Diesel fuels
Content
Characteristic features of diesel fuel
In the classification process, diesel fuel is distinguished by the following characteristics:
- cetane number, which is considered a measure of the ease of ignition;
- evaporation intensity;
- density;
- viscosity;
- thickening temperature;
- content of characteristic impurities, primarily sulfur.
The cetane number of modern grades and types of diesel fuel ranges from 40 to 60. The grades of fuel with the highest cetane number are designed for engines of cars and trucks. Such fuel is the most volatile, determines the increased smoothness of ignition and high stability during combustion. Slow speed engines (ship-mounted) use fuels with a cetane number of less than 40. This fuel has the lowest volatility, leaves the most carbon, and has the highest sulfur content.


Sulfur is a critical contaminant in any type of diesel fuel, so its percentage is especially tightly controlled. Thus, according to the rules of the European Union, the amount of sulfur in all diesel fuel producers did not exceed the level of 10 parts per million. Lower sulfur content reduces emissions of sulfur compounds associated with acid rain. Since a decrease in the percentage of sulfur in diesel fuel also entails a decrease in the cetane number, various types of additives are used in modern brands that improve engine starting conditions.
The percentage composition of the fuel significantly depends on its freshness. The main sources of diesel fuel pollution are water vapor, which, under certain conditions, are capable of condensing in tanks. Long-term storage of diesel fuel provokes fungus formation, as a result of which fuel filters and nozzles are contaminated.
It is believed that modern brands of diesel fuel are safer than gasoline (it is more difficult to ignite), and also surpass it in terms of efficiency, since they allow increasing energy efficiency per unit volume of fuel.


Sources of production
The most general classification of diesel fuel can be carried out according to the type of feedstock for its production. Traditionally, heavy oils have been the feedstock for the production of diesel fuel, after the components used for the production of gasoline or aviation rocket fuel have already been extracted from them. The second source is synthetic varieties, the production of which requires coal, as well as gas distillate. This type of diesel fuel is considered the least valuable.
The true technological breakthrough in diesel fuel technologies was the work on its production from agricultural products: the so-called biodiesel. It is curious that the world's first diesel engine was powered by peanut oil, and after industrial testing, Henry Ford came to the conclusion that the use of vegetable fuel as the main source of fuel production is certainly appropriate. Now the majority of diesel engines can operate on a working mixture, which includes 25 ... 30% of biodiesel, and this limit continues to rise steadily. Further growth in biodiesel consumption requires reprogramming of the electronic fuel injection system. The reason for this reprogramming is that biodiesel differs in some of its performance characteristics, although there is no fundamental difference between a diesel engine and a biodiesel engine.


Thus, according to the source of production, diesel fuel can be:
- From vegetable raw materials.
- From synthetic raw materials.
- From hydrocarbon raw materials.
Standardization of diesel fuel
The versatility of sources and technologies for producing diesel fuel is one of the reasons for the relatively large number of domestic standards governing its production and consumption. Let's consider them.
GOST 305-2013 defines the parameters of diesel fuel obtained from oil and gas raw materials. The indicators controlled by this standard include:
- Cetane number - 45.
- Kinematic viscosity, mm2/ s - 1,5… 6,0.
- Density, kg / m3 - 833,5… 863,4.
- Flash point ºC - 30 ... 62 (depending on the type of engine).
- pour point, ºC, not higher than -5.
The main characteristic of diesel fuel according to GOST 305-2013 is the application temperature, according to which the fuel is divided into summer L (operation at outdoor temperatures from 5ºC and above), off-season E (operation at outdoor temperatures not lower than -15ºC), winter Z (operation at outdoor temperatures not lower than -25 ... -35ºC) and arctic A (operation at outdoor temperatures from -45ºC and below).

GOST 1667-68 establishes requirements for motor fuels for medium- and low-speed marine diesel installations. The source of raw materials for such fuel is oil with a high percentage of sulfur. Fuel is divided into two types of diesel fuel and DM (the latter is used only in low-speed diesel engines).
The main operational characteristics of diesel fuel:
- Viscosity, cSt - 20 ... 36.
- Density, kg / m3 - 930.
- Flash point ºC - 65… 70.
- pour point, ºC, not lower than -5.
- Water content, %, no more than 0,5.
The main operational characteristics of DM fuel:
- Viscosity, cSt - 130.
- Density, kg / m3 - 970.
- Flash point ºC - 85.
- pour point, ºC, not lower than -10.
- Water content, %, no more than 0,5.
For both types, indicators of the composition of the fractions are regulated, as well as the percentage of the main impurities (sulfur and its compounds, acids and alkalis).

GOST 32511-2013 defines the requirements for modified diesel fuel that meets the European standard EN 590:2009+A1:2010. The basis for the development was GOST R 52368-2005. The standard defines the technical conditions for the production of environmentally friendly fuels with a limited content of sulfur-containing components. The normative indicators for the production of this diesel fuel are set as follows:
- Cetane number - 51.
- Viscosity mm2/ s - 2… .4,5.
- Density, kg / m3 - 820… 845.
- Flash point ºC - 55.
- pour point, ºC, not lower than -5 (depending on the type of fuel).
- Water content, %, no more than 0,7.
Additionally, the lubricity rate, corrosion performance, and the percentage of presence of methyl esters of complex organic acids were determined.

GOST R 53605-2009 establishes technical requirements for the main components of the feedstock used for the production of biodiesel fuel. It defines the concept of biodiesel, lists the requirements for the conversion of diesel engines, establishes restrictions on the use of methyl esters of fatty acids, which must be contained in the fuel. GOST adapted to European standard EN590:2004.
Basic technical requirements for fuel according to GOST 32511-2013:
- Cetane number - 55 ... 80.
- Density, kg / m3 - 860… 900.
- Viscosity mm2/ s - 2… .6.
- Flash point ºC - 80.
- pour point, ºFrom -5 ... -10.
- Water content, %, no more than 8.
GOST R 55475-2013 specifies the conditions for the production of winter and arctic diesel fuel, which is produced from the distillate of oil and gas products. Diesel fuel grades, the production of which is provided for by this standard, are characterized by the following parameters:
- Cetane number - 47 ... 48.
- Density, kg / m3 - 890… 850.
- Viscosity mm2/ s - 1,5… .4,5.
- Flash point ºC - 30… 40.
- pour point, ºC, not higher than -42.
- Water content, %, no more than 0,2.


Watch this video on YouTube
Brief description of brands of diesel fuel
Diesel fuel grades are distinguished by the following indicators:
According to the sulfur content, which determines the environmental friendliness of the fuel:
- class I (up to 350 mg/kg sulfur);
- class II (up to 50 mg/kg sulfur);
- class III (up to 10 mg / kg sulfur).
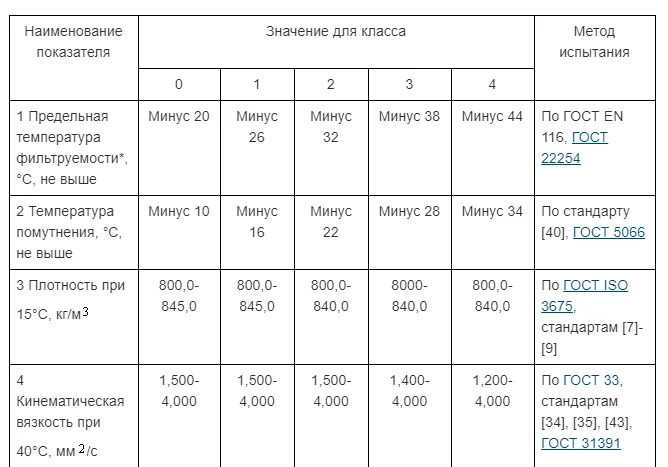
On the lower limit of filterability. 6 grades of fuel are installed:
- A - lower limit of filterability 5ºС;
- B - lower limit of filterability 0ºWITH;
- C - lower limit of filterability -5ºWITH;
- D - lower limit of filterability -10ºWITH;
- E - lower limit of filterability -15ºWITH;
- F - lower limit of filterability -20ºC.
Additionally for areas with a cold climate:
- class 0 (-20ºFROM);
- class 1 (-26ºFROM);
- class 2 (-32ºFROM);
- class 3 (-38ºFROM);
- class 4 (-44ºFROM).
For diesel plants used in regions with a cold climate, the letter K is additionally introduced into the marking, which determines the fuel production technology - catalytic dewaxing. The following brands have been installed:
- DT-Z-K3 (K4, K5) for use at temperatures not lower than -32ºWITH;
- DT-Z-K3 (K4, K5) for use at temperatures not lower than -38ºWITH;
- DT-A-K3 (K4, K5) for use at temperatures not lower than -44ºWITH;
- DT-A-K3 (K4, K5) for use at temperatures not lower than -48ºWITH;
- DT-A-K3 (K4, K5) for use at temperatures not lower than -52ºC.
A complete list of indicators is given in the quality certificates for a batch of diesel fuel.

