The device, types and principle of operation of the steering rack
Content
The steering rack is the basis of the steering of the vehicle, with which the driver directs the wheels of the car in the desired direction. Even if you are not going to repair your car yourself, then understanding how the steering rack works and how this mechanism works will be useful, because knowing its strengths and weaknesses, you will be able to drive a passenger car or jeep more carefully, extending its service life up to repair.
The engine is the heart of the car, but it's the steering system that determines where it goes. Therefore, every driver should at least in general terms understand how the steering rack of his car is arranged and what its purpose is.
From paddle to rack - the evolution of steering
In ancient times, when man had just begun to explore land and water, but the wheel had not yet become the basis of his mobility, rafts and boats became the main means of moving goods over long distances (exceeding a day's journey). These vehicles kept on the water, moving due to various forces, and to control them they used the first steering device - an oar lowered into the water, which is located at the back of the raft or boat. The effectiveness of such a mechanism was slightly higher than zero, and significant physical strength and endurance were required to direct the craft in the right direction.
As the size and displacement of ships grew, working with a steering oar required more and more physical strength, so it was replaced by a steering wheel that turned the rudder blade through a system of pulleys, that is, it was the first steering mechanism in history. The invention and spread of the wheel led to the development of land transport, but its main driving force was animals (horses or bulls), so instead of a control mechanism, training was used, that is, animals turned in the right direction for some action of the driver.
The invention of the steam plant and the internal combustion engine made it possible to get rid of draft animals and really mechanize land vehicles, after which they immediately had to invent a steering system for them that works on a different principle. Initially, they used the simplest devices, which is why the control of the first cars required enormous physical strength, then they gradually switched to various gearboxes, which increased the power of the turning force on the wheels, but forced the steering wheel to turn more intensively.
Another problem with the steering mechanism that had to be overcome is the need to turn the wheels at different angles. The trajectory of the wheel located on the inside, in relation to the turn of the side, passes along a smaller radius, which means that it must be turned more strongly than the wheel on the outside. On the first cars, this was not the case, which is why the front wheels wore out much faster than the rear ones. Then there was an understanding of the toe angle, moreover, it was possible to provide it using the principle of the initial deviation of the wheels from each other. While driving in a straight line, this has almost no effect on the rubber, but when cornering, it increases the stability and controllability of the car, and also reduces tire tread wear.
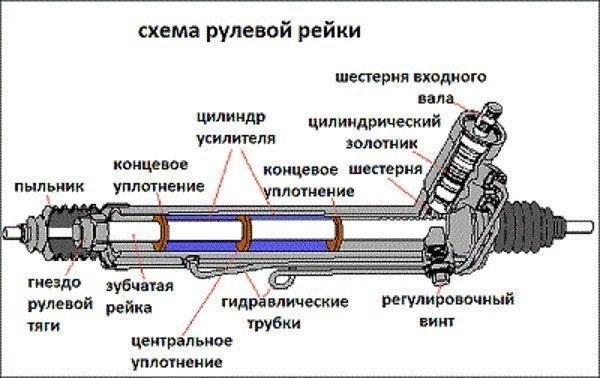
General layout
Here are the main details that form the basis of the steering rack layout:
- drive gear;
- rail;
- emphasis (clamping mechanism);
- the body;
- seals, bushings and anthers.
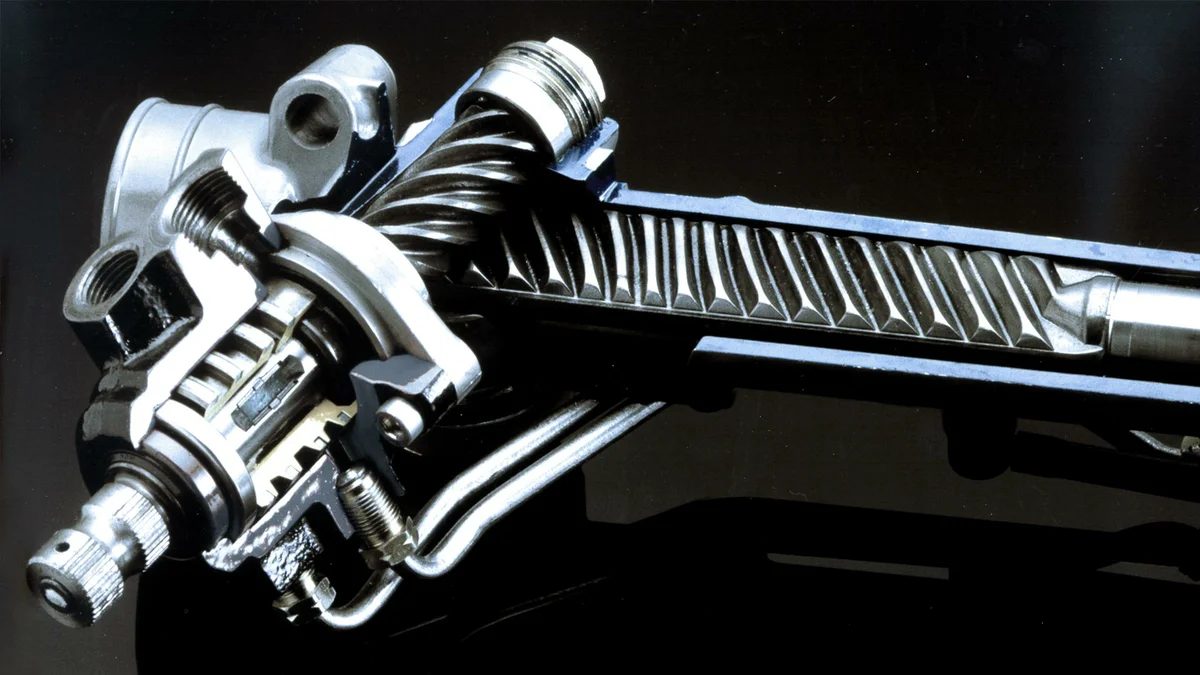

Sectional steering rack
This scheme is inherent in the rails of any car. Therefore, the answer to the question “how does the steering rack work” always begins with this list, because it shows the general structure of the unit. In addition, a lot of photos and videos have been posted on the Internet showing both the appearance of the block and its insides, which are included in the list.
pinion gear
This part is a shaft with oblique or straight teeth cut on it, equipped with bearings at both ends. This configuration provides a constant position relative to the body and rack in any position of the steering wheel. The shaft with oblique teeth is at an angle to the rail, due to which they clearly engage with the straight teeth on the rail, the shaft with straight teeth was installed on machines of the 80s and 90s of the last century, such a part is easier to manufacture, but its duration services are much less. Despite the fact that the principle of operation of spur and helical gears is the same, the latter is more reliable and not prone to jamming, which is why it has become the main one in steering mechanisms.
On all cars that have been produced since the last decade of the last century, only helical shafts are installed, this reduces the load on the contacting surfaces and extends the life of the entire mechanism, which is especially important for racks that are not equipped with a hydraulic (power steering) or electric (EUR) booster. The spur drive gear was popular in the USSR and the Russian Federation, it was put on the first versions of the steering gears of front-wheel drive vehicles, however, over time, this choice was abandoned in favor of a helical gear, because such a gearbox is more reliable and requires less effort to turn the wheel.
The drive gear is connected to the steering column by a compound shaft with cardans, which is a safety element, its purpose is to protect the driver during a collision from hitting the steering wheel in the chest. During an impact, such a shaft folds and does not transmit force to the passenger compartment, which was a serious problem in cars in the first half of the last century. Therefore, on right-handed and left-handed machines, this gear is located differently, because the rack is in the middle, and the gear is on the side of the steering wheel, that is, on the very edge of the unit.
Rail
The rack itself is a round bar of hardened steel, at one end of which there are teeth corresponding to the drive gear. On average, the length of the gear part is 15 cm, which is enough to turn the front wheels from the extreme right to the extreme left and vice versa. At the ends or in the middle of the rail, threaded holes are drilled for attaching steering rods. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the drive gear moves the rack in the appropriate direction, and, thanks to a fairly large gear ratio, the driver can correct the direction of the vehicle to within fractions of a degree.
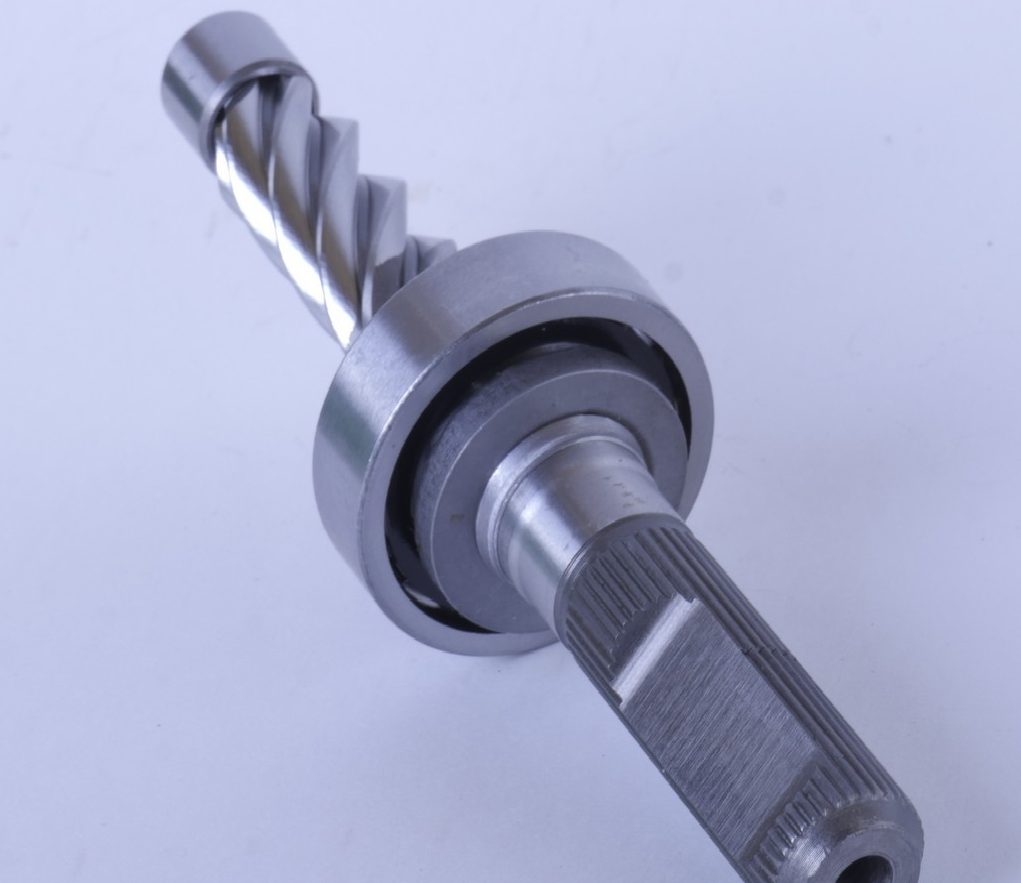

Steering rack
For the effective operation of such a mechanism, the rail is fixed with a sleeve and a clamping mechanism, which allows it to move left and right, but prevents it from moving away from the drive gear.
Clamping mechanism
When driving on uneven terrain, the steering gearbox (rack/pinion pair) experiences loads that tend to change the distance between both elements. Rigid fixation of the rack can lead to its wedging and the inability to turn the steering wheel, and therefore, to perform a maneuver. Therefore, rigid fixation is permissible only on one side of the unit body, remote from the drive gear, but there is no rigid fixation on the other side, and the rack can “play” a little, moving relative to the drive gear. This design provides not only a small backlash that prevents the mechanism from wedging, but also creates a stronger feedback, allowing the driver's hands to feel the road better.
The principle of operation of the clamping mechanism is as follows - a spring with a certain force presses the rack against the gear, ensuring tight meshing of the teeth. The force transmitted from the wheels, which presses the rack to the gear, is easily transferred by both parts, because they are made of hardened steel. But the force directed in the other direction, that is, moving both elements away from each other, is compensated by the stiffness of the spring, so the rack moves slightly away from the gear, but this does not affect the engagement of both parts.
Chassis
The body of the unit is made of aluminum alloy, and is also equipped with stiffeners, thanks to which it was possible to reduce the weight as much as possible without losing strength and rigidity. The strength of the body is enough to ensure that the loads that occur while driving, even on uneven terrain, do not damage it. At the same time, the scheme of the internal space of the body ensures the efficient operation of the entire steering mechanism. Also, the body has holes for fixing to the car body, thanks to which it collects all the steering elements together, ensuring their coordinated work.
Seals, bushings and anthers
The bushings installed between the body and the rail have high wear resistance and also provide easy movement of the bar inside the body. Oil seals protect the lubricated area of the mechanism, that is, the space around the drive gear, preventing the loss of lubricant, and also isolate it from dust and dirt. Anthers protect exposed areas of the body through which the tie rods pass. Depending on the model of the machine, they are attached to the ends or the middle of the rail, in any case, it is the anthers that protect the open areas of the body from dust and dirt.
Modifications and types
Despite the fact that at the dawn of its appearance, the rake was the best type of steering mechanism, the development of technology prompted manufacturers to further modify this device. Since the main mechanisms since the appearance of the unit, as well as the design and scheme of its operation have not changed, manufacturers have directed their efforts to increase efficiency by installing various amplifying devices.
The first was the hydraulic booster, the main advantage of which was the simplicity of design with extreme demands for proper operation, because the steering racks with power steering did not tolerate turning to the maximum angle at high engine speeds. The main disadvantage of the power steering was the dependence on the motor, because it is to it that the injection pump is connected. The principle of operation of this device is that when the steering wheel is turned, the hydraulic distributor supplies fluid to one of the two chambers, when the wheels reach the corresponding turn, the fluid supply stops. Thanks to this scheme, the force required to turn the wheels is reduced without loss of feedback, that is, the driver effectively steers and feels the road.
The next step was the development of an electric steering rack (EUR), however, the first models of these devices caused a lot of criticism, because false alarms often occurred, due to which the car spontaneously turned while driving. After all, the role of the distributor was played by a potentiometer, which, for various reasons, did not always give out correct information. Over time, this defect was almost completely eliminated, due to which the reliability of the control of the EUR is in no way inferior to the power steering. Some automakers are already using electric power steering, which combines the advantages of electric and hydraulic devices, as well as devoid of their disadvantages.
Therefore, today the following division into types of steering racks has been adopted:
- simple (mechanical) - almost never used due to low efficiency and the need to exert great effort to turn the wheels in place;
- with hydraulic booster (hydraulic) - are one of the most popular due to their simple design and high maintainability, but the booster does not work when the engine is off;
- with electric booster (electric) - they are also one of the most popular, gradually replacing units with power steering, because they work even when the engine is off, although the problem of random operation has not yet been completely eliminated;
- with an electric hydraulic booster, which combine the advantages of both previous types, that is, they work even when the engine is turned off and do not “please” the driver with random operation.
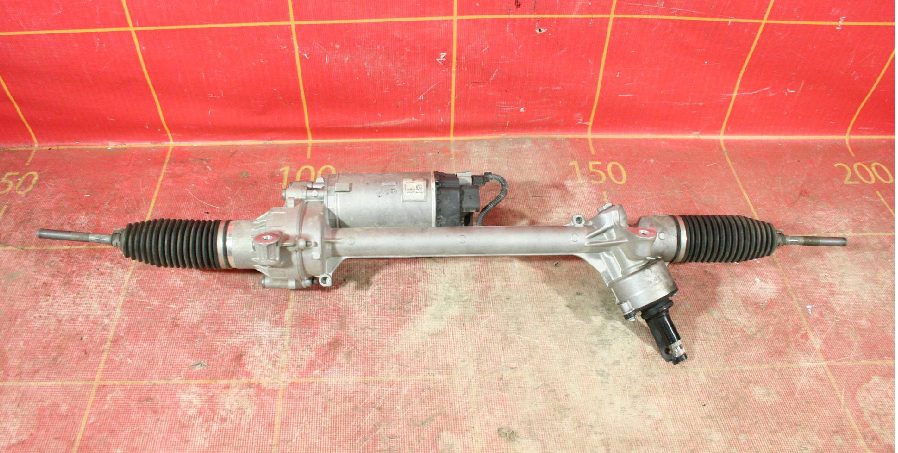

steering rack with EUR
This classification principle allows the owner or potential buyer of a passenger car to immediately evaluate all the advantages and disadvantages of the steering of a particular model.
Interchangeability
Car manufacturers almost never produce rack and pinion steering mechanisms, the exception was AvtoVAZ, but even there this work was transferred to partners, therefore, in case of severe defects in this unit, when repairs are unprofitable, it is necessary to choose not only the model, but also the manufacturer of this mechanism. One of the leaders in this market is ZF, which specializes in the production of all kinds of units, from automatic transmissions to steering mechanisms. Instead of the ZF rail, you can take a cheap Chinese analogue, because their circuit and dimensions are the same, but it will not last long, unlike the original device. Often, cars whose age has exceeded 10 years are equipped with a rail from other manufacturers, which is confirmed by photos of their markings posted on the Internet.
Often, garage craftsmen put steering racks from foreign cars, for example, various Toyota models, on domestic cars. Such a replacement requires a partial alteration of the rear wall of the engine compartment, but the car receives a much more reliable unit that surpasses AvtoVAZ products in all respects. If the rail from the same "Toyota" is also equipped with an electric or hydraulic booster, then even the old "Nine" suddenly, in terms of comfort, sharply approaches foreign cars of the same period.
Major faults
The device of the steering rack is such that this mechanism is one of the most reliable in the car, and most of the malfunctions are associated either with wear (damage) of consumables, or with traffic accidents, that is, accidents or accidents. Most often, repairmen have to change anthers and seals, as well as worn racks and drive gears, the mileage of which exceeds hundreds of thousands of kilometers. You also have to periodically tighten the clamping mechanism, which is due to the scheme of the steering mechanism, but this action does not require any replacement of parts. Much less often, the body of this unit that has cracked due to an accident requires replacement, in which case the serviceable rail, gear and clamping mechanism are transferred to the donor case.
Common reasons for repairing this node are:
- steering play;
- knocking while driving or turning;
- excessively light or tight steering.
These defects are associated with the wear of the main components that make up the steering rack, so they can also be attributed to consumables.
Where is
To understand where the steering rack is located and what it looks like, put the car on a lift or overpass, then open the hood and turn the wheels in any direction until they stop. Then follow where the steering rods lead, this is where this mechanism is located, similar to a ribbed aluminum tube, to which the cardan shaft from the steering shaft fits. If you have no auto repair experience and you don’t know where this node is located, then look at the photos and videos where the authors show the location of the rail in their cars, as well as the most convenient ways to access it: this will save you from many mistakes, including number leading to injury.
Regardless of the model and year of manufacture, this mechanism is always located on the rear wall of the engine compartment, so it can be seen from the side of the inverted wheel. For repair or replacement, it is more convenient to get to it from above, by opening the hood, or from below, by removing the engine protection, and the choice of access point depends on the model and configuration of the car.
Conclusion
The steering rack is the basis of the steering of the vehicle, with which the driver directs the wheels of the car in the desired direction. Even if you are not going to repair your car yourself, then understanding how the steering rack works and how this mechanism works will be useful, because knowing its strengths and weaknesses, you will be able to drive a passenger car or jeep more carefully, extending its service life up to repair.

