
How to test a car air conditioner compressor with a multimeter
Content
There is hardly anything more annoying than your car's cooling system blowing out hot air on a very hot summer day. What then to use it in your car?
The automotive ventilation and air conditioning system provides a certain level of comfort for many people in both hot and cold seasons.
Ironically, most people don't pay attention to it until one of its most important components goes bad and the whole system stops functioning completely.
The component we're talking about here is the A/C compressor, and as expected, not everyone knows how to diagnose it.
Let's teach you how to test a car air conditioner compressor with a multimeter if you are not sure about your electrical skills.
Let's get started.
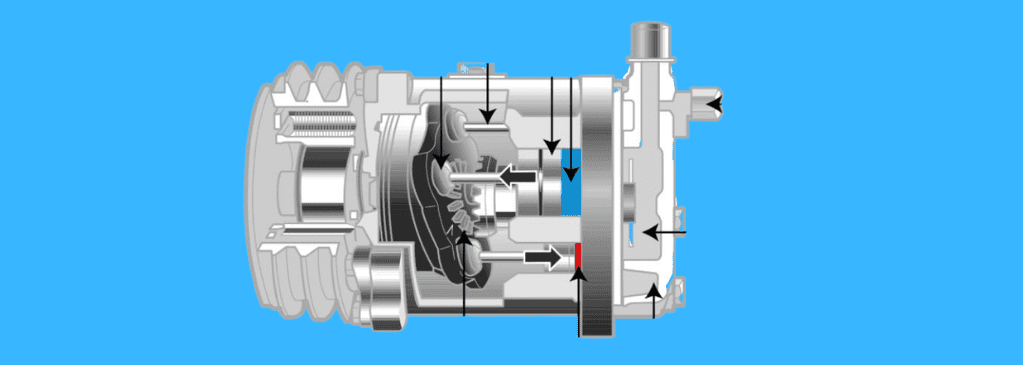
How does an AC compressor work?
An automotive A/C compressor is a component of a car engine that circulates cold refrigerant through the HVAC system.
It does this primarily through the compressor clutch, and is the solenoid that activates the A/C compressor pumping system when the PCM sends a signal to it.
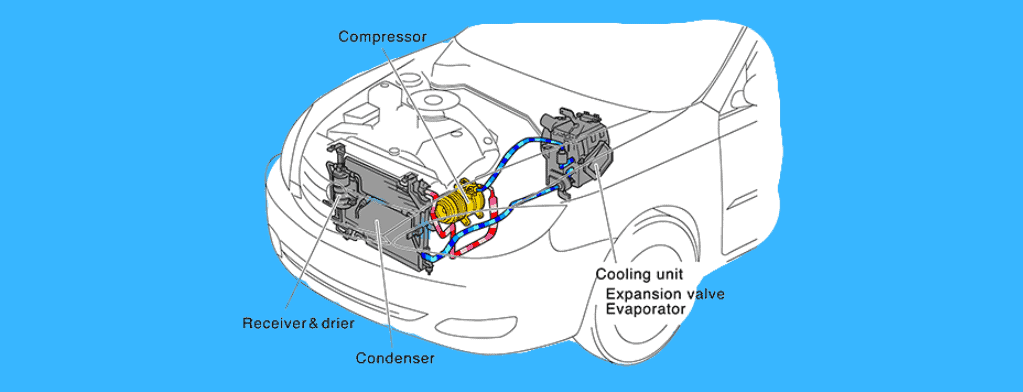
The whole air conditioning system includes six main components:
- Air conditioning compressor
- Capacitor
- Receiver dryer
- Expansion valve
- Evaporator.
The compressor acts on the cold refrigerant gas at high pressure, making it hot.
This hot gas passes into a condenser where it is converted to a high pressure liquid state.
This liquid enters a dryer receiver, which stores excess moisture, and then flows to an expansion valve, which converts the high pressure liquid into a low pressure liquid.
Now the liquid is cooled and sent to the evaporator, where it is finally converted back to a gaseous form.
The compressor is the heart of this air conditioning system, which pumps the refrigerant (blood) to keep all other components working properly.
When there is a problem with it, the whole air conditioning system works terribly and begins to show certain symptoms.
Signs of a Failing AC Compressor
Before the more obvious symptoms start to show, you'll probably notice that the air from your vents is still cool, but not as cold as it used to be.
Then you notice obvious signs like hot air escaping from your HVAC outlets.
Although it is important to note that these two symptoms can also be caused by depleted or leaking refrigerant and not by a bad A/C compressor.
RўRμRїRμSЂSЊ, more severe symptoms A/C compressor malfunctions include the AC turning on and off repeatedly during operation, or a high-pitched grinding sound (like metal scratching metal) coming from your engine.
This is usually caused by a worn A/C compressor bearing or a seized drive belt.
If you notice any of these signs, you need to check the compressor for faults.
However, in order to check the A/C compressor, you first need to find it, and it is quite difficult to keep searching without a guide.
Where is the air conditioning compressor located?
The air conditioning compressor is located in the in front of the engine (engine compartment) along with other components in an accessory belt configuration. It interacts with the accessory belt through the compressor clutch.
Necessary Equipment for Testing an AC Compressor
All the tools you need to test your car's AC compressor include
- digital multimeter,
- screwdrivers,
- Set of ratchets and sockets,
- And a manual for your car's air conditioner compressor model
How to test a car air conditioner compressor with a multimeter
Disconnect the power connector from the AC compressor clutch, place the positive test lead on one of the connector terminals, and place the negative test lead on the negative battery post. If you don't get any voltage then the compressor clutch power is bad and needs to be checked..
There are several steps before and after this procedure, and we will cover them in detail.
- Check for burns and other physical damage.
For this physical inspection and to avoid electrical shock and hazards, the first step is to disconnect the power circuit supplying current to your air conditioner.
You then unscrew and remove the bezel or access panel covering the air conditioner to expose its internal components.
This is when you inspect all wires and internal parts for burn marks and physical damage.
You will now begin a series of A/C compressor clutch tests.
- Check ground and power at A/C compressor clutch.
This first diagnostic aims to identify the condition of your compressor's clutch coils.
Set the multimeter to DC voltage and disconnect the connector from the AC compressor clutch.
Place the multimeter's positive lead on one of the connector's terminals and connect the negative lead to the negative battery post.
If you are not getting voltage, change the position of your positive lead to other terminals, or subsequently change the position of your negative lead to a different battery post.
Eventually getting voltage in one of these positions means the compressor clutch coil is the likely culprit and you need to repair or replace it.
- Checking Power Supply to AC Compressor Clutch
A zero voltage reading on your meter indicates that your problem is with the power supply to the AC compressor clutch.
Fortunately, there are certain ways to pinpoint the cause of your problem.
First, connect a positive test lead to each of terminals 2 and 3 of the compressor clutch (check them separately) and connect the negative test lead to the negative battery post.
If you don't get any readings from them, the fuse and wiring to the relay may be faulty and need to be replaced.
If you get a voltage reading, continue to place the negative test lead on terminal 3 and the positive test lead on terminal 4 of the connector.
A meter reading of zero means your PCM may be the problem, as it is not properly grounded to the coil of the control relay. This brings us to our next tests.
- Check the connectors to the pressure switch
When the previous test points to problems with grounding your PCM to the control relay coil, there are two main reasons for this.
- Your coolant is almost out or
- Your compressor pressure is at its maximum due to a faulty TMX valve or clogged ports.
Of course, low refrigerant levels can be caused by running out of freon (another name for refrigerant), and high pressure can be caused by an overfilled tank.
However, there is what we call an AC pressure switch. In a car, this is a pair of switches with valves located before and after the air conditioning compressor.
This component helps regulate the flow of refrigerant from the air reservoirs and shuts down the compressor when conditions become favourable, or extreme.
If these switches are faulty, you may have extremely low or high pressure causing the compressor to stop working.
To check the switches, you first need to check their connectors.
Disconnect the power connector, place the multimeter probes on the positive and negative terminals of the connector, and turn on the car AC at maximum power.
If you are not getting a reading, then the connector wires are bad and you need to repair or replace them.
If you get a value between 4V and 5V, the switch itself may be the problem and you'll proceed to test for continuity.
- Measure the ohmic resistance inside the switches
For the low level switch, turn the dial of the multimeter to the ohm (resistance) setting (denoted as Ω), place either probe of the multimeter on terminal 5 of the switch and the other probe on terminal 7.
If you get a beep or a value close to 0 ohms, then there is continuity.
If you get an "OL" reading, there is an open loop in its circuit and it needs to be replaced.
They are the same as for the high pressure analog, except you connect the multimeter wires to terminals 6 and 8 of the switch instead.
You are more likely to get an infinite ohm(1) reading on the multimeter if the switch is bad.
Conclusion
Checking the A/C compressor in your car is a step-by-step procedure that you should pay close attention to.
However, all you need to do is check the power supply to the A/C compressor clutch and pressure switch with a multimeter, depending on the results of your diagnosis.
You then repair/replace those components if you don't get the results you want from them. The best tactic is to completely replace the A/C compressor.
F.A.Q.
How do you test an AC compressor to see if it's working?
After you visually detect physical damage to the wires and internal components, use a multimeter to check the power supply to the compressor clutch and pressure switch.
How many volts should an AC compressor get?
The AC compressor supply voltage must be 12 volts. This is measured from the compressor clutch connector terminals as that is where the main battery power is sent.

