Car suspension. Device and purpose
Content
The car suspension connects the bearing part of the car with the wheels. In fact, this is a suspension system, which includes a number of parts and assemblies. Its essence is to take on the impact of various forces that arise in the process of moving along the road and make the connection between the body and wheels elastic.
Suspensions - front and rear - along with the frame, axle beams and wheels make up the chassis of the car.
A number of vehicle characteristics are directly determined by the type and specific design of the suspension. Among the main such parameters are handling, stability, and even smoothness.
The unsprung mass is a set of components that directly affect the road with their weight. First of all, these are wheels and suspension parts and brake mechanisms directly connected to them.
All other components and parts, whose weight is transferred to the road through the suspension, constitute the sprung mass.
The ratio of sprung and unsprung mass has a very strong effect on the driving performance of the car. The smaller the mass of the unsprung components relative to the sprung ones, the better the handling and smoothness of the ride. To some extent, this also improves the dynamics of the car.
Too much unsprung mass can cause increased suspension inertia. In this case, driving on a undulating road could damage the rear axle and lead to a serious accident.
Almost all suspension components are related to the unsprung weight of the vehicle. It is understandable, therefore, the desire of engineers to reduce the weight of the suspension in one way or another. To this end, designers are trying to reduce the dimensions of parts or use lighter alloys instead of steel. Each kilogram won gradually improves the running characteristics of the car. The same effect can be achieved by increasing the sprung mass, but for this you will have to add a very significant weight. For passenger cars, the ratio is approximately 15:1. In addition, an increase in the total mass worsens the acceleration dynamics.
In terms of comfort
A vehicle in motion constantly vibrates. In this case, relatively low-frequency and high-frequency oscillations can be distinguished.
From the point of view of comfort, the number of vibrations of the body per minute should be in the range from 60 to 120.
In addition, due to the use of tires and other elastic components, the unsprung masses experience higher frequency vibrations - about 600 per minute. The design of the suspension should keep such vibrations to a minimum so that they are not felt in the cabin.
And of course, bumps and shocks are inevitable while driving, the intensity of which depends on the condition of the road surface. Effectively combating the impact of shaking due to bumps in the road is one of the important tasks of the suspension.
In terms of manageability
The vehicle must maintain a given direction of movement and at the same time easily change it at the will of the driver. One of the functions of the suspension is to provide sufficient stabilization of the steered wheels so that the car continues to move in a straight line, regardless of random bumps that occur due to road surface defects.
With good stabilization, the steered wheels return to a neutral position with little or no driver intervention, and the car moves in a straight line, even if the steering wheel is not held.
How the wheels move in relation to the road and the body is largely determined by the kinematics of the suspension.
In terms of security
The suspension must provide optimal grip of the tires to the roadway so that the contact patch remains constant during the movement. Dynamic changes in the settings (alignment, etc.), as well as suspension geometry, should be minimal. This is especially true when driving over bumps in the road and cornering. The design must include elements that reduce roll and minimize the likelihood of skidding and overturning of the machine, in other words, provide sufficient stability.
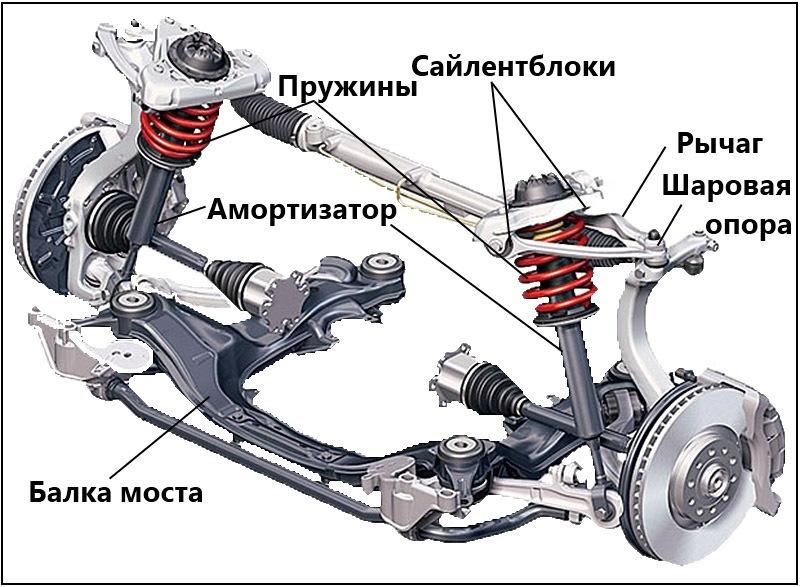
An automobile suspension usually consists of guide mechanisms, elastic components, a vibration damper, an anti-roll bar, as well as fasteners, regulating and control devices.
Guide mechanisms
First of all, these are various levers, which you can learn more about, as well as all kinds of traction, racks, extensions. It depends on them how and within what limits it is possible to move the wheels along different axes and in different planes. In addition, they transmit traction and braking forces, as well as lateral influences, for example, during a turn.
Depending on the type of guide mechanisms used, all suspensions can be divided into two large classes - dependent and independent.
In the dependent, both wheels of one axle are rigidly connected to one another by means of a bridge (cross beam). In this case, the displacement of one of the wheels, for example, when driving through a pit, will cause a similar displacement of the other.
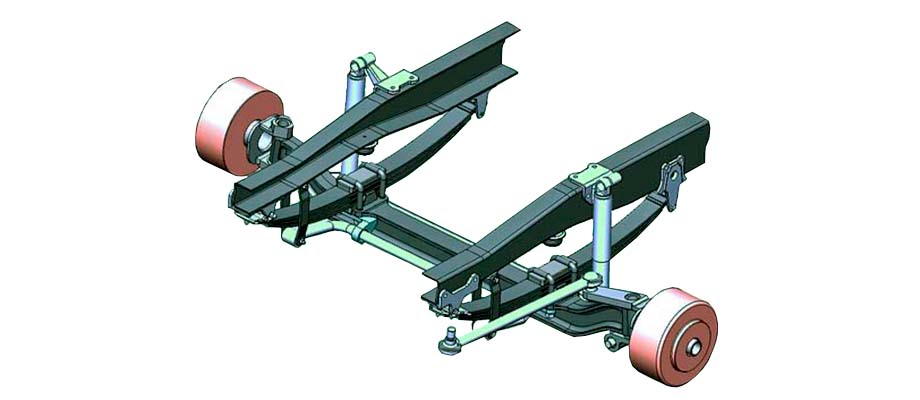
In an independent suspension, there is no such rigid connection, so vertical displacements or inclinations of one wheel have practically no effect on others.
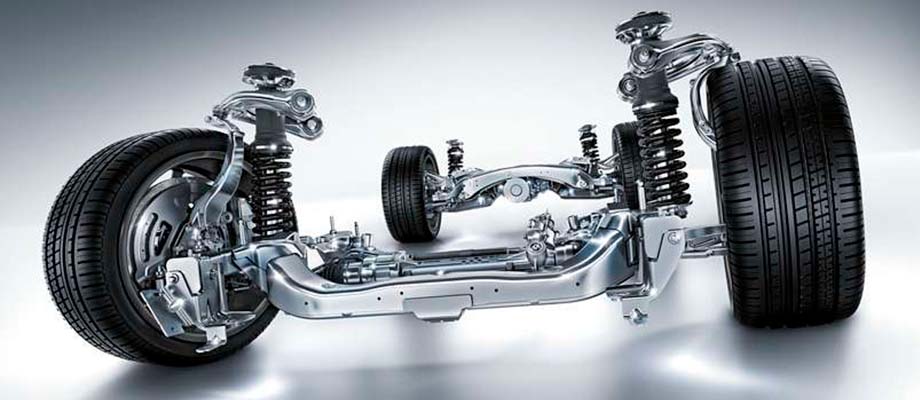

Both classes have their advantages and disadvantages, which determine the scope of their application. As for passenger cars, here a clear advantage turned out to be on the side of independent suspensions. Although the rear axle in many cases is still installed dependent, occasionally you can also find a semi-independent torsion-lever system.
On the front axle, dependent suspension, due to its high strength and simplicity of design, is still relevant on trucks, buses and some SUVs.
The comparison of dependent and independent systems is devoted to.
The design may include a different number of levers, and they may be located in different ways. According to these features, one can distinguish single-lever, double-lever and multi-link suspensions with a longitudinal, transverse or oblique arrangement.
Elastic elements
These include springs, torsion bars, various types of springs, as well as rubber-metal hinges (silent blocks), thanks to which the levers and springs are movable. Elastic elements take on shocks when hitting bumps in the road and significantly soften their impact on the body, internal combustion engine and other components and systems of the car. And of course, they increase the level of comfort for those in the cabin.
Most often, in the design of an independent suspension, cylindrical coil springs are used, made of special spring steel using a special technology. Such elastic elements are reliable, do not need maintenance and at the same time allow you to get the best smoothness. In passenger cars, springs have almost completely replaced springs.
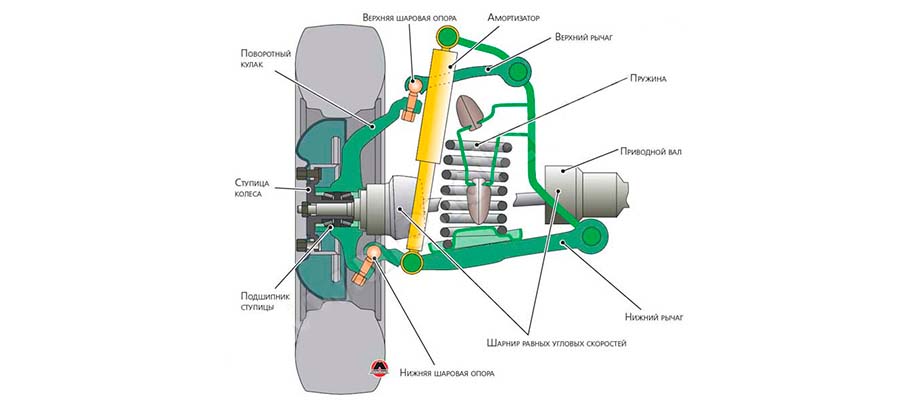
The figure shows a schematic arrangement of a spring suspension with two wishbones.
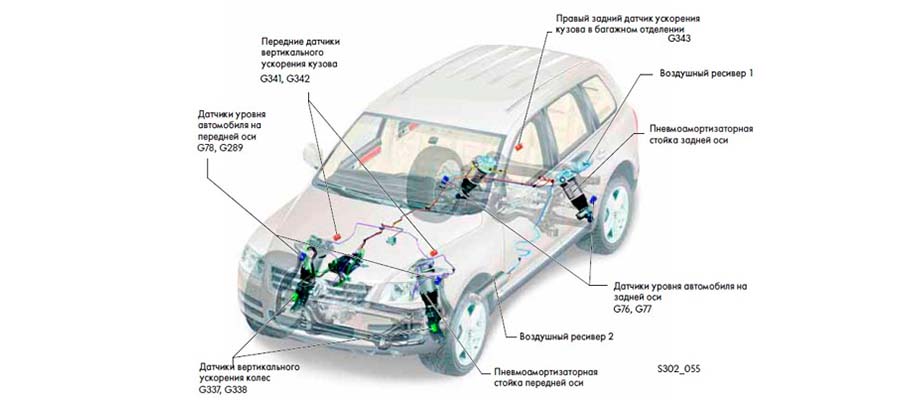
In the air suspension, air springs are used as an elastic element. By changing the gas pressure in the cylinder in this embodiment, it is possible to quickly adjust the rigidity of the system, as well as the amount of ground clearance. Automatic adaptation is achieved thanks to a system of sensors and an electronic control unit. However, the cost of such a device is very high, and it is installed only on elite cars. In addition, adaptive air suspension is very difficult and expensive to repair, and at the same time quite vulnerable on bad roads.
vibration damper
He performs his role. It is designed to dampen vibrations arising from the use of elastic components, as well as resonant phenomena. In the absence of a shock absorber, vibrations in the vertical and horizontal planes significantly reduce controllability and, in some cases, can lead to an emergency.
Very often, the damper is combined with elastic elements into one device - which immediately performs a set of functions.
Anti-roll bar
This part is installed on both the front and rear axles. It is designed to reduce lateral roll when cornering and reduce the likelihood of the machine tipping over.
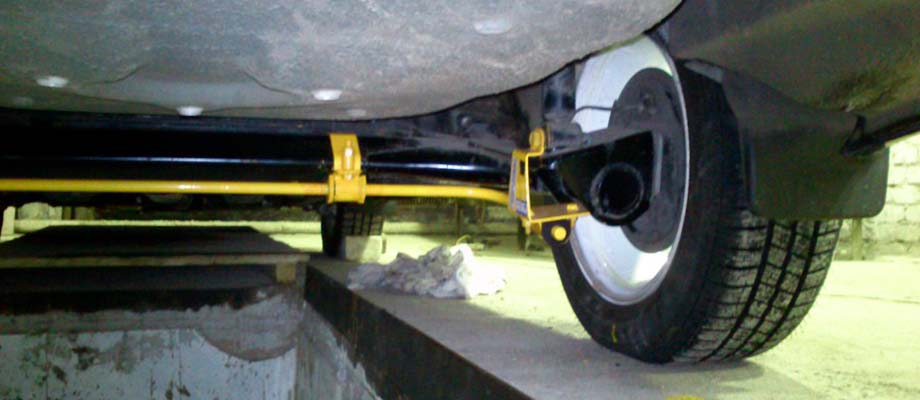

You can learn more about the device and principle of operation of the anti-roll bar.
Fasteners
To connect suspension parts to the frame and to each other, three types of fastenings are used - bolted, with and through elastic components (rubber-metal hinges and bushings). The latter, in addition to fulfilling their main task, also help reduce noise levels by absorbing vibrations in a certain frequency spectrum.
Typically, the design also provides for limiters for the travel of the levers. When the vehicle passes a significant bump, the rubber bumper will absorb the impact before the shock absorber reaches its upper or lower limit. Thus, premature failure of the shock absorber, its upper support and the lower silent block is prevented.
The topic is too broad to cover all its aspects in one article. In addition, design engineers are constantly working to improve existing devices and develop new ones. The most promising direction is systems with automatic adaptation to specific road conditions. In addition to the already mentioned air springs, for example, adjustable anti-roll bars are used, which are capable of changing their rigidity according to a signal from the ECU.
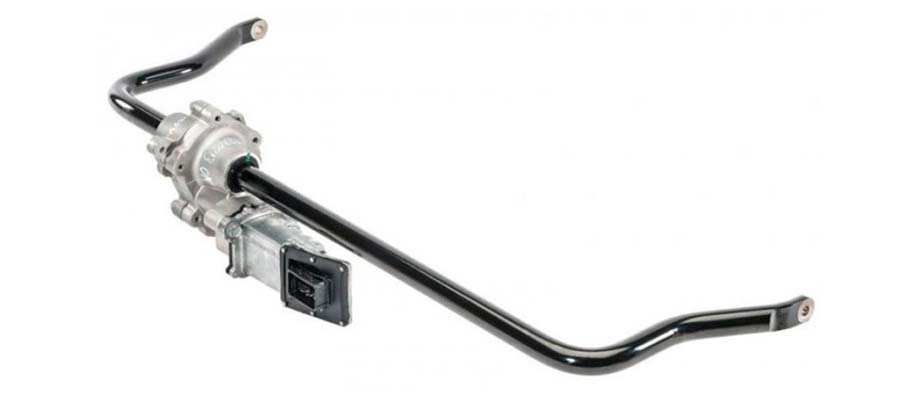

In a number of cars, adjustable shock absorbers are installed that change the stiffness of the suspension due to the operation of a solenoid valve.
In a hydropneumatic suspension, the role of elastic components is played by spheres, separate isolated sections of which are filled with gas and liquid. In the Hydractive system, the hydropneumatic sphere is part of the suspension strut.
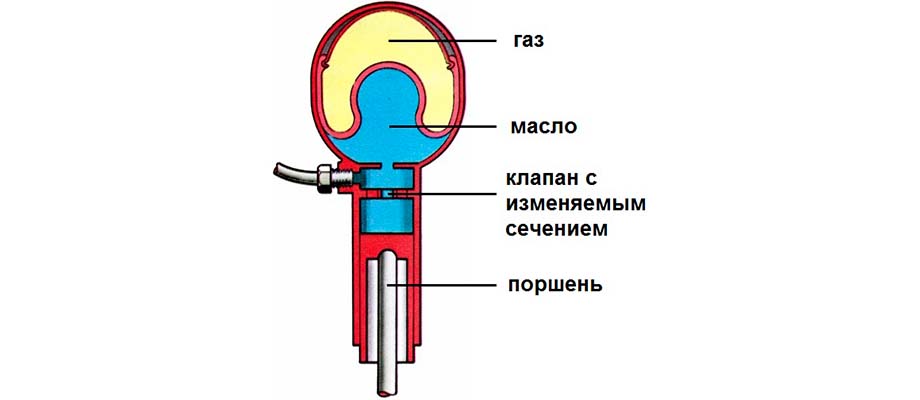
However, all these options are expensive, so most motorists have to be content with the best MacPherson and spring systems with two wishbones today.
No one is safe from problems on our roads, so it will not be superfluous to familiarize yourself with the signs of possible ones. And be sure to read.
