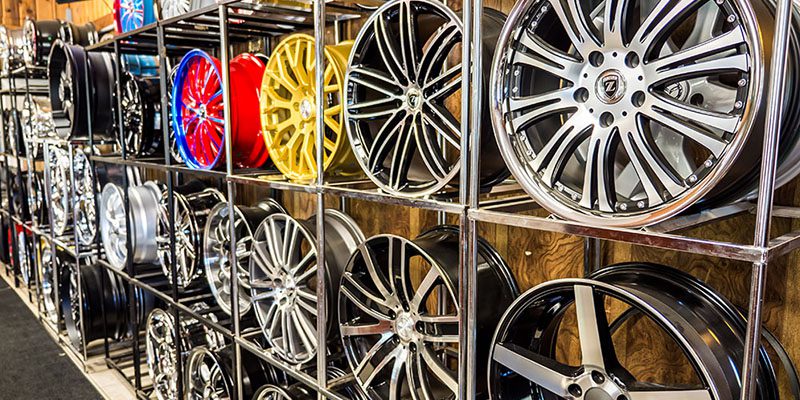

Types and parameters of rims
Content
One of the key elements of any car, without which transport is not able to travel even a meter, is the wheel. The auto parts and components market offers a huge variety of car rims. Each motorist, depending on his material capabilities, is able to choose a style of wheels that can be installed on his car to emphasize its beauty.
In addition, the car owner can use discs not only with a non-standard diameter, but also with a width. Splices are very popular among car tuning enthusiasts. The advantages and disadvantages of this category of discs are already available separate review... For now, we will focus on standard wheels that are offered by auto parts manufacturers.
They differ from each other not only in design. First of all, their differences lie in their technical parameters. Unfortunately, some motorists are guided solely by whether they like the wheel design and whether the mounting holes fit.

If the wheel rim is incorrectly selected, comfort during the trip may suffer, but in many situations, errors in such a selection are additionally fraught with accelerated wear of some suspension parts. Let's consider how to choose the right wheel rim, as well as what its modifications are.
Purpose and design of wheel disks
Despite the fact that a wide variety of rims are offered in car dealerships, their different design is intended to not only change the appearance of the car. Everyone knows that a tire is put on the disc (in detail about the varieties and structure of this element is described in another review). The disc has several holes that allow you to install the complete wheel (disc + tire) on the undercarriage hub using special bolts. Therefore, the purpose of the rim is to provide effective hub-tire-road communication.
This element is an important intermediate link that ensures the efficient movement of the vehicle on the road. The rim itself does not participate in traction. Automotive tires are responsible for this. It is distinguished by a tread pattern, materials that determine the seasonality of the product's operation. Each key parameter is indicated on the side of the tire (tire marking is discussed in detail here).
To prevent the tire from flying off the disc while the car is moving, as well as due to the effect of high air pressure in the wheel (for how much you need to inflate tires in the car, read separately), there is a special annular protrusion on the disk, which is also called a shelf. This element can have a standard, flat or expanded view.
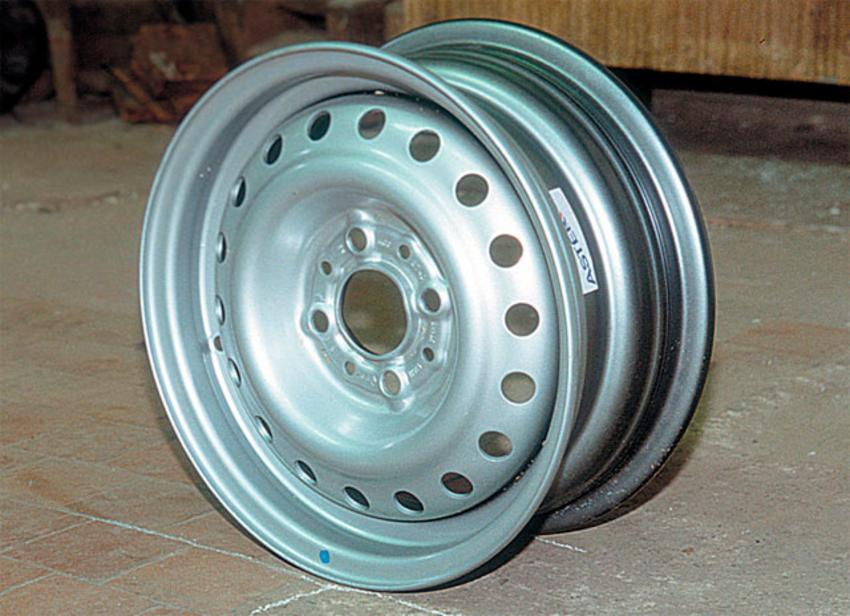

Also, the wheel rim has a flange into which the shelf smoothly goes. This part can have a different profile. The design of the disc must ensure that the entire plane of the cortical part of the tire is correctly aligned with the disc. For this reason, any rim for a car must have the maximum strength and stiffness. Also, each manufacturer tries to make as lightweight product as possible (the heavier the wheel is, the more load the chassis of the car and its transmission will experience, and the motor will consume more torque to spin the wheel).
So that the movement of the car is not accompanied by wheel beating, this element of the car's chassis is created with an ideal circle geometry. But even such a wheel can beat if the fastening of the product does not match the holes in the hub. We will talk about this in detail a little later.
Types of rims
All types of car wheels can be divided into 4 main categories;
- Stamped;
- Cast;
- Forged;
- Composite (or combined).
Each type of wheel has its own characteristics, as well as advantages and disadvantages. Let's consider in more detail each of these types separately.
Stamped or steel discs
The most common and budgetary option is stamping. It is a steel disc. It consists of several parts. Each disc element is made by stamping under a large press. They are connected into one structure by welding. To prevent the product from creating a beat, the production technology implies the alignment of each product. Additionally, each new disc, regardless of the model and materials used in the manufacturing process, is balanced immediately before being installed on the machine.

The stowaway also belongs to this category of disks. What it is, and how it differs from a regular spare wheel, is described in another article.
The advantages of such discs include:
- It is easy to stamp and connect parts of a disc, so the production of such products is cheap, which has a positive effect on the price of discs;
- Sufficient strength - each category is designed for specific car models, since the mass of the vehicle also plays an important role in the serviceability of the disks (the force of the wheel hitting an obstacle depends primarily on the weight of the car and its speed);
- In most cases, such discs are deformed upon strong impact, rather than flying apart. Thanks to this, the damage can be easily removed by rolling.
The cons of stampings are as follows:
- Since this product belongs to the budget category, the manufacturer does not manufacture discs with a special design. To make such an element look beautiful on a vehicle, motorists are offered all kinds of decorative caps, which are fixed in the rim of the discs with a steel ring. Additionally, they can be fixed by passing a plastic clamp through the hole in the disc.
- Compared to other types of discs, stampings are the heaviest;
- Although during the manufacturing process each product is treated with an anti-corrosion coating, during operation this protective layer is damaged. Dependence on humidity makes these products less attractive compared to light-alloy and forged counterparts.
Alloy wheels
The next type of rims in the circles of motorists is also called light-alloy. Most often, such products are made from aluminum alloys, but there are often options, which include magnesium. Such discs are in demand due to their strength, lower weight, and excellent balancing. In addition to these factors, casting allows the manufacturer to create products with unique designs.
The design feature of such discs is that the rim and disc are not connected to each other by welding, as is the case with a stamped analogue. In this case, these parts are one whole.
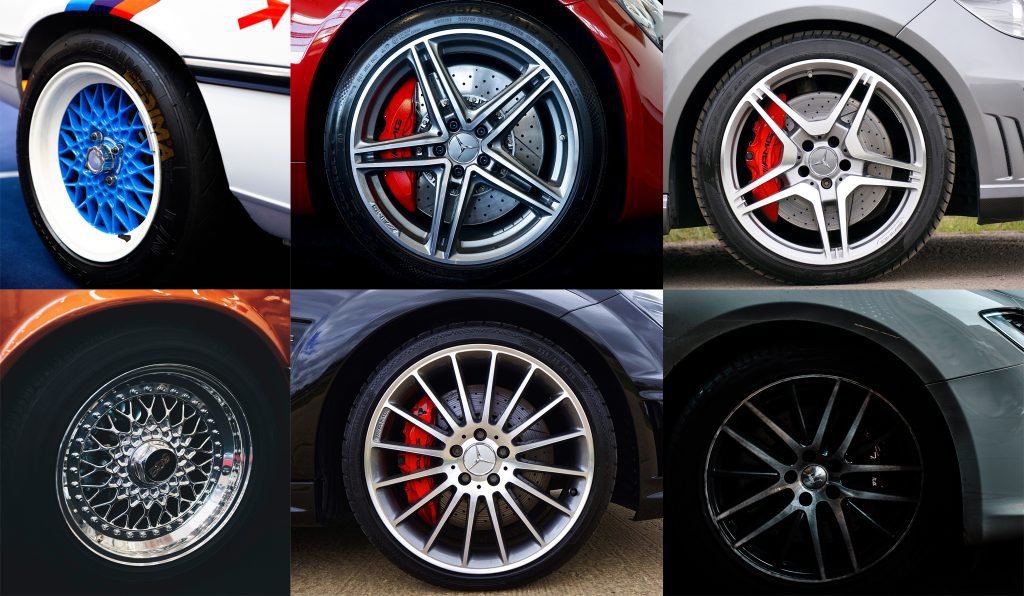

The advantages of alloy wheels are as follows:
- The entire manufacturing process is carried out with maximum precision, due to which the appearance of defective products on the market is practically excluded;
- A wide range of product designs, which makes it possible to change the appearance of the car;
- Compared to stampings, alloy wheels are much lighter (if you take the options designed for a particular car model);
- Additionally, these products provide better heat dissipation from the brake pads.
The disadvantages of light-alloy wheels include their relatively high fragility. If the car falls into a serious hole, the stamping is often simply deformed (in many cases, the rubber does not even suffer), and the cast analog can crack. This property is due to the granular structure of the metal, which is why the product does not tolerate impacts well.
The breakage of the disc is caused by the formation of microcracks, which appear as a result of small blows during the movement of the car. To make the disc more durable, the manufacturer can make the walls thicker, but this will negatively affect its weight. Another disadvantage of alloy wheels is that they are extremely difficult to recover from damage. Often, straightening and rolling of such modifications leads to the formation of additional microcracks.
The next disadvantage of casting is that during operation the product is easily damaged - scuffs, scratches and chips appear. Because of this, such discs need constant care and protection. Otherwise, they will quickly lose their beauty.
Forged wheels
As a type of light-alloy wheels, buyers are offered a forged version. The so-called "forging" is made by stamping an aluminum alloy. The material can be a mixture of aluminum, magnesium and titanium. After the creation of the product, it is processed mechanically. As a result of using this manufacturing technology, a fibrous structure is created, which forms several layers of material.
In comparison with stamped and cast analogs, these products are lighter and look more beautiful. But if such discs are compared with conventional cast counterparts, then forging has greater strength. Thanks to this, forged wheels are able to withstand heavy impacts and not crack.
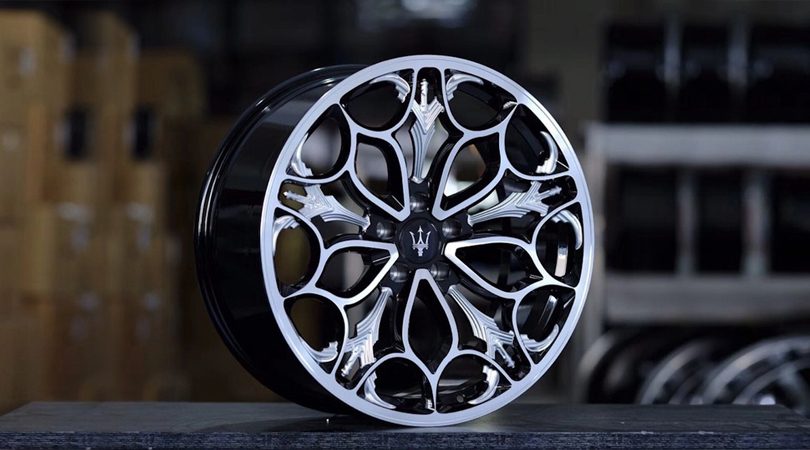

In addition to the difficulty of remanufacturing, the key disadvantage of forged wheels is the high cost of the product. Another disadvantage of forging is that with a strong impact, the product does not deform, while extinguishing energy, but transfers the force to the suspension, which can cause serious damage to this car system later.
If there is a desire to choose some kind of original disc design, then in the case of the forged version, the buyer is limited in this. The reason for this is the complexity of manufacturing.
Combined or split discs
The composite wheel embodies all the virtues of the forged and cast versions. During the manufacturing process, the manufacturer pours out the main part of the disc, but the forged element (rim) is screwed to it with bolts.
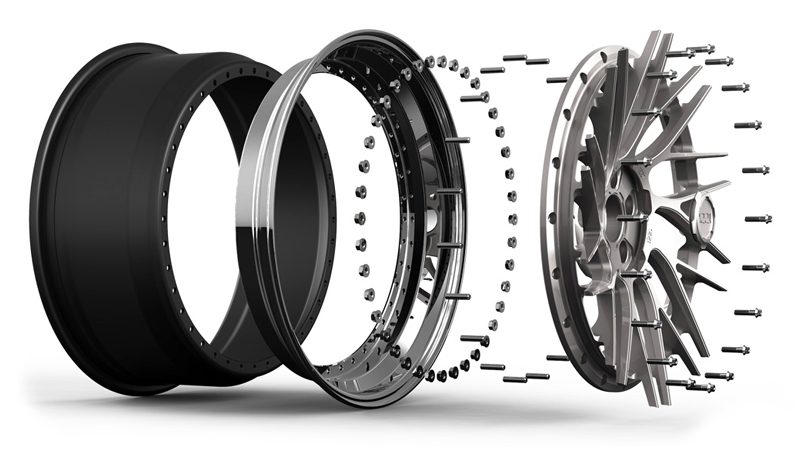

This arrangement allows you to create the most durable and beautiful discs. Such products are difficult to restore, and also cost much more than forged ones. Despite this, their merits outweigh all the cons.
In addition to the listed types of discs, which have become very popular, there are also rare and expensive designs. An example of this are the models with spokes, which are installed on collectible vintage cars. There are also composite discs. They are mainly used in supercars to facilitate transportation. They are made of heavy-duty plastic, carbon fiber and other materials.
How to choose rims according to parameters?
When choosing new discs for your iron horse, you must take into account the manufacturer's recommendations. If there is a desire to somehow distinguish your vehicle from the gray mass by installing non-standard disks, the list of acceptable options indicates not only the permissible rim diameter, but also the rubber profile compatible with a particular category of disks.
When a car's suspension is designed, it is designed taking into account the loads that a wheel with specific parameters imposes. If the motorist uses a non-standard option, then there is a high probability that the vehicle's suspension will suffer.
For some motorists, it is sufficient that the proposed new wheel for their car meets several or most of the required parameters. In fact, it is very important that everything the automaker requires is fully consistent with the product description.

When buying new discs, it is necessary to be guided not only by the design of the product and the number of holes for mounting on the hub. Here are the parameters you need to navigate:
- Rim width;
- Disc diameter;
- Departure of the disk;
- Number of mounting holes;
- Distance between mounting holes;
- Diameter of the disc bore.
Let's consider what is the peculiarity of each of the listed parameters.
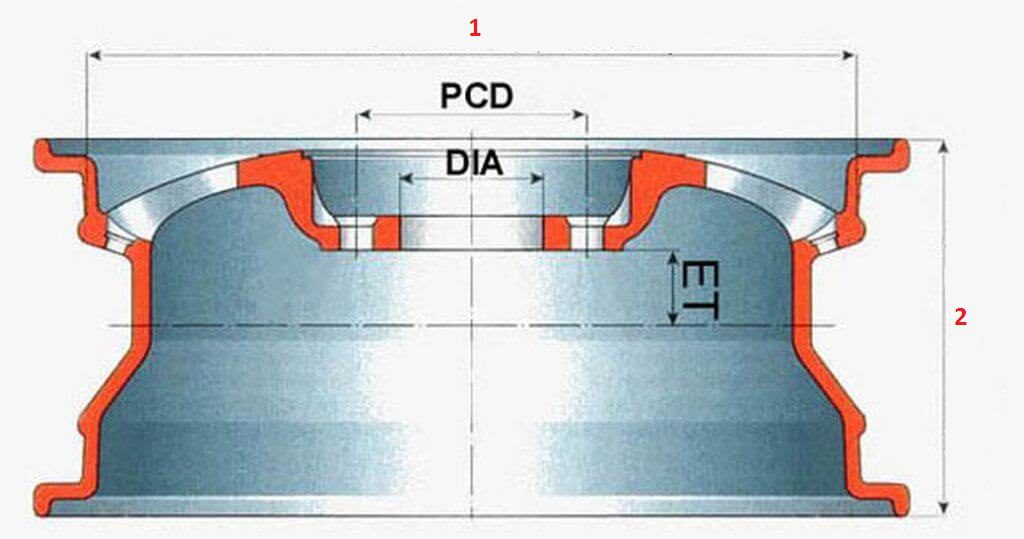
Rim width
The rim width should be understood as the distance from one rim flange to the other inside. When new tires are selected, this parameter should be approximately 30 percent less than the tire profile. Car manufacturers do not recommend using discs that are not standard for a particular model. They can be narrower or wider.
2 Rim width
As a result of strong stretching or narrowing of the tire, its tread deforms. As most motorists know, this parameter has a negative effect on the driving characteristics of the vehicle, and especially on its adhesion to the road surface. Read more about tire treads in another review.
Manufacturers set the permissible parameter for the deviation of the width of the disc from the norm within a maximum of one inch (for discs up to 14 '' in diameter) or one and a half inches if the disc diameter is above 15 ''.
Disc diameter
Perhaps this is the most basic parameter by which most motorists select new wheels. Despite the fact that it is very important for the correct operation of the car, this parameter is not the only one important. In terms of disc diameter, the product line includes disc models ranging in diameter from ten to 22 inches. The most common is the 13-16-inch version.
For each car model, the manufacturer sets its own rim size. Moreover, the list always indicates the standard size, as well as the permissible one. If you install discs of a non-standard diameter, you will also have to select tires with a modified profile. The reason is that the wheel arch is not dimensionless. Even if the diameter of the wheel itself allows it to be installed in free space, it must be borne in mind that the front wheels must also turn.

If their diameter is too large, then the turning radius of the car will increase significantly (for details on the importance of such a parameter as the turning radius, read separately). And if plastic protection is also installed in the wheel arch, then the maneuverability of the car will be greatly affected. Low profile tires are very popular among young people.
They allow you to install the maximum enlarged rims on the car, even if they are not indicated in the list provided by the manufacturer. We will not talk in detail about the operation of a car on low-profile tires now. There are separate detailed article... But in short, this tuning has several significant drawbacks, because of which there is no reason, except for aesthetics, to use discs with too large a diameter.
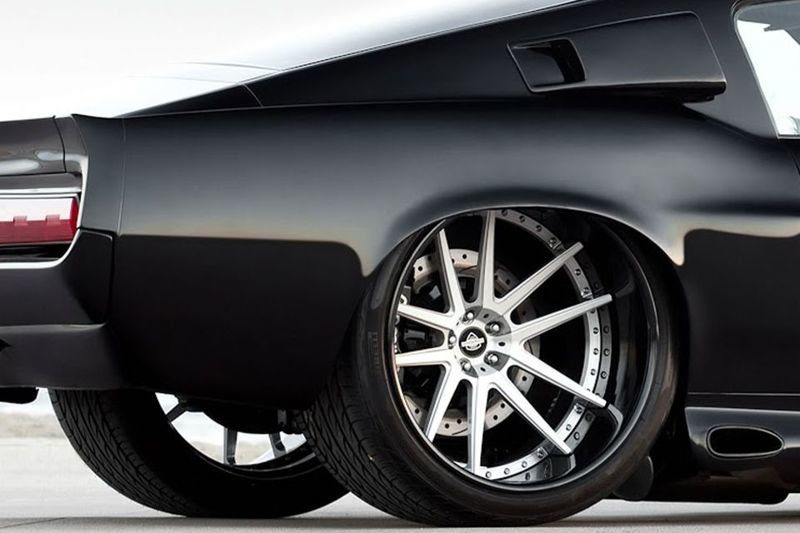
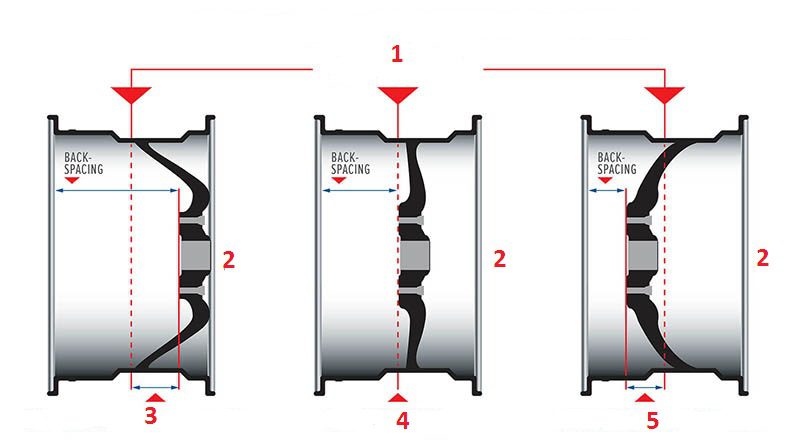
Departure disk
The concept of disc overhang means the distance to which the middle of the disc (in the longitudinal visual section) will protrude beyond the mounting part of the wheel. This parameter is measured from the base of the contact surface of the disc with the hub to the axial section of the disc.
There are three categories of disks, differing in offset:
- Zero departure. This is when the conventional vertical, passing in the middle of the longitudinal section of the disc, touches the central part of the contact surface of the disc with the hub;
- Positive departure. This is a modification in which the outer part of the disc is recessed relative to the hub (the central element of the disc is located as close as possible to the outer part of the disc);
- Negative outreach. This is an option in which the mounting part of the wheel is recessed as much as possible relative to the outer edge of the disc.
In the disc markings, this parameter is indicated by the ET marking, and is measured in millimeters. The maximum allowable positive overhang is + 40mm. The same applies to the maximum permissible negative departure, and in the documentation it will be indicated as ET -40mm.
2 Front of disc
3 Positive disc overhang
4 Zero disc offset
5 Negative disk offset
The ET indicator is set by the automaker, since the engineers of each car brand develop different modifications of the car's chassis. If the driver does not adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the displacement of the disks, he risks quickly spoiling the suspension of the car (its structure and varieties are discussed in detail here). In addition, the car's handling will be noticeably reduced.
Accelerated wear of the bogie and suspension elements is due to the fact that the non-standard offset of the disc changes the load that the wheel exerts on the levers, bearings, bearings and hub during driving, especially on uneven surfaces. The track width also depends on the disc departure. This is also an important factor, since a car that does not fall into a knurled track, for example, on a dirt or snowy road, will constantly jump out of the track, and the driver will find it much more difficult to drive.
Diameter of mounting holes and their number
This parameter in the marking of car rims is designated as PCD. This abbreviation indicates the distance between the center parts of the mounting holes (first number) and the number of mounting bolts required to secure the wheel to the hub (second number, and it is indicated after the “x” or “*”). The order in which these parameters are written may differ from manufacturer to manufacturer. On the territory of the CIS countries, marking of the 5x115 type is often used.
Standard parameters, depending on the car model, the distance between the centers of the mounting holes can range from 98 mm to 140 mm. The number of such holes varies from four to six.
If the number of mounting holes is not difficult to determine visually, then it is impossible to understand the distance between the centers of these holes, so you need to pay attention to the product labeling. Some motorists believe that the bolt pattern with parameters such as 98x4 and 100x4 is an insignificant difference. But this couple of millimeters plays a big role in misalignment of the disc, which can cause it to become a little distorted.
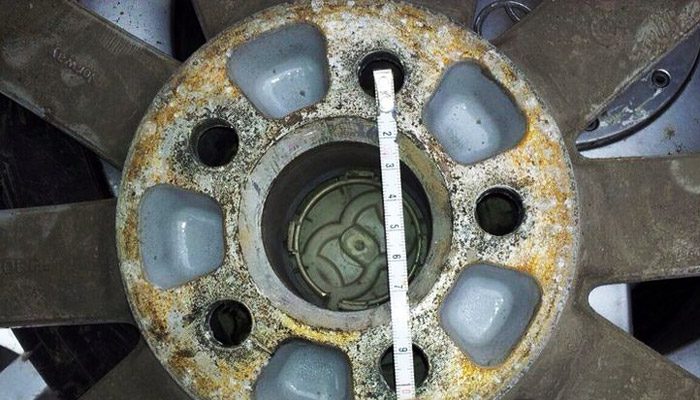

If in city mode this may not even be noticed, then having driven onto the highway, the driver will immediately feel the beating of the wheels that are at a standstill. If you are constantly driving at high speeds in this way, you should expect the undercarriage parts to wear out faster. Additionally, you will have to change tires due to their uneven wear (for details about other breakdowns that affect tire wear, see here).
Disc center hole diameter
Usually disc manufacturers make this hole slightly larger than the diameter of the hub itself, so that it is easier for the motorist to pick up and install the disc on the car. The standard options for most cars are 50-70 millimeters in size (they are different for each car model). If a standard wheel is selected, then this parameter should match perfectly.
When buying a non-standard disc, you should pay attention to the presence of special spacer rings that allow you to install non-standard discs on a car. The centering of these large bore discs is done using PCD parameters.
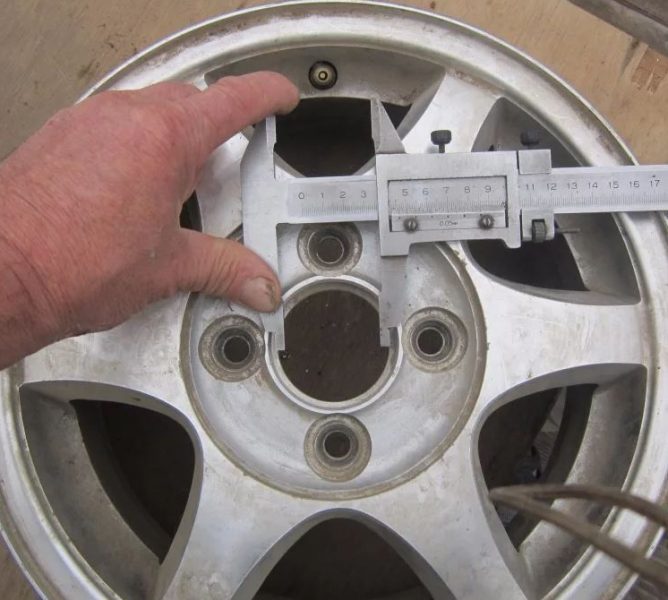

In addition, you should pay attention to the fact that in most cars, limiter pins are installed on the hubs of the drive wheels. They reduce the torque load on the mounting bolts. For safety reasons, they should not be removed if the holes on the discs are not aligned with these elements. An example of this is situations where wheel bolts are not properly clamped. In the process of driving, they are unscrewed.
If it were not for these studs, the thread of the bolts or inside the hub would break off due to the runout of the wheel, which would make it difficult to mount / dismantle the wheel further. When the driver hears a strong beat when coasting or when braking by the engine, stop immediately and check the tightening of the bolts, especially on the drive wheels.
Where is the disc label located?
Regardless of what material the manufacturer uses for the manufacture of this product, the car model for which the product is relied on, as well as the technology used in production, the marking will necessarily be present on the wheel rim. On many standard discs, this information is printed on the front of the product, but in order to preserve its appearance, such information can often be found on the back of the rim.

Often the markings are applied between the mounting holes. For the sake of preserving information, numbers and letters are applied by embossing, and not using stickers, which may deteriorate during operation. When choosing a new product, the motorist must be able to independently "read" the symbols that the manufacturer indicates on their products.
Decoding of wheel rim marking
So that motorists are not at a loss as to how the disc markings are correctly deciphered, the symbolism is standardized, regardless of the country of production. Consider what information the marking of the rim carries with it. Here is one of the inscriptions that can be seen on the disk: 6.5Jx15H2 5x112 ET39 DIA (or d) 57.1.
The decoding of these symbols is as follows:
| Character number in order: | Symbol: | Indicates: | Description: |
| 1 | 6.5 | Rim width | Internal distance between the edges of the shelves. Measured in inches (one inch equals approximately 2.5 centimeters). According to this parameter, rubber is selected. Ideal when the rim is in the middle of the tire width range. |
| 2 | J | Rim Edge Type | Describes the shape of the rim edge. In this part, the rubber adheres tightly to the rim, due to which the air in the wheel is retained by the rigidity of the court and a perfect fit of the products. In the standard marking, this letter is mainly used, but some manufacturers also indicate additional parameters. For example, these are the symbols P; D; IN; TO; JK; JJ. Depending on which symbol is used, the manufacturer additionally indicates: The radius of the semicircle of the edge; The shape of the profile part of the edge; How many degrees are the shelves inclined relative to the central axis of the disc; Height of the shelves and other parameters. |
| 3 | Х | Disc type | Indicates which product category the product belongs to, for example, monolith (x symbol) or split construction (using - symbol). Conventional cars and oversized trucks are equipped with X-type discs. Collapsible models are designed for large-sized vehicles. The reason is that for such vehicles the most rigid rubber is used, which cannot be put on the wheel without disassembling the rim. |
| 4 | 15 | Disc diameter | This is not really the net diameter of the disc at the edges of the rim. This is the rim mount, which indicates which cortical diameter can be fitted to a particular rim model. In this case, it's 15 inches. Often motorists call this parameter the radius of the disk. This figure must necessarily coincide with the figure indicated on the tire itself. |
| 5 | N2 | Number of annular protrusions | This parameter is also called the number of rolls (or Humps). In this modification, these protrusions are located on both sides of the disc (number 2). This part of the design is primarily intended for the tubeless rubber mounting feature. If one letter H is used, then the hump is located on only one side of the disk. The FH marking indicates a flat hump shape (from the word Flat). AH markings may also occur, indicating an asymmetric collar shape. |
| 6 | 5 | Number of mounting holes | This number should always match the number of mounting holes on the hub itself. There are so-called universal rims, which have two options for mounting holes. Thanks to this, a specific disc can be adapted to another car model. But this is extremely rare in production. More often, such options are found in the secondary market, when the motorist independently drilled holes for another hub. In this case, five bolt holes are specified. This number in the marking is always next to another number. They are separated from each other by the letter x or by * |
| 7 | 112 | Mounting hole spacing | This figure indicates the distance between the centers of the adjacent mounting holes, and it is measured in millimeters. In this case, this parameter is 112mm. Even if there is a couple of millimeters between the distance of the holes on the disc and on the hub, you should not use such options, because in this case you will have to tighten the bolts slightly at an angle, and this always leads to a slight distortion of the disc. If the disks are beautiful, and the motorist does not want to sell them or it is not possible in the near future to replace them with more suitable bolt pattern options, you can use special wheel bolts with an eccentric. They allow you to correctly fix the disc, the bolt pattern of which does not correspond to the required parameter by a couple of millimeters. |
| 8 | ET39 | Departure disk | As we have already considered, this is the distance of the mounting part of the disk relative to the central axis of the entire disk (its visual longitudinal section). This parameter is measured in millimeters. In this case, the departure is positive. If there is a "-" sign between letters and numbers, this indicates a negative overhang. The maximum deviation from the center should not exceed 40mm. |
| 9 | d57.1 | Mounting or hub hole diameter | Part of the hub should fit into this hole, making it easier to install the heavy disc in place. This parameter is measured in millimeters. In the marking under consideration, it is 57.1mm. A hole of 50-70 mm can be used in the discs. The disc must also be matched to this parameter of the hub girdle. If the diameter of this hole on the disc is a couple of millimeters larger than on the hub, the product can be installed. |
So, as you can see, the choice of new wheels can directly affect not only the appearance of the car, but also its safety. It is not pleasant when a tire bursts or a wheel flies off the hub. But it is worse if this happens through the fault of the motorist himself. For this reason, the selection of this element of the vehicle must be approached with all seriousness.
Additionally, we suggest watching a short video on how to select disks for your car:
Questions and answers:
How to decipher the parameters of the rims? W is the width of the disc. D - diameter. PCD - the number of mounting bolts and the distance between them (often marked as 4x100 ...) ET - overhang. DIA or d is the diameter of the mating plane.
What is the rim size? The size of a rim is a combination of all parameters (offset, type of rims, etc.), and not just its diameter or the number of mounting bolts.
Where is the disk size listed? In many cases, these markings are applied to the inside or outside of the disc. Some manufacturers use stickers or factory stamping.
