- Electronic sensors collect and send information about road conditions to the ECU.
- The control unit analyzes the data, sends commands to the actuators.
- The shock struts and stabilizers adjust the performance to suit the situation.
When the commands come from the manual control unit, the driver himself selects the adaptation mode: normal, comfortable or "sport".
Types of adaptive suspensions
Flexible mechanisms are divided into types, depending on the tasks performed:
- affect the rigidity of elastic elements;
- together with stiffness, they adapt the ground clearance;
- change the position of the anti-roll bars;
- control the body part relative to the horizontal plane;
- adjust to the owner's driving style and track conditions.
Each automaker combines the control functions of the ECU in its own way.
What cars are put on
From a curiosity of the second half of the last century, an adjustable chassis is gradually moving into the category of ordinary things. Today, inexpensive Korean and Japanese cars are equipped with a progressive device.
Citroen laid the foundation for the production of active suspensions by introducing the Hydractiv multi-mode hydropneumatic system into the car design. But then the electronics were still poorly developed, so the legendary Adaptive Drive of the BMW concern became more perfect. This was followed by the Adaptive Chassis Control of the Volkswagen plant.
Adjustment
Roughly imagining on which roads the movement will be, the driver from his place can adjust the adaptation himself. On highways, the "sport" mode works better, on bumpy canvases - "comfort" or "off-road".
Malfunctions
Most often, continuously operating sensors break down: mechanical reading devices fail. In general, reliable shock absorbers leak.
But the most problematic is the air suspension. In the system, compressors fail, air springs leak, lines rust.

Manual and automatic air suspension modes
Advantages and disadvantages
Limited features in standard suspension options are compensated and multiplied in active designs.
The mechanism of a new level (although already non-innovative) promises the car owner many benefits:
- excellent handling at any speed;
- reliable vehicle stability on difficult road surfaces;
- an unparalleled level of comfort;
- excellent smoothness of the course;
- safety of movement;
- the ability to independently adjust the parameters of the chassis, depending on the circumstances.
The suspension would be perfect if not for some of the disadvantages of the device:
- high price, which is ultimately reflected in the price tag of the car;
- the complexity of the design, entailing expensive repairs and maintenance of equipment;
- difficulties in self-assembly of the device.
But you have to pay for comfort, so many motorists choose the adaptive suspension.
