P0134 Lack of activity in the oxygen sensor circuit (bank 2, sensor 1)
Content
OBD-II Trouble Code - P0134 - Data Sheet
Lack of activity in the O2 sensor circuit (block 1, sensor 1)
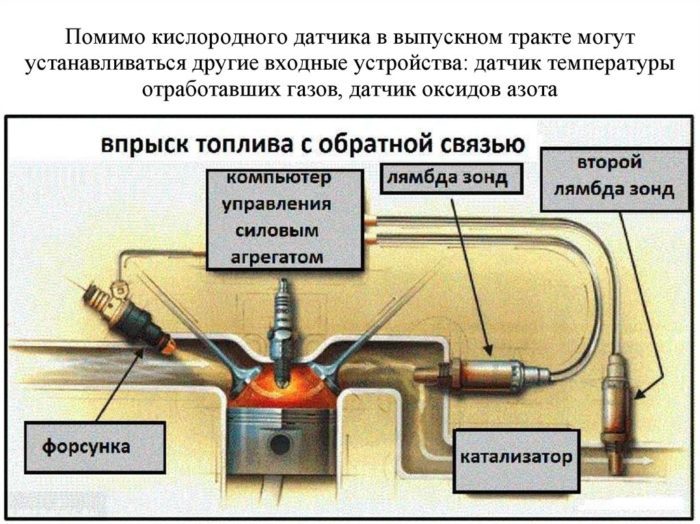
DTC P0134 is set when the engine control unit (ECU, ECM, or PCM) detects a malfunction in the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1, bank 1) circuit.
What does trouble code P0134 mean?
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a generic transmission code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles. Although general, specific repair steps may differ depending on the brand / model.
This code applies to the front oxygen sensor on block 1. Generally, the oxygen sensor is inactive. That's why:
The powertrain control module (PCM) provides a base voltage of approximately 450 mV to the oxygen sensor signal circuit. When cold, the PCM detects a high internal sensor resistance. As the sensor heats up, the resistance decreases and it starts to generate voltage depending on the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. When the PCM determines that the time it takes to warm up the sensor is more than one minute or that the voltage is inactive (other than outside 391-491 mV, it considers the sensor as inactive or open and sets code P0134.
Possible symptoms
The symptoms most commonly associated with this error code are as follows:
Turn on the corresponding engine warning light.
- While driving, there is a feeling of a general malfunction of the vehicle.
- Black smoke with an unpleasant odor comes out of the exhaust pipe.
- Excessive fuel consumption.
- A general engine malfunction that runs inefficiently.
- Poorly running / missing engine
- Blowing black smoke
- Poor fuel economy
- Die, stutter
However, these symptoms may also appear in combination with other error codes.
Causes of the P0134 code
The engine control module performs the task of monitoring the health of the front oxygen sensor in bank 1. If the sensor warm-up time does not correspond to the vehicle's standard values, DTC P0134 is automatically activated. As you know, the lambda probe registers the amount of oxygen and fuel that have passed through the exhaust in order to check the correct ratio of these two components in the mixture. When the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases is less than normal, the engine control module reduces the amount of fuel accordingly. The reason for this lies in the fact that when there is a lack of oxygen, the engine automatically consumes more fuel, and therefore emits more carbon monoxide into the atmosphere. The front heated oxygen sensor is usually located in the exhaust manifold and has a closed zirconia ceramic tube. Zirconium produces a voltage of approximately 1 volt in the richest conditions and 0 volts in the worst conditions. The ideal air-fuel ratio is between the two values above. When the values transmitted by the oxygen sensor are disabled, the engine control unit will cause the activation of a malfunction code signaling this malfunction on the instrument panel. Zirconium produces a voltage of approximately 1 volt in the richest conditions and 0 volts in the worst conditions. The ideal air-fuel ratio is between the two values above. When the values transmitted by the oxygen sensor are disabled, the engine control unit will cause the activation of a malfunction code signaling this malfunction on the instrument panel. Zirconium produces a voltage of approximately 1 volt in the richest conditions and 0 volts in the worst conditions. The ideal air-fuel ratio is between the two values above. When the values transmitted by the oxygen sensor are disabled, the engine control unit will cause the activation of a malfunction code signaling this malfunction on the instrument panel.
The most common reasons to track down this code are as follows:
- Malfunction of the heating circuit.
- Injector malfunction.
- Intake system malfunction.
- Heating circuit fuse defective.
- Oxygen sensor wiring problem, either exposed wire or short circuit.
- Defective connections, e.g. due to corrosion.
- Leak in the engine.
- Drain hole defect.
- Rusty exhaust pipe.
- Too much current.
- Incorrect fuel pressure.
- Problem with the engine control module, sending incorrect codes.
Possible solutions
The most common solution is to replace the oxygen sensor. But this does not exclude the possibility:
- Rusty exhaust pipe
- Inspect wiring and connector (s) for problems.
- Too much amperage blows the heater fuse (still needs replacement of the sensor, but also replacement of the blown fuse)
- Replace PCM (only as a last resort after considering all other options.
Repair Tips
After the vehicle is taken to the workshop, the mechanic will usually perform the following steps to properly diagnose the problem:
- Scan for error codes with an appropriate OBC-II scanner. Once this is done and after the codes have been reset, we will continue to test drive on the road to see if the codes reappear.
- Checking the oxygen sensor.
- Exhaust pipe inspection.
- It is strongly not recommended to replace the oxygen sensor without having carried out a whole series of preliminary checks, since the cause may be, for example, a short circuit.
Generally, the repair that most often cleans up this code is as follows:
- Replacing or repairing faulty wiring.
- Replacement or repair of the oxygen sensor.
- Exhaust pipe replacement or repair.
- Replacement or repair of the heater fuse.
Driving with this error code, while possible, is not recommended. In fact, you may end up having trouble starting the machine; in addition, serious damage to the catalytic converter may occur. For this reason, you should take your vehicle to a workshop as soon as possible. Given the complexity of the interventions required, a do-it-yourself option in a home garage is not feasible.
It is difficult to estimate the upcoming costs, since a lot depends on the results of the diagnostics carried out by the mechanic. Typically, the cost of replacing a factory heated oxygen sensor, depending on the model, can be from 100 to 500 euros.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What does code P0134 mean?
DTC P0134 indicates a malfunction in the heated oxygen sensor circuit (sensor 1, bank 1).
What causes the P0134 code?
There can be several reasons for the P0134 code, from leaks and air intrusion to a faulty oxygen sensor or catalyst.
How to fix code P0134?
Carefully check all components connected to the heated oxygen sensor system.
Can code P0134 go away on its own?
In some cases, this code may disappear on its own, but only temporarily. For this reason, it is always advisable not to underestimate a thing.
Can I drive with code P0134?
Driving with this error code, while possible, is not recommended. In fact, you may end up having trouble starting the machine; in addition, serious damage to the catalytic converter may occur.
How much does it cost to fix code P0134?
On average, the cost of replacing a heated oxygen sensor in a workshop, depending on the model, can range from 100 to 500 euros.
Need more help with your p0134 code?
If you still need help with DTC P0134, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.

One comment
gabriel matos
hey guys i need help, i have a jetta 2.5 2008 it is giving the code p0134 lack of voltage in the o2 sensor, this fault code only appears when you drive about 50km with i have done everything and nothing solves it i changed it too any solution?