Wheel bolt pattern - how to do it right?
If you like to read car magazines and look at new car models, you probably noticed that they look much better at auto shows than those serial models that are offered in showrooms. That's right, any auto show is designed to ensure that manufacturers show their new developments in a favorable light and draw public attention to them.
Many drivers love styling their cars. We have already written on our website Vodi.su about various types of styling and tuning: disc lighting, an equalizer on the rear window, an increase in engine power. Here I would like to talk about disks. You can give the car a sporty look by lowering the clearance and installing non-standard cast or forged wheels with low-profile rubber mounted on them.

It would seem that everything is simple - remove the old disks, buy new ones, screw them to the hub and enjoy the new look of your car. However, you need to be able to choose the right wheels, which are marked in a special way. That is, you need to learn how to read the markings of rims.
Wheel marking - basic parameters
In fact, when choosing a rim, you need to pay attention to many parameters, and not just the width of the rim, the number of bolt holes and the diameter.
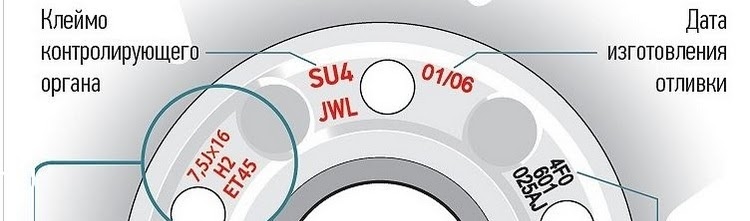
Let's take a simple example. 7.5 Jx16 H2 5/112 ET 35 d 66.6. What do all these numbers and letters mean?
So, 7,5x16 - this is the size in inches, the width of the rim and the bore diameter.
An important point - the “x” icon means that the disk is one-piece, that is, not stamped, but most likely cast or forged.
Latin letter "J" indicates that the rim edges are adapted for XNUMXWD vehicles.
If you were looking for an XNUMXxXNUMX wheel drive, you would be looking for a wheel marked "JJ".
There are other designations - JK, K, P, D and so on. But it is the "J" or "JJ" types that are the most common today. In any case, the instructions should indicate which types of disc are suitable for your machine.
N2 - this designation indicates that there are two annular protrusions on the rim - hampa (Hamps). They are needed so that tubeless tires do not slip. There may also be discs with one hump (H1), without them at all, or with protrusions of a special design, respectively, they will be designated CH, AH, FH. It is worth noting that if you want to install Runflat tires, then H2 wheels will be needed.

What is 5/112 we will consider below, because this parameter just shows the bolt pattern of the disk.
ET 35 - disc ejection. This parameter indicates how much the plane of application of the disc to the hub deviates from the axis of symmetry of the rim.
Departure can be:
- positive - the application area goes beyond the axis of symmetry, and to the outside;
- negative - the application area is concave inward;
- zero - the hub and the axis of symmetry of the disk coincide.
If you want to carry out tuning, then you need to pay special attention to the offset of the disk - a deviation from the standard indicators is allowed, but not more than a few millimeters, otherwise the load will increase both on the disks themselves and on the hub, and accordingly on the entire suspension and steering control.
D 66,6 is the diameter of the central hole. If you cannot find exactly the same diameter, then you can buy discs with a larger diameter of the central hole. In this case, you will have to pick up a special set of spacer rings, due to which the dimensions can be adjusted to the diameter of the landing cylinder on the hub you need.
Razorovka wheel disks
If everything is more or less clear with the dimensions and design features, then the bolt pattern may raise questions for many.
In the example above, we see an indicator of 5/112. This means that the disc is screwed to the hub with 5 bolts, and 112 is the diameter of the circle on which these 5 wheel bolt holes are located.
It often happens that this parameter for different models differs by fractions of a millimeter. For example, Zhiguli wheels come with a 4/98 bolt pattern. If you buy 4/100 discs, then they will not be visually different, and they will sit on their seat without any problems. But while driving, this discrepancy will quickly remind you of itself - a beating will appear, which will gradually lead to disk deformation, hubs, wheel bearings will quickly break, the suspension will suffer, and with it your safety. You will also feel the vibrations of the steering wheel. If measures are not taken in time, then the wheel may simply come off.
You can calculate the bolt pattern yourself.
To do this, you need:
- count the number of bolts;
- measure the distance between two adjacent bolts with a caliper;
- depending on the number of bolts, multiply the resulting distance by 1,155 (3 bolts), 1,414 (4), 1,701 (5).
If as a result of this simple mathematical operation a fractional number came out, then it is allowed to round it up. In addition, any manufacturer has bolt patterns, and if you have an indicator of 111 for a Mercedes, then in the catalog you can see that Mercedes does not use discs with such a bolt pattern, respectively, the correct choice would be 112.

Therefore, we recommend that you do not listen to would-be consultants in car dealerships who will prove to you that an extra millimeter or even a fraction of a millimeter does not make much difference. Demand to pick up a disk of the size for you, as indicated in the instructions.
Please also note that even with a slight discrepancy, you will not be able to fully tighten the bolts, hence all the troubles associated with the beating of the disk.
When selecting discs, you also need to look at whether the holes fit the diameter of the hub bolts. If you buy a disc complete with hub bolts or studs, then the thread should also fit. All these parameters can be found in numerous reference books.
Let's give an example: we select a disk on a Mazda 3.
Using the reference book from open access, we find:
- loosening - 5x114,3;
- hub hole diameter - 67,1;
- departure - ET50;
- the size and thread of the wheel studs is M12x150.
That is, even if we want to choose larger diameter and wider rims so that the car looks more sporty and “cool”, then the bolt pattern and offset parameters should still remain the same. Otherwise, we run the risk of breaking the suspension of our Mazda Troechka, and the repair will result in unforeseen expenses. In any case, if you can’t find the information yourself, you can contact the official service station, dealer’s car dealership or spare parts store, whose employees should have all this information.
Loading…
