Stabilizer legs: what is it, location and principle of operation
Content
No modern car rolls off the assembly line without a stabilizer. This is an important part that is essential for the efficient operation of the vehicle's suspension. Earlier we discussedwhat are stabilizer bushings, their malfunctions, as well as the importance of these elements. Now consider the detail, which is called the stabilizer bar. How to replace the stabilizer bar on a VAZ 2108-99, read separate review.
What is a stabilizer bar?
Let us briefly recall why you need a stabilizer. When the car is going straight, its body is parallel to the road. As soon as it starts to turn, due to the speed, the center of gravity of the car moves to the side. This causes the vehicle to roll.
Since when the car is tilted, the load on the wheels is unevenly distributed, the tires begin to lose contact with the road surface. This effect not only negatively affects driving comfort, but also increases the risk of an accident due to the vehicle becoming unstable.

To minimize, and in some cases (at low speed) eliminate this effect altogether, engineers have developed an anti-roll bar. In its original form, this part was simply attached to the subframe and suspension elements. By the way, the stabilizer is used in independent type suspensions.
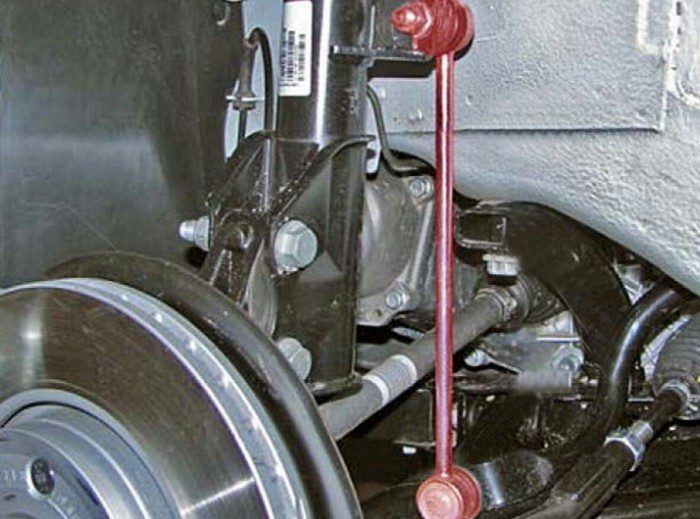
The strut in the lateral stability system can have different shapes, but this mount allows you to correctly fix the edges of the stabilizer from the point of view of physics. In different models, the part has a different shape and type of fastener, but the principle of operation and purpose remains the same.
What are stabilizer struts for?
So that the steel bar (the stabilizer itself looks like this) is connected to the car body and suspension elements, but at the same time does not interfere with the shock absorbers to perform their function, it is attached to special rods.
The presence of a rack has the following effects:
- The car has minimal roll when cornering, which improves ride comfort;
- A stable connection of the wheels with the road surface is ensured, since the rod creates a force opposite to the tilt of the body;
- The suspension is more responsive depending on the strut type.

So what if there were no racks at all?
It is difficult to imagine a modern car without such a unit. If you imagine such a car for a minute, then such a car would be extremely unstable on the road. Springs and shock absorbers would provide a smooth rocking motion of the car body. The body of such a vehicle would stop swinging only at a complete stop, and while driving, the inertia force constantly increases. Because of this, the heavy body would sway more and more with every bump and turn of the steering wheel.
The stabilizer provides a rigid coupling of the body and suspension, but at the same time allows the shock absorbers to practice vertical movements, which is extremely necessary for comfort and safety while driving (details on the operation of shock absorbers Read here).
Of course, it would be possible to drive a car without a stabilizer. It's not like the wheels aren't spinning at all. But what kind of ride would it be if during acceleration it “squatted” on the rear wheels, and when braking it would “peck” forward? And you could completely forget about high-speed turns. Continuous roller coaster in terms of comfort. But this is just the tip of the iceberg.

When the car picks up speed, inertia forces the body's center of gravity to the rear wheels. If the vehicle is rear-wheel drive, it will only benefit. What about front wheel drive models? In this case, even simply pressing the accelerator would cause the front wheels to slip, since there is minimal pressure on them.
But what is dangerous about the absence of a stabilizer during braking. The braking system slows down all wheels of the vehicle. As soon as the car slows down, inertia forces the body's center of gravity to the front. As a result, the rear axle is completely unloaded, while the front axle, on the contrary, has a maximum load. Because of this, the rear wheels will skid (at the same time the rubber wears out more), and the strongest pressure is exerted on the shock absorbers of the front axle.
On bends, such a car would simply fly off the track, because even the slightest turn of the steering wheel at speed would create the feeling of the car overturning. Road safety with such vehicles could be forgotten.

The lateral stabilization system itself has been developed and improved over many decades. In modern versions, the struts provide better stability when side loading occurs.
The device and the principle of operation
The rack itself is most often presented in the form of a rod, the length of which depends on the modification of the shock absorbers and the entire suspension of the machine. Each manufacturer develops its own types of racks, which we will talk about a little later. It must provide a movable fastening of the suspension elements, therefore at its ends there are either hinges or bushings, and sometimes there are a combination of these elements.
In some places, the stem has a smaller diameter. In that place, the elements of the rack are connected. This is done so that in the event of an excessive load and an emergency, the breakdown is minimally critical for the suspension of the machine (the rack will break at the thinnest point). This solution makes the failure of the assembly predictable and without disastrous consequences for the bottom of the car.

Since the stabilizer effect is manifested on bends, the conditional situation will be precisely the car's passing a bend. At this moment, the body tilts. The stabilizer bar rises on one side, and on the other - on the contrary, falls. Since its edges are connected with a rod connecting the left and right sides, a twisting force is created in its center (one end is twisted in one direction and the other in the opposite direction).
The force opposite to roll lifts the collapsed body part, thereby loading the side that could lose traction due to inertia. This system does not need to adjust the stiffness, since with a stronger tilt, the auto stabilizer twists more, responding to the pressure of the rack, thereby creating a opposing force of a greater magnitude. Although at the moment there are already models with active stabilization systems that work depending on which road surface the car is driving on (often such cars have a mode switch on the gear selector).
Here's a short video on how the rack works:
Types of stabilizer struts
As already mentioned, different manufacturers have developed their own modifications of struts for lateral stabilization of vehicles. All modern cars have a front stabilizer by default, but there are also models with a similar element mounted on the rear axle, even if the car is front wheel drive. There are three types of racks:
- Articulated;
- Bushings;
- Hinge bushings (used less often depending on the features of the body structure and suspension).
Budget cars are equipped with modifications with bushings. It is a small steel rod with eyelets at the ends. Bushings are inserted into them. On one side, a stabilizer bar is placed in the bushing, and the other part of the rack is fixed to the suspension arm.


If a hinged modification is used in the car, then often it is the same steel rod (its length is different in each car model), at the ends of which hinges are installed. They are necessary for the mobility of the node. Their fastening pins are directed in opposite directions from each other (there are analogs with the same direction of the fingers or with an offset of several degrees relative to each other).
Some automatic stabilizers use hydraulic cylinders instead of struts, which adjust the stiffness of the rod depending on the type of road. The toughest mode is on a winding road, the middle position is most often suitable for a dirt road. Off-road, the active stabilizer is most often turned off.
Also, the stabilizer struts differ in the principle of attachment. By default, the stabilizer itself is attached to one side. In some cars, the second part of the strut is fixed to the suspension arms. There is another type of attachment - to the shock absorber strut or the steering knuckle of the wheel. Depending on this, the rack will have its own mounting holes.


Stabilizer malfunctions, their symptoms, condition check
The more elements in the suspension nodes, the higher the likelihood of a malfunction in it. Here are the main problems with stabilizer struts:
| Element: | Malfunction: | Sign: | Diagnostics: | Repairs: |
| Rubber bushings | Tear, crack, wear out, lose elasticity | Knocks appear; the stabilizer copes with its function worse, which is why the roll on bends increases | Visual inspection; scheduled maintenance | Replacing bushings |
| Hinges | Working out between the pin and the mount; working out between the inner part of the hinge body and the spherical part of the pin. Because of this, a backlash appears | Knocks, clicks and other extraneous noises while cornering, increased body tilt on bends | Using a lever (you can use a mount), swing the stabilizer near the mount to the rack, and in some car models the same action is performed with the rack itself | When a depletion appears in a metal sleeve, no restoration work will help - you need to replace the rack (or press in a new hinge, if the rack design allows this) |
Another common sign of a faulty technical condition of this unit is that the car arbitrarily leaves the side. Another symptom indicating a possible malfunction in the lateral stabilization system is the need to steer, even on straight sections of the road.
If these signs begin to appear, then it is necessary to replace the worn out parts. It would be more practical to do this on both sides of the car, so as not to carry out repair work twice as often.
Here is one of the options for replacing the racks:


Watch this video on YouTube
Can I ride without stabilizer struts?
If you simply answer this question, then yes - you can ride without struts and stabilizer. But, as we have already said, this significantly increases the chance of getting even in a minor, but still an accident. Safety rules should not be neglected. If the manufacturer has provided for the installation of these parts in the car, then their work is required for the stability of the vehicle.
Regardless of the manufacturer, the racks must be checked every 20 thousand kilometers. This is especially important if the car often drives off-road or on bad roads. But even if the mentioned signs began to appear relatively quickly after replacing the elements, it is necessary to carry out repair work.
Best stabilizer struts
There is a wide variety of stanchions in the automotive aftermarket, but remember that they are not interchangeable. For this reason, the selection of the part must be made either by the car model or by the VIN code.
You should not experiment with supposedly improved counterparts in custom sizes. If the manufacturer has provided for a 25 centimeters stand, then you need to look for the same one. Moreover, there are plenty of options for one modification, so you can find both a budgetary and a more expensive option.


As for the original spare parts, most of them are intended for cars moving on more or less flat roads, so they have to be changed more often. The cost of such a part will be several times higher than its domestic counterpart.
The leading positions among manufacturers of stabilizer stands are occupied by:
- German manufacturer Lemforder;
- Joint Sino-German production of Toprun;
- STR - South Korean manufacturer;
- Russian company - Links Master.
So, without a stabilizer bar, the car won't be as docile as the manufacturer intended. To ensure safety and comfort, it is important to periodically look under the car and analyze what is changing in the suspension units.
Questions and answers:
How often do you need to change the stabilizer struts? Replacement of the stabilizer struts is carried out in case of their malfunction: damage to the bushings, backlash or swaying during diagnostics, knocking while driving.
What are the functions of the stabilizer struts? They attach the stabilizer to the car body. The fixation is carried out on hinges so that the elastic part remains movable when attached to the steering knuckle or hub.
Can I ride if the stabilizer struts knock? Yes, but the wear of the stabilizer struts leads to: the yaw of the car, drifts, the need to steer even on straight sections, the rocking of the car.

One comment
K. Kaunda
The translation into Norwegian in this article is on a par with a bush of gooseberries on a late August evening. Exemplary (sic) irony.