
How to measure DC amps with a multimeter
Content
Electricity and electronic components are absolutely nothing without current or an amplifier.
When you're working on an electronic circuit, you may need to check the amps going through it to diagnose the problem you're having.
There is a lot of confusion when it comes to measuring amperage, and this is due to the different types of amperage as well as its similarity to voltage.
In this guide, we will walk through the entire process of measuring DC current with a multimeter.
Let's get started.

What are amperes or amperage?
The DC amplifier is just one type of amplifier. You need to know what an "amp" is before you can understand why measuring DC current is not as easy as you might expect.
"Ampere" is the SI unit for measuring current, while "Ampere" is simply a measure of the amount of current flowing through a circuit.
Many people confuse current with voltage, and we assure you that there is a difference.
Current differs from voltage in that voltage is a measure of the speed of current (amps) flowing through a circuit.
Take current as water in a pipe, and voltage as the amount of pressure pushing that water through or out of the pipe.
The pipe in this case is an electrical circuit.
Now there are two types of current measurement; DC amplifier and AC amplifier.
How is a DC amplifier different from an AC amplifier?
Direct current (DC) amplifier refers to current that flows in one direction.
On the other hand, alternating current (AC) amplifier refers to current that flows in both directions.
DC amplifier measurements are usually more common for battery-powered devices, as power is only drawn from the battery rather than transferred to it.
The AC amplifier is more commonly found in appliances or devices that use transformers.
AC and DC amps have the same current. From what has been said, the only difference between the two is that power or current only flows in one direction with a DC amplifier, while with an AC amplifier it flows in both directions.
Moving forward, what tools do you need to accurately measure the DC current of an electronic component or circuit?
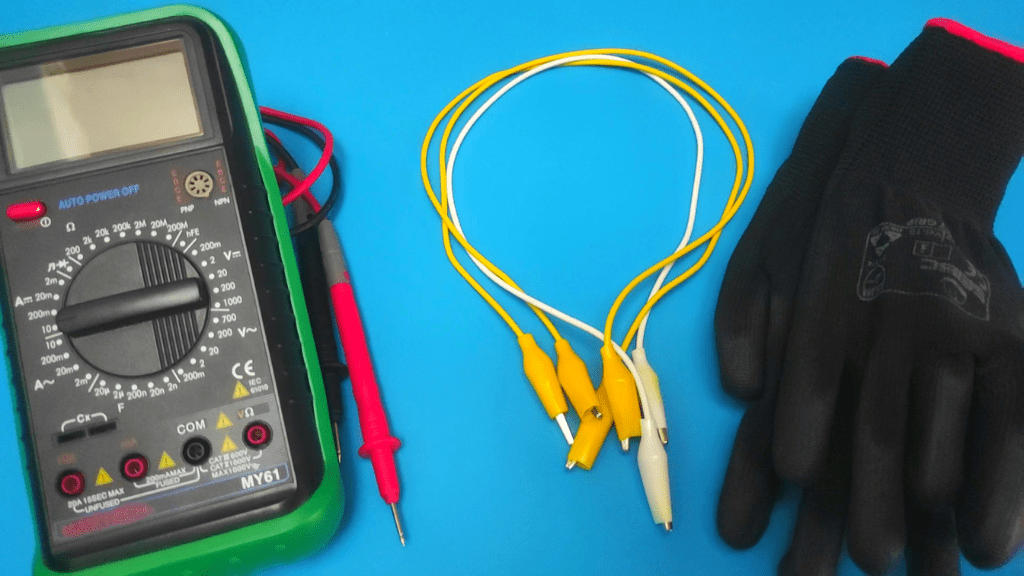
Tools needed to measure DC current
To measure DC amps you will need
- Multimeter for measurements
- Crocodile clips for easy connections
- Insulated gloves for protection
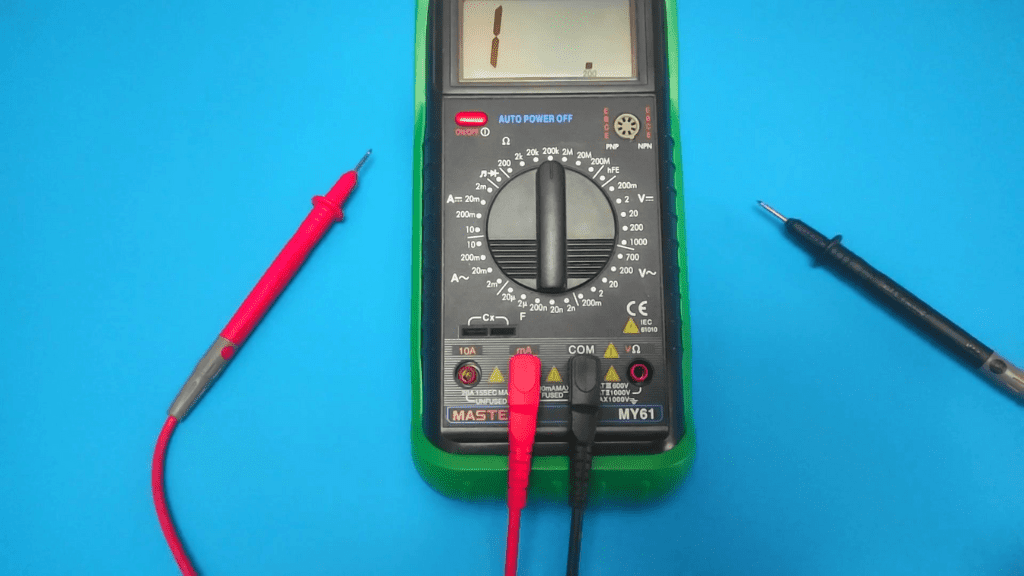

You can also use a clamp meter to measure DC power in a circuit, but this article will focus on how you can use a multimeter to test a DC amplifier.
How to measure DC amps with a multimeter
Connect the black lead to the "COM" port, connect the red lead to the port marked "A" or "10A", and set the multimeter to the nearest DC amplifier range for the device specifications. Place the probes on the appropriate terminals and check the results on the meter screen.
There is more information about each of these steps, and we will go over them in detail.
- Connect the black lead of the multimeter to the "COM" port.
A digital multimeter usually works with two probes; red positive probe and black negative probe.
Each of these probes has a large end that connects to the meter and a pointed metal end that goes to the device you want to test.
In addition, the multimeter has three ports to which probes are connected.
They are "COM" slot, "10A" slot and "VΩmA" slot. The "COM" and "10A" slots are important when it comes to DC amplifier.
Insert the large end of the black probe into the slot labeled "COM" on the meter. Alternatively, this slot may be labeled "-", meaning "negative".
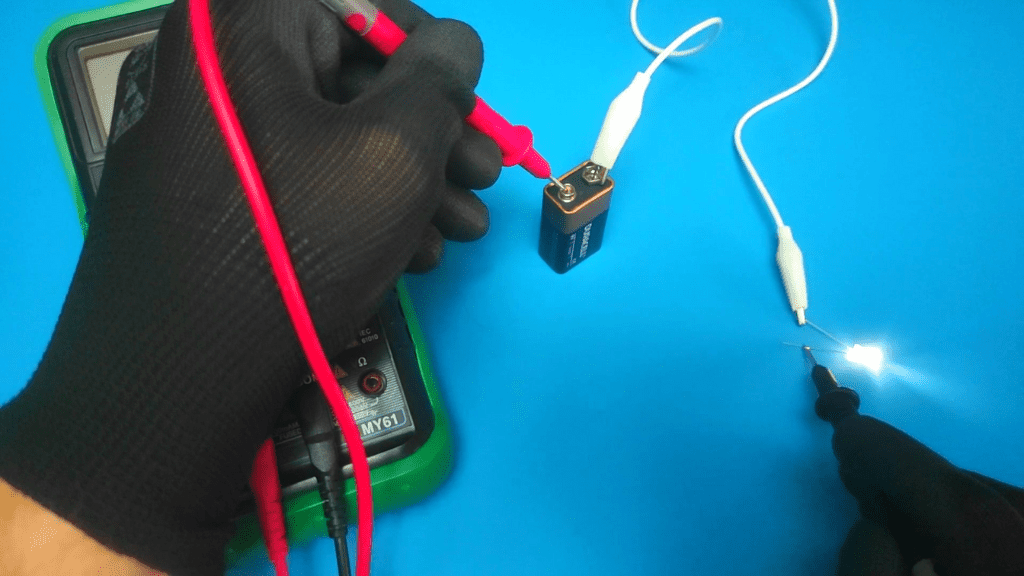
- Connect the red multimeter lead to the port labeled "A" or "10A".
The red probe is now inserted into either the slot labeled "A" or the slot labeled "VΩmA". "A" or "10A" are used to measure currents below 10 Amps.
While the "mA" slot represents a milliamp (weak current) up to 300mA. "V" in the same slot represents voltage and "Ω" represents ohms or resistance.
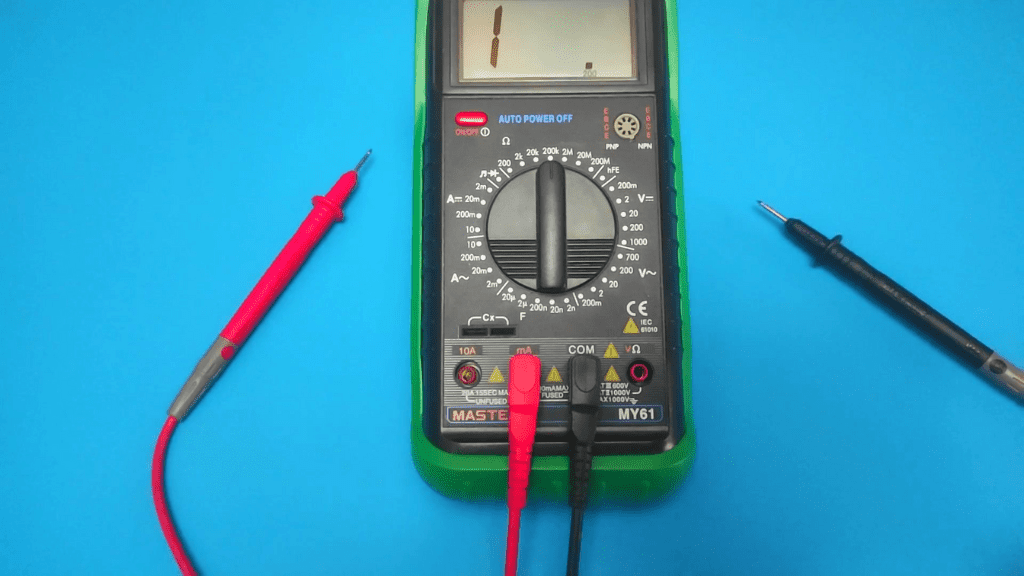

For any DC amplifier tests you wish to perform, always use slots "A" or "10A" to avoid overloading the meter.
- Set the multimeter to the nearest DC range
The DC amplifier is indicated on the multimeter by the letter "A-" (with three dots).
On the side where you see this symbol, you also see a range of numbers, with the best DMMs having five ranges (200u, 2m, 20m, 200m, and 10A).
They represent the maximum current you expect from the device or wire you want to test.
"μ" is a microamp, "m" is a milliamp, and "A" or "10A" is the standard measurement for whole amps.
If you want to set the multimeter to the DC range, turn the dial to the nearest higher value on the multimeter.
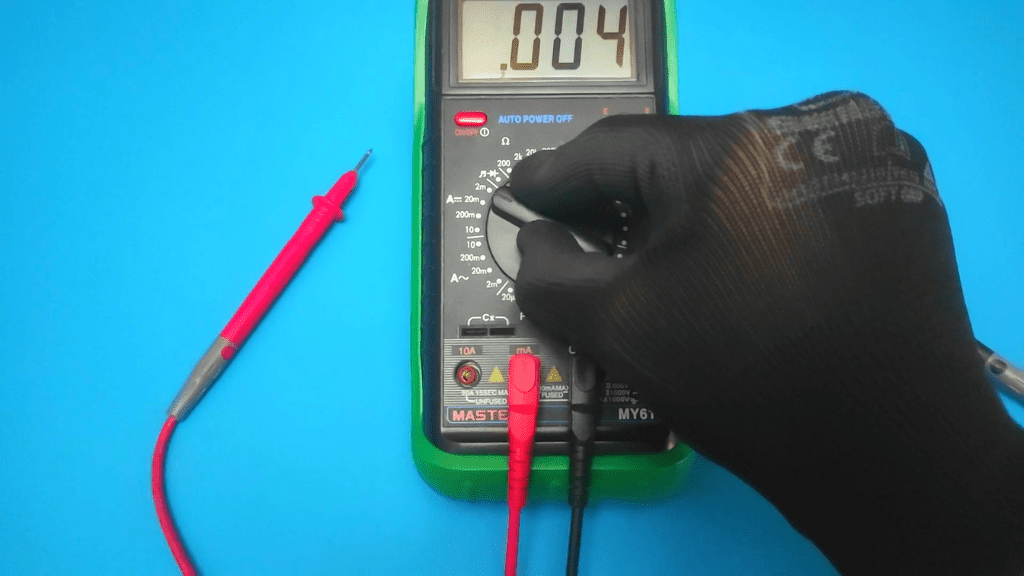

For example, if you want to measure a device with a specific 9 amp DC current, you set the multimeter to the 10 amp range.
To obtain the appropriate value, check the specifications of your device or electrical system for DC output voltage.
Selecting a higher range prevents overloading the multimeter, so it is very important to set these values and ranges correctly.
Setting the multimeter to the "10A" range is the best way to prevent overload. You also get results that can be converted to milliamps or microamps.
Some multimeters have an autorange feature that allows you to skip this manual setting.
However, knowing this is extremely important, as most multimeters require manual adjustment.
- Place the multimeter on the appropriate terminals
Whether it's loose wires in your car, connector terminals of various devices, or the DC batteries themselves, you connect the multimeter's leads to the appropriate points to test the DC amplifier.
These points vary by device, and some of them require terminal polarity.
This means that you need to position the multimeter leads between the device and the power supply. So use a multimeter to complete the circuit.
When measuring DC current, the multimeter acts as a wire to carry current.
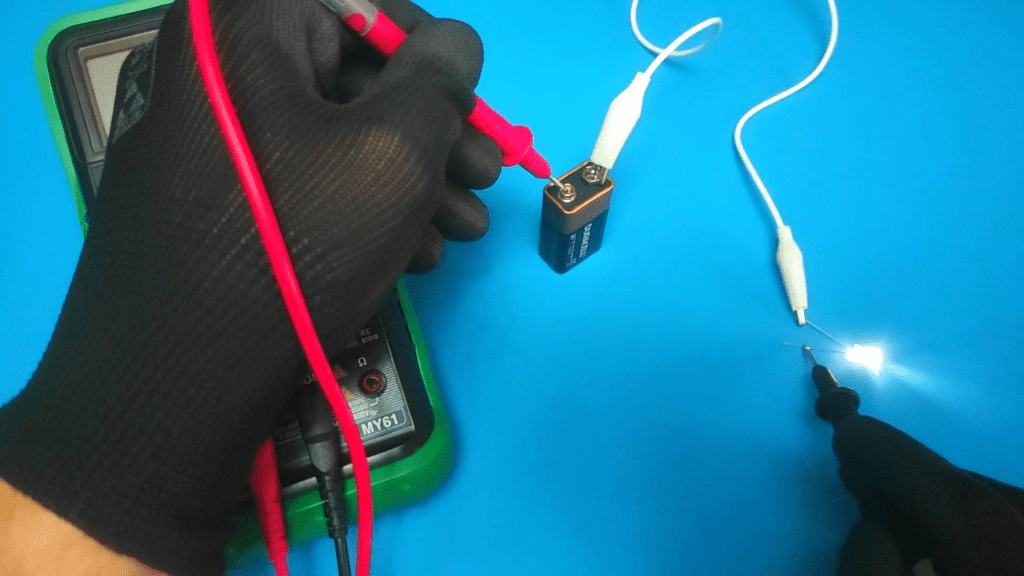
For example, you should place the red wire on the positive terminal of the battery and the black wire on the positive terminal of the device.
When testing an electric fence, the probe settings are completely different.
Some electrical components do not require this, so a little research should be done before diagnosing with a multimeter.
- Check the multimeter screen for results
As with probe placement, the results you expect from a multimeter will vary depending on the device you want to diagnose.
For example, a 9V battery is expected to give you a constant reading of about 0.9 amps, while testing an O2 sensor will show a reading of 0.2 to 1.5 amps.
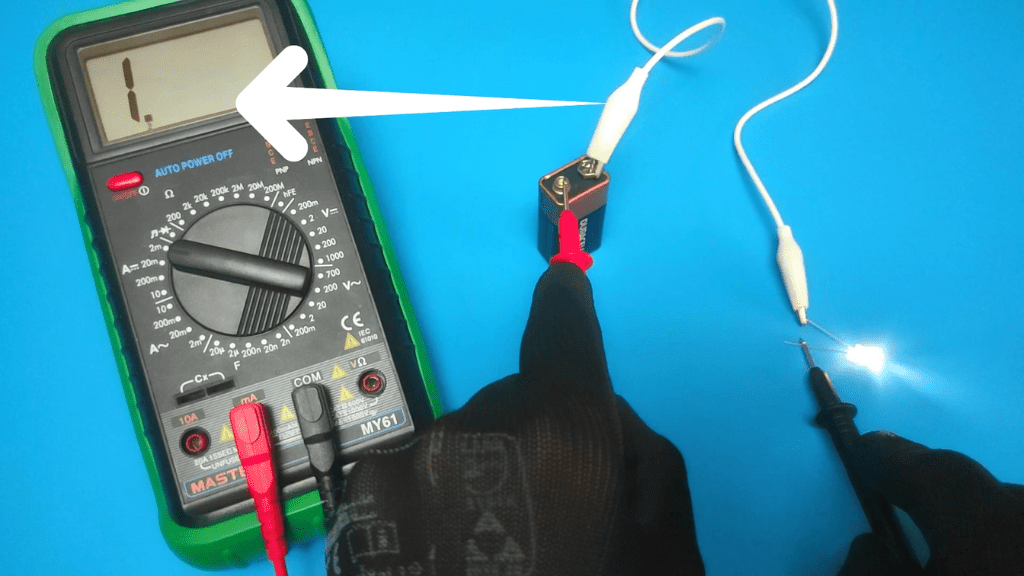
Also, when looking at the results, of course, a value that does not meet the required device specifications means that the DC current in the circuit is either insufficient or excessive.
Minor deviations in measurements are common.
Some devices, however, consider a small deviation too large, so you also do research to find out the exact results for the particular electronic component you are testing.
You can also watch our DC amplifier measurement video here:
Using Clamps to Measure DC Current
A clamp meter is a non-contact device that you use to measure current, voltage, or resistance in a wire. It works just like a multimeter, but instead of using probes to touch exposed terminals, you simply place a wire (even insulated) between the terminals.
Measuring DC current with a clamp meter is easier than measuring with a multimeter.
What's more, you can measure currents that range up to 1000A, and are typically at least 40A (which is a large measurement compared to a normal multimeter's maximum range of 10A).
This means that a clamp meter is a better option for measuring circuits or wires that carry a large number of amps.
To use it, you simply set it to the appropriate amp range (40A, 400A, or 1000A) and place the wire between the meter's terminals.
Your meter displays the measurement value when the wire is correctly aligned between the clamps.
Conclusion
Measuring a DC amplifier basically requires you to pay attention to the characteristics of the device or electrical component being diagnosed.
Any other procedure is as simple as it gets; insert the multimeter leads into the correct sockets, place the wires on the appropriate electrical terminals, and check the readings on the multimeter screen.
F.A.Q.
What is the amp symbol on a multimeter?
The amplifier is indicated by the letter "A-" with three dots on the multimeter. In this section, you also see a range of numbers including 200u, 2m, 20m, 200m, and 10A. The "10A" range is the safest of all.
What happens if you measure DC voltage with an AC multimeter?
If you measure DC voltage while setting AC voltage using the correct polarity, the multimeter will give you inaccurate results. You get zero value (0) when you reverse the polarity.

