What is a car crankcase system?
Content
Crankcase gas system
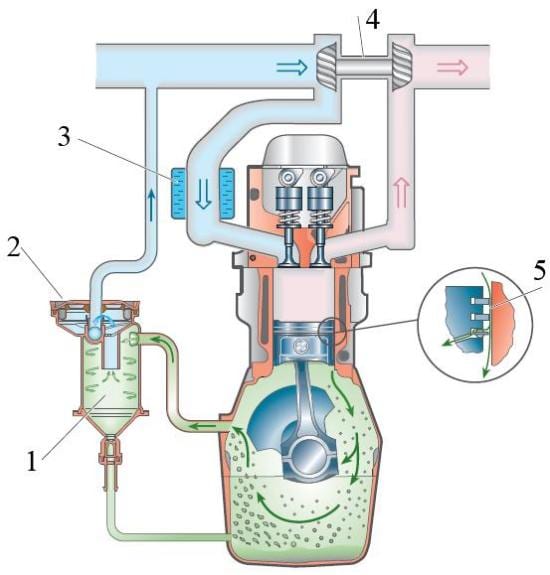
The crankcase ventilation system or the crankcase gas system is designed to reduce emissions of harmful substances from the crankcase into the atmosphere. When the engine is running, exhaust fumes can flow out of the combustion chambers in the crankcase. Carter also contains oil, gasoline and steam. Together they are called crankcase gases. The accumulation of crankcase gases affects the properties and composition of engine oil, destroys the metal parts of the engine. Modern engines use a forced crankcase ventilation system. The crankcase ventilation system of different manufacturers and different engines can have a different design. However, the following main structural elements of this system are distinguished: an oil separator, crankcase ventilation and air nozzles. An oil separator prevents oil vapor from entering the combustion chamber of the engine, thereby reducing soot formation.
Overview of the gas card system
There are labyrinth and cyclic methods for separating oil from gases. Modern engines are equipped with a combined oil separator. In the labyrinth oil separator, the crankcase slows down, which is why large droplets of oil settle on the walls and enter the engine crankcase. Centrifugal oil separator produces an additional separation of oil from crankcase gases. The crankcase gases passing through the oil separator enter a rotational motion. Particles of oil under the action of centrifugal force settle on the walls of the oil separator and fall into the crankcase. To prevent turbulence of the crankcase after a centrifugal oil separator, a labyrinth-type starting stabilizer is used. This is the final separation of oil from gases. Crankcase ventilation system.
Crankcase gas system operation
The crankcase ventilation valve is used to regulate the pressure of the crankcase gases entering the intake manifold. With a small drain valve, it is open. If there is significant flow in the inlet, the valve closes. The operation of the crankcase ventilation system is based on the use of the vacuum that occurs in the intake manifold of the engine. When diluted, gases are removed from the crankcase. In the oil separator, the crankcase gases are cleaned of oil. Then the gases are directed through the nozzles into the intake manifold, where they are mixed with air and burned in the combustion chambers. For turbocharged engines, crankcase ventilation throttle control is provided. Gas vapor recovery system. The evaporative emission control system is designed to prevent the release of gasoline vapor into the atmosphere.
Where is the crankcase system used?
Vapors are formed when gasoline is heated in a fuel tank, as well as at reduced atmospheric pressure. Gasoline vapors accumulate in the system when the engine starts, are displayed in the intake manifold and burn out in the engine. The system is used on all modern models of gasoline engines. The gasoline vapor recovery system combines a coal adsorber. Solenoid valve for cleaning and connecting pipelines. The basis of the system design is an adsorber that collects gasoline vapors from a fuel tank. The adsorber is filled with granules of activated carbon, which directly absorb and store gasoline vapors. The adsorber has three external connections: a fuel tank. Through it, fuel vapor enters the adsorber through the intake manifold with the atmosphere. Through an air filter or a separate inlet valve.
Crankcase gas system diagram
Creates a pressure drop that is necessary for cleaning. Scheme of a gas vapor recovery system. The adsorber is freed from accumulated gasoline vapor by purging (regenerating). To control the regeneration process, an EVAP solenoid valve is included in the EVAP system. The valve is the drive mechanism of the engine management system and is located in the pipeline connecting the container to the intake manifold. The container is blown under certain engine operating conditions (crankshaft speed, load). At idle and with a cold engine, cleaning is not performed. When working with the electronic control unit, the solenoid valve opens.
Crankcase gas system principle
Gasoline vapors located in the adsorber are fed by vacuum to the intake manifold. They are sent to the collector and then burned in the combustion chambers of the engine. The amount of gasoline vapor delivered is controlled by the valve opening time. At the same time, the engine maintains an optimal ratio of air to fuel. In turbo engines, the turbocharger does not create vacuum in the intake manifold. Therefore, an additional two-way valve is included in the EVAP system, which is activated and sends fuel vapor when the container is pumped into the intake manifold or to the compressor inlet under piston pressure.
Questions and answers:
Why do blow-by gases appear? Due to wear on the piston group. When the O-rings wear out, compression forces some of the gases into the crankcase. In modern engines, the EGR system directs such gases for afterburning in the cylinder.
How to check crankcase gases correctly? The appearance of oil stains in the air filter, oil seals and at the junction of the valve cover, oil drips appear, around the filler neck and on the valve cover, oil drips, blue smoke from the exhaust.
What is crankcase ventilation for? This system minimizes the emission of harmful substances (a mixture of oil, exhaust gases and unburned fuel into the atmosphere) due to their afterburning in the cylinders.

