Brake mechanisms and vehicle systems
Content
As its name implies, the brake mechanism performs the braking process in the car, that is, it prevents the wheel from rotating in order to reduce speed or stop it completely. To date, most automakers use a friction type of brake devices, the principle of which is to organize the friction force between rotating and stationary elements.
Typically, the brakes are located in the inner cavity of the wheel itself, in which case such a mechanism is called a wheel mechanism. If the braking device is included in the transmission (behind the gearbox), then the mechanism is called transmission.
Regardless of the location and shape of the rotating parts, any brake mechanism is designed to create the highest possible braking torque, which does not depend on the wear of the parts, the presence of condensate on the surface of the pads or their degree of heating during friction. A prerequisite for the rapid operation of the mechanism is the design of the device with a minimum gap between two contacting surfaces. During long-term operation, the value of this gap will invariably increase due to wear.
Three types of braking systems in a car
Today, all vehicles are equipped with three types of brake mechanisms. To successfully and safely drive a car, you need to use the following types of brake systems:
- Working. It is this system that provides a reduction in speed on the road and guarantees a complete stop of the vehicle.
- spare. It is used in the event that, for some objective reason, the working system has failed. Functionally, it works in the same way as a working one, that is, it performs braking and stopping the car. Structurally, it can be implemented as a fully automatic system or be part of a working one.
- Parking. It is used to stabilize the position of the vehicle during parking for a long time.
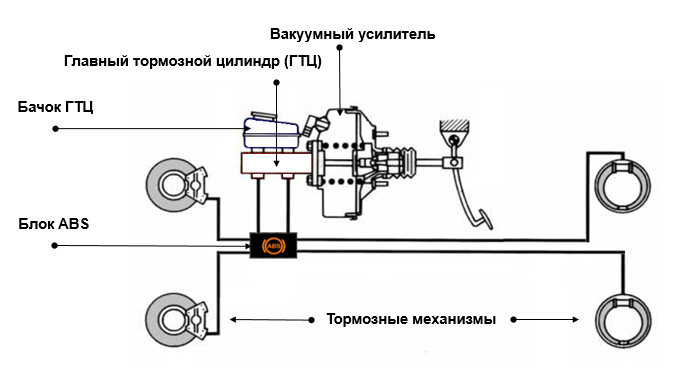
In modern cars, it is customary to use not only three types of brake systems, but also various auxiliary mechanisms that are designed to enhance braking performance. These are brake booster, ABS, emergency braking controller, electric differential lock and more. Practically in all cars presented in the Favorit Motors group of companies, there are auxiliary devices for the efficiency of passing the braking distance.
Brake device
Structurally, the mechanism connects two elements - the brake device itself and its drive. Let's consider each of them separately.
The brake device in modern cars
The mechanism is characterized by the work of moving and fixed parts, between which friction occurs, which, ultimately, reduces the speed of the car.
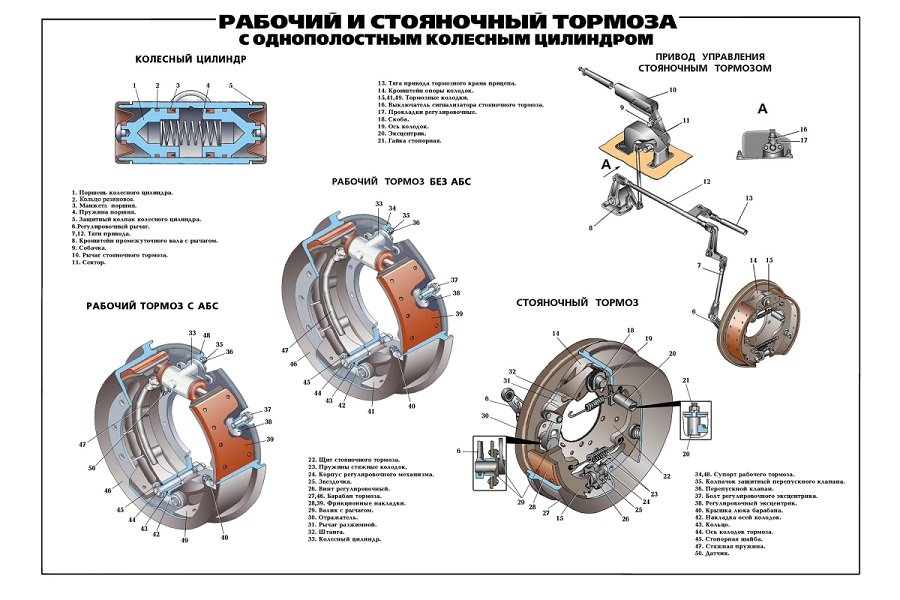
Depending on the shape of the rotating parts, there are two types of braking devices: drum and disc. The main difference between them is that the moving elements of drum brakes are pads and bands, while disc brakes are only pads.
The drum mechanism itself acts as a fixed (rotating) part.
A traditional disc brake consists of one disc that rotates and two pads that are fixed and placed inside the caliper on both sides. The caliper itself is securely fixed to the bracket. At the base of the caliper there are working cylinders that, at the time of braking, contact the pads to the disc.
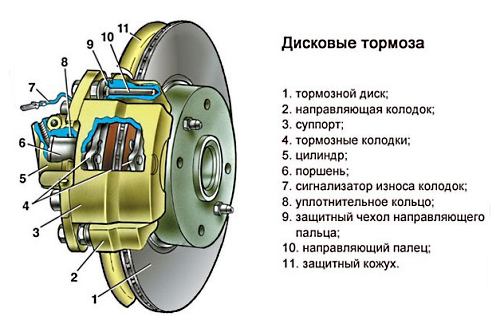
Working at full power, the brake disc is very hot from friction with the pad. To cool it, the mechanism uses fresh air flows. The disc has holes on its surface through which excess heat is removed and cold air enters. A brake disc with special holes is called a ventilated disc. On some car models (mainly racing and high-speed applications) ceramic discs are used, which have a much lower thermal conductivity.
Today, in order to protect the driver, brake pads are equipped with sensors that show the level of wear. At the right time, when the corresponding indicator lights up on the panel, you just need to come to the car service and carry out a replacement. Specialists of Favorit Motors Group of Companies have extensive experience and all the necessary modern equipment for dismantling old brake pads and installing new ones. Contacting the company will not take much time, while the quality of work will be at the height that will ensure really comfortable and safe driving.
Main types of brake actuators
The main purpose of this drive is to provide the ability to control the brake mechanism. To date, there are five types of drives, each of which performs its functions in the car and allows you to quickly and clearly give a signal to the braking mechanism:
- Mechanical. Scope of application - exclusively in the parking system. The mechanical type of drive combines several elements (traction system, levers, cables, tips, equalizers, etc.). This drive allows you to signal the parking brake to lock the vehicle in one place, even on an inclined plane. It is usually used in parking lots or in courtyards, when the car owner leaves the car for the night.
- Electric. The scope of application is also the parking system. The drive in this case receives a signal from the electric foot pedal.
- Hydraulic. The main and most common type of brake actuator that is used in a working system. The drive is a combination of several elements (brake pedal, brake booster, brake cylinder, wheel cylinders, hoses and pipelines).
- Vacuum. This type of drive is also often found on modern cars. The essence of its work is the same as that of the hydraulic one, however, the characteristic difference is that when you press the pedal, an additional vacuum gain is created. That is, the role of the hydraulic brake booster is excluded.
- Combined. Also applicable only in the service brake system. The specifics of the work lies in the fact that the brake cylinder, after pressing the pedal, presses on the brake fluid and forces it to flow under high pressure to the brake cylinders. The use of a double cylinder allows the high pressure to be divided into two circuits. Thus, if one of the circuits fails, the system will still fully function.
The principle of operation of the brake system on a car
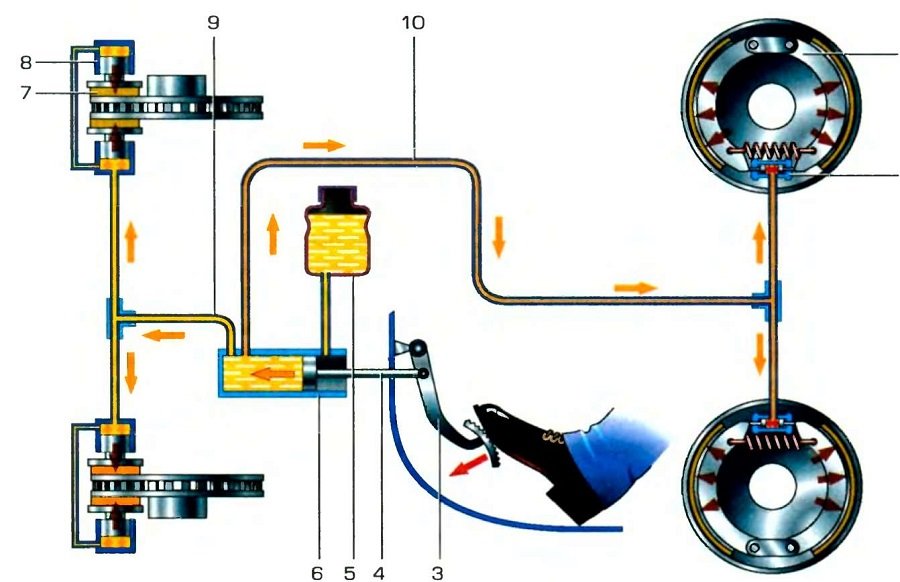
Due to the fact that vehicles with different types of working brake system are common today, the principle of operation of the brake mechanism will be considered using the most commonly used hydraulic brake system as an example.
As soon as the driver presses the brake pedal, the load immediately begins to be transferred to the brake booster. The booster generates additional pressure and transfers it to the brake master cylinder. The piston of the cylinder immediately pumps fluid through special hoses and delivers it to those cylinders that are installed on the wheels themselves. As a result, the pressure of the brake fluid in the hose is greatly increased. The liquid enters the pistons of the wheel cylinders, which begin to rotate the pads towards the drum.
As soon as the driver presses the pedal harder or repeats the pressure, the brake fluid pressure in the entire system will increase accordingly. As the pressure increases, the friction between the pads and the drum device will increase, which will slow down the speed of rotation of the wheels. Thus, there is a direct relationship between the force of pressing the pedal and the deceleration of the car.
After the driver releases the brake pedal, it returns to its original position. Together with it, the piston of the main cylinder stops pressurizing, the pads are retracted from the drum. The brake fluid pressure drops.
The performance of the entire braking system depends entirely on the performance of each of its elements. The braking system is one of the most important in the car, so it does not tolerate neglect. If you suspect any defects in its operation, or the appearance of an indication from the pad sensor, you should immediately contact the professionals. Favorit Motors Group of Companies offers its services for diagnosing the degree of wear and replacing any components of the braking system. The quality of work and the provision of reasonable prices for services are guaranteed.

