P205C Low rate of reducing agent tank temperature sensor circuit
Content
- P205C Low rate of reducing agent tank temperature sensor circuit
- OBD-II DTC Datasheet
- What does this mean?
- What is the severity of this DTC?
- What are some of the symptoms of the code?
- What are some of the common causes for the code?
- What are some steps to troubleshoot the P205C?
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Related DTC discussions
- Need more help with a P205C code?
P205C Low rate of reducing agent tank temperature sensor circuit
OBD-II DTC Datasheet
Low signal level in the reducing agent tank temperature sensor circuit
What does this mean?
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a generic transmission code and applies to many OBD-II vehicles (1996 and newer). This may include but is not limited to Mercedes, Sprinter, Ford, GMC, Chevrolet, etc. While general, the exact repair steps may vary depending on the model year, make, model and transmission configuration.
A stored code P205C means the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected an insufficient voltage in the reductant tank temperature sensor circuit. This code is displayed exclusively on vehicles with a clean diesel engine.
The catalyst system is responsible for reducing (mostly) all exhaust emissions, although some applications are also equipped with a NOx trap.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems take another step in reducing NOx emissions. However, today's larger, more powerful diesel engines cannot meet strict federal (US) emission standards with just an EGR system, a particulate filter / catalytic converter, and a NOx trap. For this reason, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems have been invented.
SCR systems inject a reductant formulation or Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) into the exhaust gases upstream of the particulate filter, NOx trap and / or catalytic converter through a reductant injection valve (solenoid). The precisely calculated DEF injection raises the temperature of the filter element and allows it to work more efficiently. It extends the service life of the filter elements and helps reduce emissions of harmful exhaust gases into the atmosphere. The entire SCR system is controlled and monitored by either the PCM or a stand-alone controller (which interacts with the PCM). In any case, the controller monitors the O2, NOx and exhaust gas temperature sensors (as well as other inputs) to determine the appropriate timing for the DEF (reductant) injection. Precision DEF injection is required to keep the exhaust gas temperature within acceptable parameters and to optimize the filtration of pollutants.
The reductant / regeneration pump is used to pressurize the DEF in the reductant liquid system for use when needed. The PCM monitors the supply pump voltage for continuous fluctuations and load percentage. The PCM also monitors one or more pressure sensors in the reductant supply system to determine if there is a leak in the system.
If the PCM detects that the voltage on the reductant tank temperature sensor circuit is too low, below the acceptable circuit range, a code P205C will be stored and a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) may be illuminated. MIL illumination may require multiple ignition cycles - in case of failure.
Example of a tank for reducing agent DEF: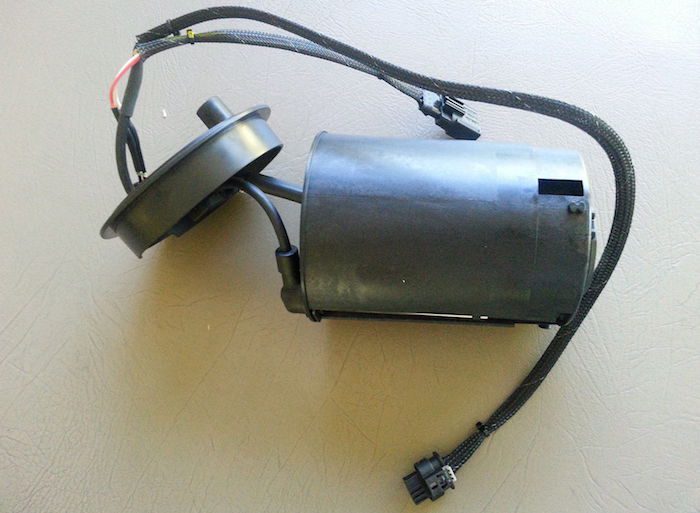 
What is the severity of this DTC?
A stored P205C code should be treated as serious and rectified as soon as possible. The SCR system could be disabled because of this. Catalyst damage can occur if the conditions that contributed to the code persistence are not corrected in a timely manner.
What are some of the symptoms of the code?
Symptoms of a P205C trouble code may include:
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Excessive black smoke from vehicle exhaust
- Reduced engine performance
- Other codes related to SCR
What are some of the common causes for the code?
Reasons for this code may include:
- Reducing agent tank temperature sensor defective
- Open or short circuit in the reducing agent tank temperature sensor circuit
- Bad SCR / PCM controller or programming error
What are some steps to troubleshoot the P205C?
To diagnose the P205C code, you will need a diagnostic scanner, a digital volt / ohmmeter (DVOM), and a source of vehicle-specific diagnostic information.
You can use your vehicle information source to find a Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) that matches your vehicle's year, make and model; as well as engine displacement, stored codes and symptoms detected. If you find it, it can provide useful diagnostic information.
Use a scanner (connected to the vehicle's diagnostic socket) to retrieve all stored codes and associated freeze frame data. It is recommended that you write down this information before clearing the codes and then test drive the vehicle until the PCM enters ready mode or the code is cleared.
If the PCM enters ready mode at this time, the code is intermittent and can be much more difficult to diagnose. In this case, the conditions that contributed to the retention of the code may need to worsen before an accurate diagnosis can be made.
If the code is reset immediately, the next diagnostic step will require you to search your vehicle information source for diagnostic block diagrams, pinouts, connector faceplates, and component test procedures / specifications.
Step 1
Use the DVOM to test the reductant temperature sensor according to the manufacturer's specifications. Components that fail the test within the maximum allowable parameters should be considered defective.
Step 2
If the actual reductant temperature is within specifications, the P205C code is stored and the sensor in question is operational, use the DVOM to test the input and output circuits between the temperature sensor and the PCM / SCR controller. Disconnect all controllers before using the DVOM for testing.
- Reductant temperature sensor codes are usually associated with a faulty or disconnected sensor.
Related DTC discussions
- There are currently no related topics in our forums. Post a new topic on the forum now.
Need more help with a P205C code?
If you still need help with DTC P205C, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.
