P210C Throttle Actuator B - Engine Circuit Low
Content
P210C Throttle Actuator B - Engine Circuit Low
OBD-II DTC Datasheet
Low signal level in the control motor circuit of the throttle actuator B
What does this mean?
This Generic Transmission / Engine DTC usually applies to all OBDII equipped engines with electric throttle actuators, but is more common in some Ford and Nissan vehicles.
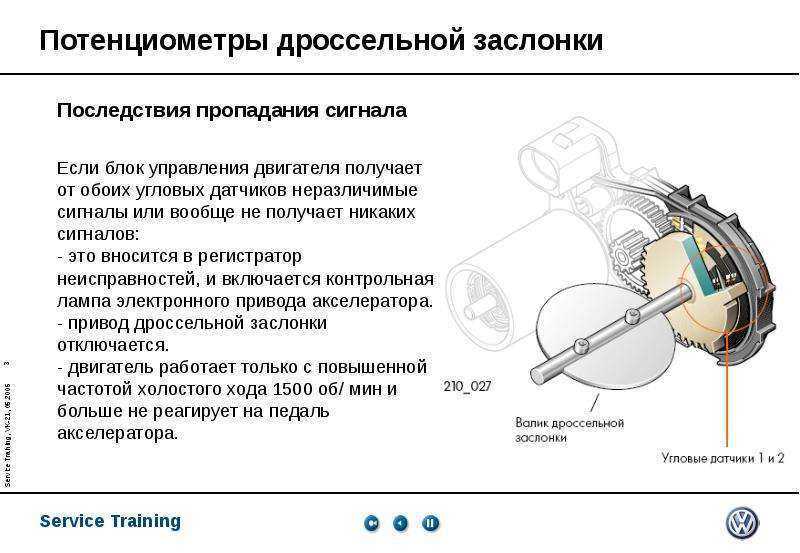
Throttle Actuator B (TA-B) can usually be found mounted at the front of the engine, on top of the engine, inside the wheel arches, or opposite a bulkhead. The TA-B is controlled by an electrical signal from the powertrain control module (PCM).
The PCM receives input to determine when and how long it takes for the TA-B to operate. These inputs are voltage signals received from the coolant temperature, intake air temperature, engine speed, and air conditioning pressure sensors. Once the PCM receives this input, it can change the signal to TA-B.
P210C is usually installed due to electrical problems (TA-B circuit). They should not be overlooked during the troubleshooting phase, especially when dealing with an intermittent problem.
Troubleshooting steps may vary depending on manufacturer, TA-B type, and wire colors.
Corresponding throttle actuator control motor B circuit codes are:
- P210A Open circuit of the throttle actuator motor "B"
- P210B Throttle Actuator "B" Motor Control Circuit Range / Performance
- P210D Throttle actuator "B" motor control circuit high
Code severity and symptoms
The severity is usually very severe due to the impact on the cooling system. Since this is usually an electrical fault, the PCM cannot fully compensate for it. Partial compensation usually means that the engine has a fixed idle speed (usually around 1000 - 1200 rpm).
Symptoms of a P210C engine code may include:
- Fault indicator light is on
- Fixed idle speed
- Unable to overclock the engine
reasons
Usually the reason for installing this code is:
- Open or short in throttle actuator circuit - likely
- Faulty throttle actuator - probably
- Failed PCM – Unlikely
Diagnostic and repair procedures
A good starting point is always to check the Technical Service Bulletins (TSB) for your particular vehicle. Your problem may be a known issue with a known manufacturer-released fix and could save you time and money while troubleshooting.
Then find the throttle actuator B (TA-B) on your specific vehicle. This drive is usually installed at the front of the engine, on top of the engine, inside the wheel arches, or opposite a bulkhead. Once found, visually inspect the connector and wiring. Look for scratches, scuffs, exposed wires, burn marks, or molten plastic. Disconnect the connector and carefully inspect the terminals (metal parts) inside the connector. See if they look burnt or have a green tint indicating corrosion. If you need to clean the terminals, use an electrical contact cleaner and a plastic bristle brush. Allow to dry and apply electrical grease where the terminals touch.
If you have a scan tool, clear the DTCs from memory and see if P210C code returns. If this is not the case, then there is most likely a connection problem.
For this code, this is the most common area of concern, as are the relay / relay connections, with an actuator error close to a second.
If the code returns, we will need to test the drive and associated circuits. There are usually 2 wires on each throttle actuator. Disconnect the harness going to the throttle actuator first. Using a digital volt ohmmeter (DVOM), connect one lead of the meter to one terminal of the drive. Connect the remaining meter lead to the other terminal on the drive. It must not be open or short-circuited. Check the resistance characteristics for your specific vehicle. If the drive motor is open or shorted (infinite resistance or no resistance / 0 ohms), replace the throttle actuator.
If this test passes, with the DVOM, make sure you have 12V in the throttle actuator power circuit (red wire to the actuator power circuit, black wire to good ground). With a scan tool that can activate the throttle actuator, turn on the throttle actuator. If the actuator is not 12 volts, repair the wiring from the PCM or relay to the actuator, or possibly a faulty PCM.
If this is normal, make sure you have a good ground at the throttle actuator. Connect a test lamp to the 12 V battery positive (red terminal) and touch the other end of a test lamp to the ground circuit that leads to the throttle actuator circuit ground. Using a scan tool to actuate the throttle actuator, check to see if the test lamp illuminates each time the scan tool actuates the actuator. If the test lamp does not light up, it indicates a faulty circuit. If it illuminates, wiggle the wiring harness going to the actuator to see if the test lamp blinks, indicating an intermittent connection.
If all previous tests pass and you keep getting P210C, it will most likely indicate a faulty throttle actuator, although the failed PCM cannot be ruled out until the throttle actuator is replaced. If you are unsure, seek help from a qualified automotive diagnostician. To install correctly, the PCM must be programmed or calibrated for the vehicle.
Related DTC discussions
- There are currently no related topics in our forums. Post a new topic on the forum now.
Need more help with code p210c?
If you still need help with DTC P210C, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.

