How long does it take to charge the car battery with the charger
Content
In the practice of motorists, two methods of charging a storage battery (AKB) are used - with a constant charging current and with a constant charging voltage. Each of the methods used has its own disadvantages and advantages, and the battery charging time is determined by a combination of factors. Before you start charging a new battery that you just bought or that has been removed from your vehicle when it is discharged, it must be carefully prepared for charging.
Preparing the battery for charging
The new battery must be filled to the required level with electrolyte of the regulated density. When the battery is removed from the vehicle, it is necessary to clean the oxidized terminals from dirt. The case of a maintenance-free battery should be wiped with a cloth moistened with a solution of soda ash (better) or baking soda, or diluted ammonia.

If the battery is serviced (the battery banks are equipped with plugs for filling and topping up electrolyte), then it is necessary to thoroughly clean the top cover (with the plugs screwed in) additionally, so that accidental dirt does not get into the electrolyte when unscrewing the plugs. This will certainly lead to battery failure. After cleaning, you can unscrew the plugs and measure the level and density of the electrolyte.
If necessary, add electrolyte or distilled water to the required level. The choice between adding electrolyte or water is based on the measured density of the electrolyte in the battery. After adding liquid, the plugs should be left open so that the battery "breathes" during charging and does not burst with gases released during charging. Also, through the filler holes, you will have to periodically check the temperature of the electrolyte in order to avoid overheating and boiling.
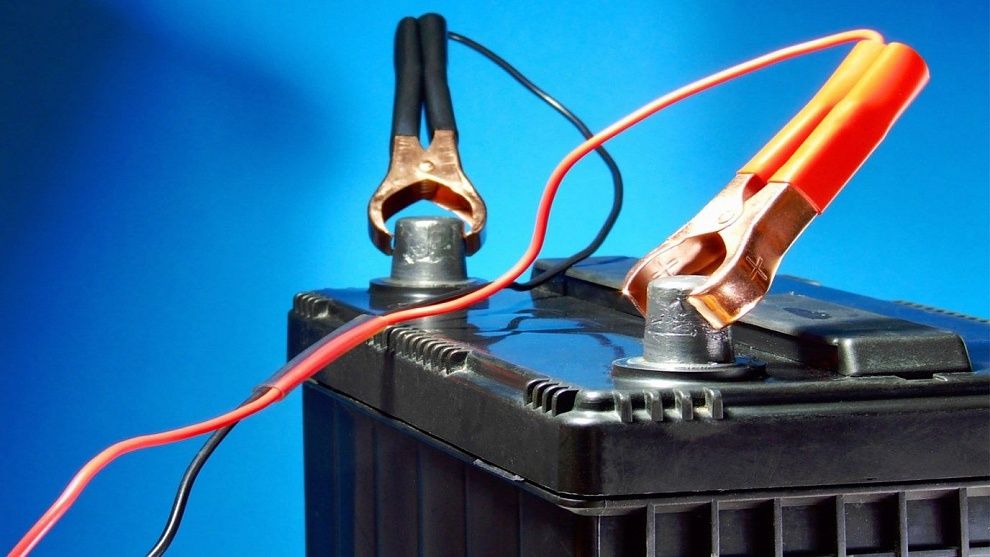
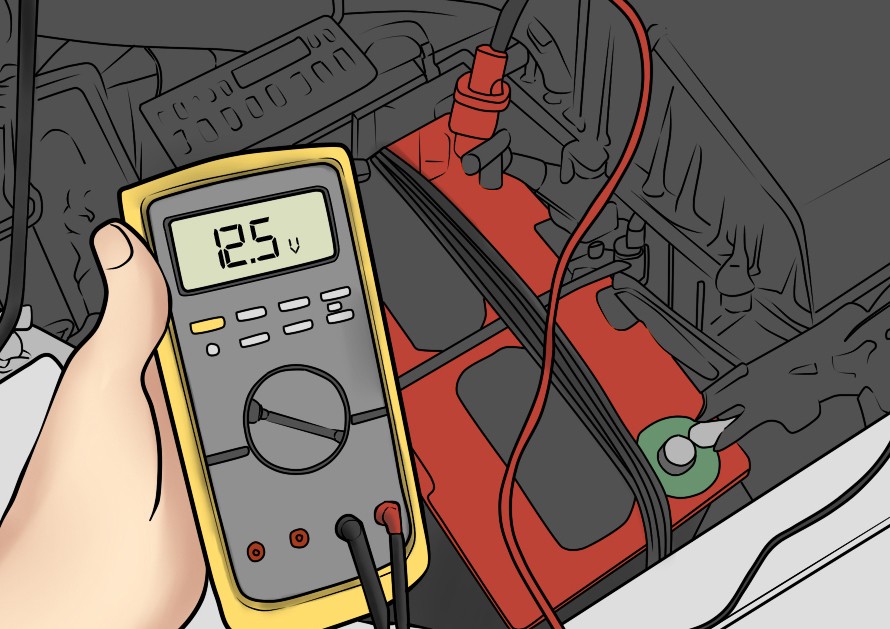
Next, connect the charger (charger) to the output contacts of the battery, always observing the polarity ("plus" and "minus"). In this case, at first, the "crocodiles" of the charger's wires are connected to the terminals of the battery, then the power cord is connected to the mains, and only after that the charger is turned on. This is done to exclude the ignition of the oxygen-hydrogen mixture released from the battery or its explosion when sparking at the moment of connecting the "crocodiles".
Read also on our portal avtotachki.com: car battery life.
For the same purpose, the order of disconnecting the battery is reversed: first, the charger is turned off, and only then the "crocodiles" are disconnected. The oxygen-hydrogen mixture is formed as a result of combining the hydrogen released during the operation of the battery with atmospheric oxygen.
DC battery charging
In this case, constant current is understood as the constancy of the charging current. This method is the most common of the two used. The electrolyte temperature in the battery prepared for charging should not reach 35 ° C. The charging current of a new or discharged battery in amperes is set equal to 10% of its capacity in ampere-hours (example: with a capacity of 60 Ah, a current of 6 A is set). This current will either be automatically maintained by the charger, or it will have to be regulated by a switch on the charger panel or by a rheostat.
When charging, the voltage at the output terminals of the battery should be monitored, it will increase during charging, and when it reaches a value of 2,4 V for each bank (i.e. 14,4 V for the entire battery), the charging current should be halved for a new battery and twice or three times for the used one. With this current, the battery is charged until abundant gas formation in all battery banks. Two-stage charging allows you to accelerate battery charging and reduce the intensity of gas release that destroys the battery plate.

If the battery is slightly discharged, it is quite possible to charge it in one-stage mode with a current equal to 10% of the battery capacity. Excessive gas evolution is also a sign of charging completion. There are additional signs that the charge is complete:
- unchanged electrolyte density within 3 hours;
- the voltage at the battery terminals reaches a value of 2,5-2,7 V per section (or 15,0-16,2 V for the battery as a whole) and this voltage remains unchanged for 3 hours.
To control the charging process, it is necessary to check the density, level and temperature of the electrolyte in the battery banks every 2-3 hours. The temperature should not rise above 45 ° C. If the temperature limit is exceeded, either stop charging for a while and wait for the electrolyte temperature to drop to 30-35 ° C, then continue charging at the same current, or reduce the charging current by 2 times.
Based on the state of a new uncharged battery, its charge can last up to 20-25 hours. The charge time of a battery that has had time to work depends on the degree of destruction of its plates, the operating time and the degree of discharge, and can reach 14-16 hours or more when the battery is deeply discharged.
Charging the battery with constant voltage
In constant charging voltage mode, it is recommended to charge maintenance-free batteries. To do this, the voltage at the output terminals of the battery should not exceed 14,4 V, and the charge is completed when the charge current drops below 0,2 A. Charging the battery in this mode requires a charger while maintaining a constant output voltage of 13,8-14,4 V.
In this mode, the charge current is not regulated, but the charger is automatically set depending on the degree of battery discharge (as well as the temperature of the electrolyte, etc.). With a constant charging voltage of 13,8-14,4 V, the battery can be charged in any condition without the risk of excessive gassing and overheating of the electrolyte. Even in the case of a completely discharged battery, the charging current does not exceed the value of its nominal capacity.

At a non-negative electrolyte temperature, the battery charges up to 50-60% of its capacity in the first hour of charging, another 15-20% in the second hour, and only 6-8% in the third hour. In total, in 4-5 hours of charging, the battery is charged to 90-95% of its full capacity, although the charging time may be different. Charging completion is indicated by a drop in the charging current below 0,2 A.
This method does not allow charging the battery up to 100% of its capacity, since for this it is necessary to increase the voltage at the battery terminals (and, accordingly, the output voltage of the charger) to 16,2 A. This method has the following advantages:
- the battery charges faster than constant current charging;
- the method is easier to implement in practice, since there is no need to regulate the current during charging, in addition, the battery can be charged without removing it from the vehicle.
When operating the battery on a car, it is also charged in a constant charge voltage mode (which is provided by a car generator). In the "field" conditions, it is possible to charge a "planted" battery from the mains of another car by agreement with its owner. In this case, the load will be lower than with the traditional "lighting" method. The time required for such a charge to be able to start independently depends on the temperature of the environment and the depth of discharge of its own battery.
The most battery damage occurs when a discharged battery is installed, with a capacity below 12,55 V. When the vehicle is first started with such a battery, permanent damage and irreversible loss capacity and durability battery .
Therefore, before each installation of the battery on the vehicle, it is necessary to check the battery capacity and only then proceed with the installation.
FAST CHARGING AND HOW TO DO IT SAFELY
LIQUID ELECTROLYTE BATTERIES - FAST CHARGING
Fast charging in progress when the battery is discharging when you need to quickly start the car engine. This electrical charging method is characterized by charging with a higher current and a shorter charging time than usual from 2 to 4 hours . During this type of fast electrical charging, the temperature of the battery must be monitored (it must not exceed 50-55 ° С ). If necessary, in the event of a "recharge" of the battery, it is necessary to reduce the charge current so that the battery does not heat up and so that there is no long-term unwanted damage or explosion of the battery itself.
In the case of fast charging, the charging current should not exceed 25% from the rated battery capacity in Ah (C20).
EXAMPLE: A 100 Ah battery is charged with a current of approx. 25 A. If a charger is used for electric charging without charging current regulation, the charging current is limited as follows:
- BATTERIES FOR MOTORCYCLES 3 - 5 A
- BATTERIES FOR VEHICLES 15 - 25 A
- BATTERIES FOR HEAVY VEHICLES 30 - 50 A
After the quick charge procedure, the battery will not be fully charged. . The vehicle's alternator completes the electrical charge of the battery while driving. Therefore, it is recommended in such cases to use the vehicle for some time before the first stop and decommissioning.
In such a situation, the simultaneous eclectic charging of several batteries in parallel is not recommended, since it is impossible to rationally distribute the current and the effect necessary to start the car without damaging the battery will not be achieved.
At the end of the electric accelerated charge of the battery density electrolyte must be the same in all chambers (the maximum allowable difference between the maximum and minimum values must not exceed 0,030 kg / l ) and in all six chambers must be greater than or equal to 1,260 kg/l at +25°C. What can be checked only with batteries that have covers and open access to the electrolyte.
Open circuit voltage in volts must be greater than or equal to 12,6 AT. If not, repeat the electrical charge. If the voltage is still unsatisfactory after this, replace the battery, because a dead battery is probably permanently damaged and not intended for further use.
BATTERY AGM - FAST CHARGING
Fast charging in progress when the battery is discharged and when you need to quickly start the car engine. The battery is electrically charged with a larger initial charging current, which shortens the charging time, and with battery temperature control ( maximum 45-50°C ).
In the case of fast charging, it is recommended to limit the charging current to 30% - 50% from the nominal battery capacity in Ah (C20). So, for example, for a battery with a nominal capacity of 70 Ah, the initial charging current must be within 20-35 A.
In short, the recommended fast charging options are:
- DC voltage: 14,40 - 14,80 V
- Maximum current 0,3 to 0,5 rated capacity in Ah (C20)
- Charging time: 2 - 4 hours
Not recommended at the same time as charging several batteries in parallel due to the inability to rationally distribute the current.
After the quick charge procedure, the battery will not be fully charged. . The vehicle's alternator completes the electrical charge of the battery while driving. Therefore, as with wet batteries, after installing a fast-charged battery, you must use the vehicle for a certain period of time. At the end of the charging process, the battery should reach a uniform voltage. If this doesn't happen, replace the battery even if it can still start the car engine.
The inability to achieve this characteristic (meaning that the battery always remains charged with constant current), combined with a high internal temperature, indicates wear and tear , i.e. about the onset of sulfation, and loss of basic battery properties . Therefore, it is recommended to replace the battery even if it can still start the car engine.
Fast charging, like any battery charging, is a very sensitive and somewhat dangerous procedure. Both from electric shock and from an explosion if the temperature of the battery is not controlled. Therefore, we also provide you with safety instructions for use.
SAFETY REGULATIONS
Batteries contain sulfuric acid (corrosive) and emit explosive gas especially during electric charging. Following the prescribed precautions reduces the absolute risk of injury. The use of personal protective equipment and equipment is mandatory - gloves, goggles, suitable clothing, face shield .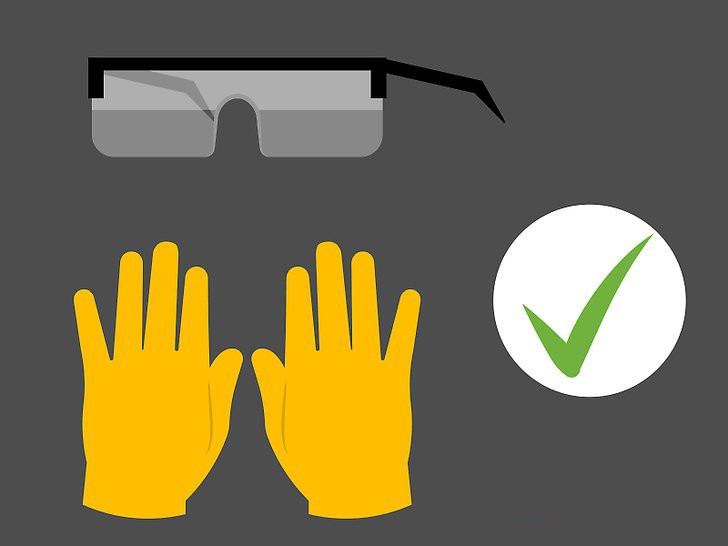

Never place and/or leave metallic objects on the battery while charging. If metal objects come into contact with the battery terminals, it may cause a short circuit, which may cause the battery to explode.
When installing a battery in a vehicle, always connect the positive pole (+) first. When disassembling a battery, always disconnect the negative pole (-) first.
Always keep the battery away from open flames, lit cigarettes and sparks.
Wipe the battery with a damp antistatic cloth ( in no case woolen and in no case dry ) a few hours after electric charging, so that the released gases have time to completely dissipate in the air.
Do not lean over a running battery or during installation and disassembly.
In the event of a sulfuric acid spill, always use chemical absorbent.