fuel tank car
Content
Fuel tank - a container for storing a supply of liquid fuel directly on board the vehicle.
The design of the fuel tank, its location and main components and systems must comply with the technical specifications, the requirements of traffic rules, fire safety, environmental protection laws.

Any “improvements” made by the owner to the fuel tank or a change in the place of its installation are regarded by the Road Safety Inspectorate as “unauthorized interference with the vehicle structure”.
Features of the location of the tank in the car
Under the terms of passive safety, the fuel tank is located outside the passenger compartment, in the area of the body, which is least subjected to deformation during an accident. In cars with a monocoque body, this is the area within the wheelbase, under the rear seat. With a frame structure, the TB is mounted in the same place, between the longitudinal spars.
One or more tanks of trucks are located on the outer sides of the frame in the wheelbase of the first and second axles. This is partly due to the fact that truck testing procedures, "crash tests" for side impact, are not performed.

In cases where the exhaust gas system passes in the immediate vicinity of the TB, heat shields are installed.
Types of fuel tanks and materials of manufacture
International and Russian environmental laws are constantly being improved and their requirements are being tightened.
According to the Euro-II protocol, which is partly valid on the territory of our country, the fuel tank must be sealed and the evaporation of fuel into the environment is not allowed.
For safety reasons, the rules of technical inspection of vehicles prohibit leakage of fuel from tanks and power systems.
Fuel tanks are made from the following materials:
- Steel - mainly used in trucks. Premium passenger cars can use aluminum coated steel.
- Aluminum alloys are used to a limited extent due to complex welding technologies;
- Plastic (high pressure polyethylene) is the cheapest material, suitable for all types of liquid fuels.
High-pressure cylinders serving as a fuel reservoir in gas engines are not considered in this article.
All manufacturers are striving to increase the on-board fuel supply. This increases the comfort of the individual owner and is economically advantageous in long-distance transport of goods.
For passenger cars, the unofficial norm is 400 km on one full gas station. A further increase in the capacity of TB leads to an increase in the curb weight of the vehicle and, consequently, to a strengthening of the suspension.
The dimensions of the TB are limited by reasonable limits and by the requirements of designers who compose the interior, trunk and “barrel” under them, while trying to maintain normal ground clearance.
For trucks, the size and volume of tanks are limited only by the cost of production of the machine and its purpose.
Imagine the tank of the famous American truck Freightliner, crossing the continents with a consumption of up to 50 liters per 100 km.
Do not exceed the nominal capacity of the tank and pour fuel "under the plug".
Design of modern fuel tanks
In order to unify the main components of the transmission, running gear, load-bearing body frame, leading automakers produce several brands and models on a single platform.
The concept of a "single platform" extends to fuel tanks.
Metal containers are assembled from stamped parts connected by welding. At some factories, welded joints are additionally covered with sealant.
Plastic TBs are produced by hot forming.
All finished TBs are tested by the manufacturer for strength and tightness.
The main components of the fuel tank
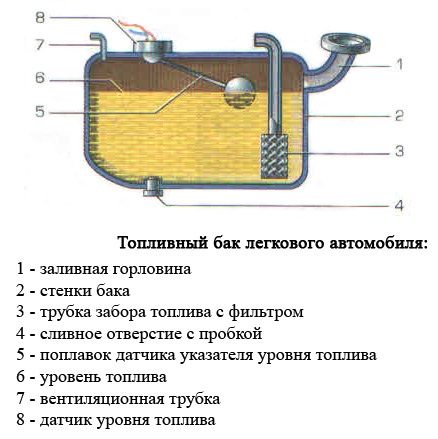
Regardless of the hull shape and capacity, the TB of an injection gasoline engine has the following components and parts:
- The filler neck located under the protective and decorative hatch on the rear sidewall (rear wing) of the body. The neck communicates with the tank by a filling pipeline, often flexible or of complex configuration. A flexible membrane is sometimes installed in the upper part of the pipeline, "hugging" the barrel of the filling nozzle. The membrane prevents dust and precipitation from entering the tank.
The hatch on the body is easy to open, it can have a locking mechanism controlled from the driver's seat.
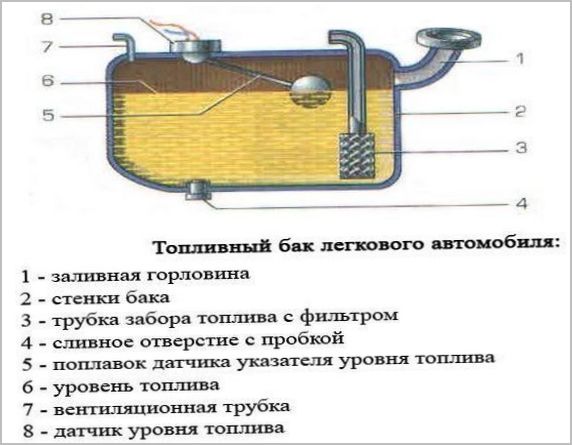
The fuel tank neck of trucks is located directly on the fuel tank body and does not have a filler pipeline.
- Filler cap, plastic plug with external or internal thread, with O-rings or gaskets.
- Pit, a recess in the lower surface of the TB body for collecting sludge and contaminants.
- Fuel intake with a mesh built-in filter (on carburetor and diesel vehicles), located above the pit, below the bottom of the fuel tank.
- Mounting opening with a sealed cover for installing a fuel module for injection engines, a float fuel level sensor for carburetor and diesel engines. In the cover of the mounting opening there are sealed through pipes for passing the fuel supply line and connecting wires of the fuel module or float sensor.
- A hole with a sealed cover and a branch pipe for the passage of the fuel return pipeline ("return").
- Drain plug in the center of the pit. (Does not apply to petrol injection systems.)
- Threaded fittings for connecting the ventilation line and adsorber pipeline.
On the outer surfaces of the fuel tanks of diesel vehicles, electric thermoelements can be installed to heat the fuel at low temperatures.
Design and operation of the ventilation and vapor recovery system.
All types of liquid fuels are prone to evaporation and temperature changes in volume, which causes a discrepancy between atmospheric pressure and tank pressure.
In carburetor and diesel engines before the Euro-II era, this problem was solved by a “breathing” hole in the filler cap.
The tanks of cars with an injection ("injector") engine are equipped with closed ventilation systems that do not have direct communication with the atmosphere.
The air inlet, when the pressure in the tank decreases, is controlled by the inlet valve, which opens with the pressure of the outside air, and closes after equalizing the pressures inside and outside.
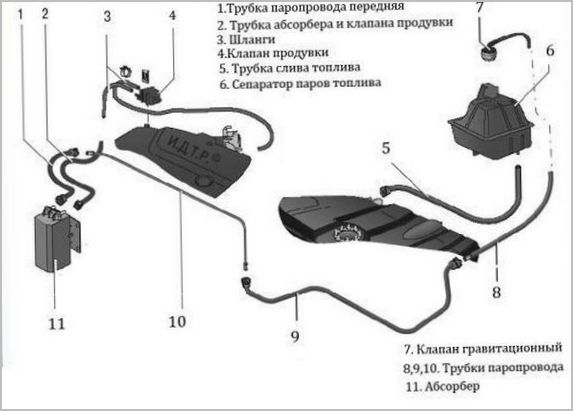
The fuel vapors formed in the tank are sucked in by the intake piping through the ventilation duct when the engine is running and burned in the cylinders.
When the engine is turned off, gasoline vapors are captured by the separator, the condensate from which flows back into the tank, and is absorbed by the adsorber.
The separator-adsorber system is quite complicated, we will talk about it in another article.
The fuel tank requires maintenance, which consists in checking the tightness of its systems and cleaning the tank from contamination. In steel tanks, corrosion products and rust can also be added to precipitation from gasoline or diesel fuel.
It is recommended to clean and flush the tank every time the installation opening is opened by unscrewing the drain plug.
Experts do not advise using various “means for cleaning the fuel system” without opening the fuel tank, deposits washed off from the bottom and walls through the fuel intake will go into the filters and fuel equipment.