What is the difference between a diesel engine and a gasoline engine?
Content
- Another ignition initiation?
- Injection time
- Compression ratio?
- Burning rate
- Does the diesel engine heat up less?
- Weight / design?
- Different engine speed
- Another gearbox?
- Differences between diesel and gasoline?
- Overall performance: the difference?
- Vibration / Noise?
- Pollution
- Glow plugs?
- Air intake, difference?
- More torque? Limited engine speed?
- Which is better?
Everyone knows that a diesel engine has a distinct feel to a gasoline engine. However, it would be interesting to take a closer look at the characteristics that differentiate these two types of engines.

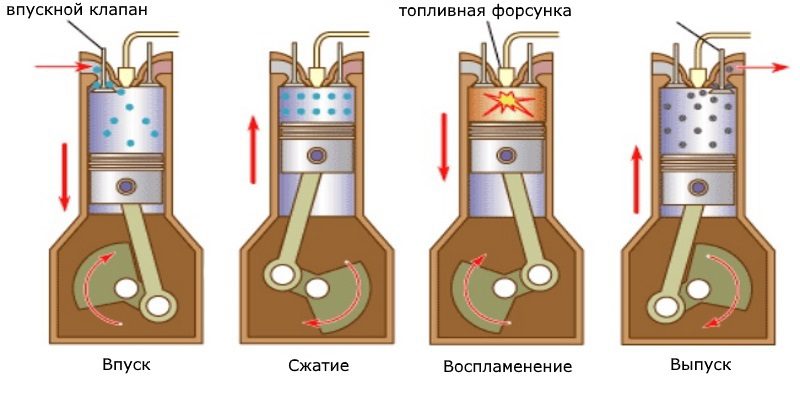
Another ignition initiation?
Spontaneous combustion exists for diesel fuel, which avoids ignition controlled by spark plugs. And it is precisely because of this principle that a diesel engine ignites spontaneously more easily than a gasoline engine ... During combustion, oil can only ignite in the cylinders when it is sucked in (for example, by a turbocharger or a breather).
But to get back to spontaneous combustion in principle, you need to know that the more you compress the gas, the more it heats up. Thus, this is the principle of diesel fuel: the incoming air is sufficiently compressed so that the diesel fuel naturally ignites on contact. This is why a diesel has a higher compression ratio (it takes a lot of pressure to make the gas burn).

Also, in a gasoline engine, the air / fuel mixture is usually more homogeneous (evenly distributed / mixed in the chamber) because gasoline often uses indirect injection (so this is not really the case for a gasoline injection engine. Direct and diesel engines with direct injection. too). Therefore, note that modern gasolines practically only operate with direct injection, so this difference is reduced.
Injection time
While the gasoline engine injects fuel during air intake (when the piston goes down to the PMB and the intake valve is open) in the case of direct injection (indirect fuel is supplied simultaneously with air), the diesel will wait for the piston to be reassembled in the compression phase for fuel injection.
Compression ratio?
The compression ratio is higher for a diesel engine (two to three times higher for diesels), so it has better efficiency and lower consumption (this is not the only reason for the reduction in consumption). In fact, the amount of compressed air will be less (hence more compressed when the piston is at top dead center) on a diesel engine than on a gasoline engine, because it is this compression that should provide enough heat to ignite the diesel. This is the main purpose of this increased compression, but not only ... In fact, we ensure that the temperature required to ignite diesel fuel is significantly exceeded in order to improve combustion and limit the amount of unburned particles: small particles. On the other hand, it increases NOx (which results from hot combustion). For this, boost is used, which allows air to be fed to the engine and therefore increases the compression (and therefore the temperature).
Thanks to the high compression ratio, the diesel has more torque at lower revs.
While gasoline engines have a compression ratio of 6 to 11:1 (6-7 for older engines and 9-11 for new direct injection engines), diesels have a compression ratio of 20 to 25:1 (the old ones had about 25 , while recent ones tend to be less.20: The reason is due to the democratization of turbocharging, which allows you to get high compressions without the need for a high base engine compression ratio.High compression and boost can lead to too high pressures.So we reduce the compression ratio a little, but we compensate by increasing the pressure in the chambers: due to the supply of air and fuel).
Burning rate
The combustion rate of a gasoline engine is higher due to its controlled ignition (coils / spark plugs that allow sparks), partly because of this (I mean partly because other factors are involved) that high speeds are better tolerated for unleaded gasoline ... engines. Therefore, diesels may not completely burn fuel at the top of the tachometer (the piston cycle rate is higher than the combustion rate), which can then cause black smoke to appear (the lower the engine compression ratio, the higher). (the more you like this smoke). It can also appear when the mixture is too rich, namely too much fuel versus oxidizer, hence significant smoke on reprogrammed engines, whose injection becomes very generous in the fuel flow. (copyright fiches-auto.fr)
Does the diesel engine heat up less?

The fact that it is more difficult for a diesel engine to reach temperatures is due to several factors, including what I said earlier: namely, the distribution of diesel fuel in the combustion chamber. Due to less contact with the cylinder wall, heat is less easily transferred to the surrounding metal (there is a layer of air between the cylinder wall and the combustion site).
In addition and Mostly, the large thickness of the cylinder block slows down the spread of heat through it. The more material heats up, the longer it takes ...
Finally, a lower average engine speed means that there will be fewer “explosions” and therefore less heat over the same period of time.
Weight / design?
Diesel is heavier because it needs to be more resistant to strong cylinder compressions. Therefore, the materials used are more stable (cast iron, etc.), and the segmentation is more reliable. Therefore, diesel-powered cars are heavier, so they tend to be less balanced in terms of front and rear weight distribution. As a result, gasoline generally behaves more dynamically and in a more balanced way.
But in terms of reliability, the diesel wins, because the block is more stable.
Different engine speed
The rotational speed of diesels is less important compared to gasoline of the same characteristic (number of cylinders). The reasons for this are due to the reinforcement of materials on the diesel (connecting rods, crankshaft, etc.), which therefore causes more inertia in the engine (more difficult to set in motion as it takes longer to wait for the diesel speed to drop ... this is due to the greater mass of moving parts). In addition, combustion is not controlled by the spark of a candle, it is less controllable and therefore lasts longer. This slows down all cycles and therefore the motor speed.
Finally, due to the longer stroke of the pistons (adapted to the combustion rate), they take longer to move forward and backward. (copyright fiches-auto.fr)

Here is the tachometer of two 308s: gasoline and diesel. Don't you notice the difference?
Another gearbox?
The fact that the engine speed is different will necessarily increase the gear ratio to match this characteristic. However, be careful, this change is not felt by the driver, it is of a technical nature to compensate for the diesel engine's reduced crankshaft speed.
Differences between diesel and gasoline?

Diesel fuel provides slightly more energy than gasoline for the same volume. Fuel efficiency itself in itself slightly better with fuel oil.
As with production, diesel and gasoline are extracted differently as the crude oil must be heated to a higher temperature for diesel fuel. But what is certain is that if you want to ditch diesel, you also have to throw away a significant portion of the oil you collect, because the latter contains 22% gasoline and 27% diesel.
Read more about the production and extraction of diesel and gasoline here.
Overall performance: the difference?
Diesel engine overall efficiency (no fuel as shown above) is better with 42% for diesel and 36% for gasoline (according to ifpenergiesnouvelles.fr). Efficiency is the conversion of starting energy (in the form of fuel in the case of an engine) into a resultant mechanical force. So with a diesel engine we have a maximum of 42%, so the heat and turbulence of the exhaust gases make up the remaining 58% (so the wasted energy ... Very bad).
Vibration / Noise?
Diesel vibrates more accurately because it has a higher compression ratio. The stronger the compression, the greater the vibration resulting from combustion (due to the stronger expansion). This explains that ...
Note, however, that this phenomenon is mitigated by pre-injection, which softens things (only at low speed, then it starts to rumble louder), apparently only on a direct injection engine.
Pollution
Fine particles
Diesel usually emits more fine particles than gasoline because, regardless of the technology, the air / fuel mixture is not very uniform. In fact, whether direct or indirect injection, the fuel is injected late, resulting in a medium mixture and unburning. On gasoline, these two components are mixed prior to intake (indirect injection) or one is injected during the intake phase (direct injection), resulting in a good combination of fuel and oxidizer.
Note, however, that modern gasoline engines "like" to run lean at certain stages (to reduce consumption: dosage and limit pumping losses), and this lean mixture causes a heterogeneous mixture and fines. This is why they now have particulate filters.
Therefore, a homogeneous mixture and hot combustion are required to limit the number of particles. Improved uniformity with direct injection is achieved by high pressure injection: better fuel vaporization.
In line with recent standards, legislation required diesel fuel to be cleaned of fine particles [Edit: gasoline is too recent]. As a result, modern diesel engines filter 99% of them (with a hot engine ...), which can be considered very acceptable! Thus, when combined with low consumption, diesel fuel remains a relevant solution from an environmental and health point of view, even if it can make people cringe.
The opposite effect, the system allowed gasoline engines until recently to refuse 10 times more, even if the permitted mass of the latter should be less than 10% for gasoline. Because we have to distinguish between mass and particles: in 5 grams of particles there can be 5 particles weighing 1 g (an unreal figure, this is for understanding) or 5 particles 000 grams (and we are not interested in mass, but in their size: the smaller it is, the more it is harmful to health, since large particles are very well removed / filtered by our lungs).
The problem is that when switching to direct injection, gasoline engines now produce more fine particles than diesel engines equipped with a particulate filter (the media is strangely silent about this, with the exception of Autoplus, which is often the exception). But more generally, it should be remembered that diesel produced more pollutants than gasoline when it was directly injected. So you don't really need to look at the fuel (petrol / diesel) to see if the engine is polluting and harmful to health, but if it has high pressure direct injection ... what causes the formation of fine particles and NOx (something that the media did not seem to understand, hence the massive misinformation that caused exaggerated damage to diesel fuel).
To summarize, diesels and gasoline are becoming more and more similar in emissions ... And this is why gasolines released after 2018 have DPF for many. And even though diesel produces more NOx (a lung irritant), they are now very limited by the addition of an SCR catalyst, which triggers a chemical reaction that destroys (or rather transforms) most of them.
In short, the winner in this misinformation story is the tax-boosting state. Indeed, many people have switched to gasoline and now consume much more than before ... By the way, it is very disturbing to see to what extent the media can influence the masses, even if the information is partially incorrect. (copyright fiches-auto.fr)
Nox
Diesel naturally emits more than gasoline because the combustion is not very homogeneous. This causes many hot spots in the combustion chamber (over 2000 degrees) which are sources of NOx emissions. Indeed, what causes NOx to appear is the heat of combustion: the hotter it is, the more NOx. The EGR valve for petrol and diesel also limits this by lowering the combustion temperature.
Note, however, that modern gasolines also produce quite a lot of lean mixture / stratified charge (only possible with direct injection) as this increases operating temperatures.
Basically, it should be remembered that both engines produce the same pollutants, but the proportions change depending on whether we are talking about direct or indirect injection. And therefore, above all, the type of injection causes fluctuations in the emission of pollutants, not just the fact that the engine is diesel or gasoline.
Read: Pollutants Emitted by Diesel Fuel.
Glow plugs?

The diesel engine has glow plugs. Since it ignites spontaneously, this requires a minimum temperature in the combustion chamber. Otherwise, the air / diesel mixture will not necessarily reach sufficient temperature.
Preheating also limits cold contamination: the candles remain lit even after starting to speed up the heating of the combustion chambers.
Air intake, difference?
The diesel does not have a throttle valve (controlled by a computer on gasoline, except for gasoline with variable valves, which in this case does not need a throttle valve) because a diesel always draws in the same amount of air. This eliminates the need for a regulating flap like a throttle valve or variable valves do.
As a result, a negative vacuum is created at the intake of the gasoline engine. This depression (which is not found on a diesel) is used to service other engine components. For example, it is used by the brake booster to assist when braking (liquid, disc type), this is what prevents the pedal from tightening (which you can notice when the engine is off, the brake pedal becomes very stiff after three strokes.). For a diesel engine, it is necessary to install an additional vacuum pump, which does not contribute to a simpler design of everything (the more, the less benefit! Because this increases the number of breakdowns and complicates the work.
School enrollment DIESEL
On diesel fuel, the pressure is at least 1 bar, as air enters the intake port at will. Therefore, it should be understood that the flow rate changes (depending on the speed), but the pressure remains unchanged.
School enrollment ESSENCE
(Low load)
When you accelerate a little, the throttle body doesn't open very much to restrict airflow. This causes a kind of traffic jam. The engine draws in air from one side (right), while the throttle valve restricts the flow (left): a vacuum is created at the inlet, and then the pressure is between 0 and 1 bar.
More torque? Limited engine speed?
On a diesel engine, power is transmitted in a different way: the thrust on a diesel engine is stronger (compared to gasoline of the same power), but lasts less (a much shorter range of speeds). Thus, we usually get the impression that a diesel engine runs harder than gasoline of the same power. However, this is not entirely true, because it is rather the way in which power comes, which is different, more "distributed" in essence. And then the generalization of the turbines contributes to an even larger gap ...
Indeed, we should not be limited to just torque, power is important! The diesel will have more torque because its power is transmitted in a smaller rev range. So basically (I'm taking the numbers at random) if I distribute 100 hp. at 4000 rpm (small range like a diesel), my torque curve will be located in a smaller area, so maximum torque or more will be required (at a certain speed, because the torque changes from one speed to another) to match a gasoline engine with a power of 100 hp. will propagate at 6500 rpm (so the torque curve will be logically flatter, which will make it less high).
So instead of saying that the diesel has more torque, it is better to say that this diesel does not do the same, and that in any case, it is the power factor that is critical to the performance of the engine (not the torque).
Which is better?

Honestly, no ... The choice will only be based on needs and desires. This way, everyone will find the engine they need according to their life and daily activities.
For those looking for pleasure, the gasoline engine seems much more appropriate: climbing more aggressive towers, less weight, greater engine rev range, less odors in the case of a convertible, less inertia (more sporty feel), etc.
On the other hand, a modern supercharged diesel engine will have the advantage that it will have much more torque at low rpm (no need to drive towers to get the "juice", which is ideal for trucks), consumption will be lower (better performance). and therefore useful for those who ride a lot.
On the other hand, modern diesels have turned into real gas factories (turbo, EGR valve, breather, auxiliary vacuum pump, high pressure injection, etc.), which leads to high risks in terms of reliability. The more we stick to simplicity (of course, all proportions are preserved, because otherwise we ride a bike ...), the better! But unfortunately, gasoline engines have also joined the club by adopting high pressure direct injection (this is what causes an increase in pollution, or rather substances harmful to living things).
The situation is changing, and we should not dwell on outdated prejudices, for example, "diesel fuel pollutes much more than gasoline." In fact, the opposite is true, as diesel uses less fossil energy and emits the same pollutants as gasoline. Thanks to direct injection, which appeared en masse on gasoline ...).
Read: Mazda block that tries to combine the qualities of diesel and gasoline in one engine.
Thanks in advance to anyone who finds the elements that will serve to complete this article! To take part, go to the bottom of the page.
All comments and reactions
Dernier comment posted:
Author (Date: 2021 09:07:13)
c 'Est Trés Trés okay?
(Your post will be visible under the comment after verification)
Comments continued (51 Ã 89) >> нажмите здесь
Write a comment
Do you like turbo engines?
