The principle of operation and design of hydraulic valve compensators
Content
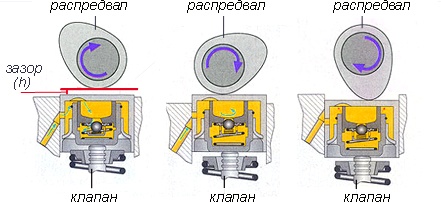
Engine gas distribution parts are subjected to heavy loads and high temperatures during operation. They expand unevenly when heated because they are made from different alloys. To form the normal operation of the valves, the design must provide for a special thermal gap between them and the camshaft cams, which closes when the engine is running.
The gap must always be within the prescribed limits, so the valves must be periodically adjusted, that is, select pushers or washers of a suitable size. Hydraulic compensators allow you to get rid of the need to adjust the thermal gap and reduce noise when the engine is cold.
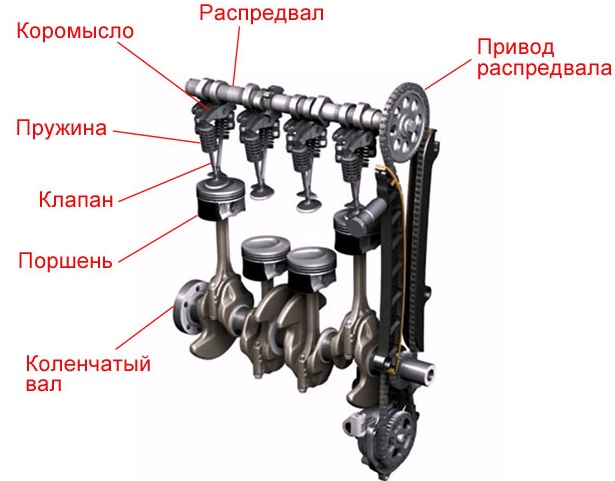
Hydraulic compensator design
Hydraulic compensators automatically correct the change in the thermal gap. The prefix "hydro" denotes the action of some liquid in the operation of the product. This fluid is oil supplied under pressure to the compensators. A sophisticated and precise spring system inside regulates the clearance.
The use of hydraulic lifters has the following advantages:
- there is no need for periodic adjustment of the valves;
- correct operation of the timing;
- noise reduction during engine operation;
- increase in the resource of the gas distribution mechanism nodes.
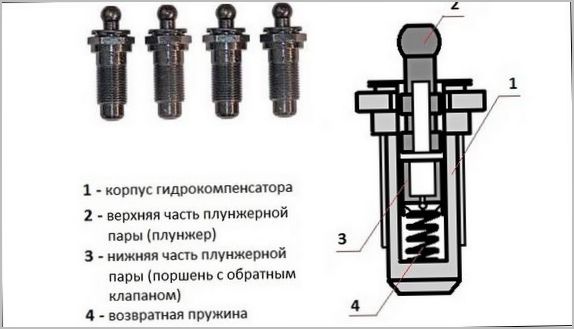
The main components of the hydraulic compensator are:
- the body;
- plunger or plunger pair;
- plunger bushing;
- plunger spring;
- plunger valve (ball).
How hydraulic lifters work
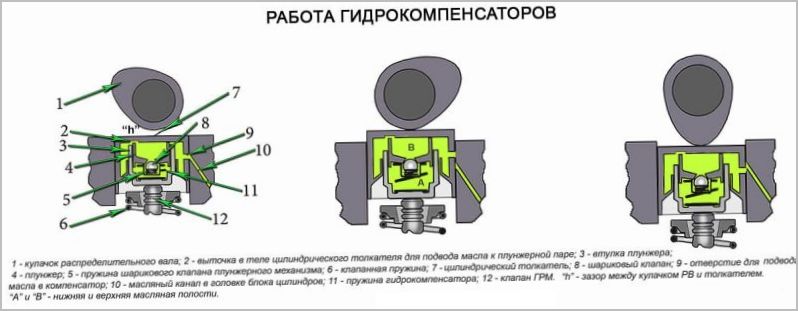
The operation of the device can be described in several stages:
- The camshaft cam does not exert pressure on the compensator and faces it with its back side, with a small gap between them. The plunger spring inside the compensator pushes the plunger out of the sleeve. At this moment, a cavity is created under the plunger, which is filled with oil under pressure through the combined channel and hole in the body. The oil volume is filled to the required level and the ball valve is closed by a spring. The pusher rests against the cam, the movement of the plunger stops and the oil channel closes. In this case, the gap disappears.
- When the cam begins to turn, it presses on the hydraulic compensator and moves it down. Due to the accumulated volume of oil, the plunger pair becomes rigid and transmits force to the valve. The pressure valve opens and the air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber.
- When moving down, some oil flows out of the cavity under the plunger. After the cam has passed the active phase of the impact, the working cycle is repeated again.
The hydraulic compensator also regulates the gap resulting from the natural wear of the timing parts. This is a simple, but at the same time complex mechanism for manufacturing with precise fitting of parts.
The correct operation of hydraulic lifters largely depends on the oil pressure in the system and its viscosity. Very viscous and cold oil will not be able to get into the body of the pusher in the required amount. Low pressure and leaks also reduce the efficiency of the mechanism.
Types of hydraulic compensators
Depending on the timing equipment, there are four main types of hydraulic lifters:
- hydraulic pushers;
- roller hydraulic pushers;
- hydro support;
- hydraulic supports that are installed under the rocker arms or levers.
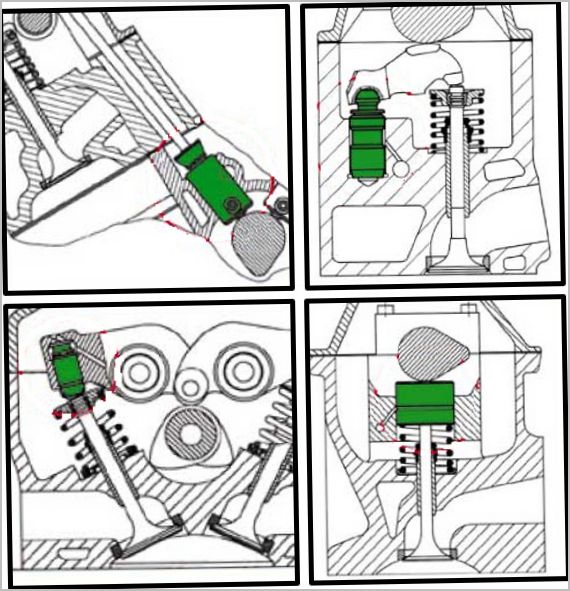
All types have a slightly different design, but have the same principle of operation. The most common in modern cars are conventional hydraulic tappets with a flat support for the camshaft cam. These mechanisms are mounted directly on the valve stem. The camshaft cam acts directly on the hydraulic pusher.
When the camshaft is in the lower position, hydraulic supports are installed under the levers and rocker arms. In this arrangement, the cam pushes the mechanism from below and the force is transmitted to the valve by a lever or rocker arm.
Roller hydro bearings work on the same principle. Rollers in contact with the cams are used to reduce friction. Roller hydraulic bearings are mainly used on Japanese engines.
Advantages and disadvantages
Hydraulic compensators prevent many technical problems during engine operation. There is no need to adjust the thermal gap, for example with washers. Hydraulic tappets also reduce noise and shock loads. Smooth and correct operation reduces wear on the timing parts.
Among the advantages there are also disadvantages. Engines with hydraulic compensators have their own characteristics. The most obvious of these is the uneven operation of a cold engine at start-up. There are characteristic knocks that disappear when temperature and pressure are reached. This is due to insufficient oil pressure at startup. It does not enter the compensators, so there is a knock.
Another disadvantage is the cost of parts and services. If it is necessary to replace it, it should be entrusted to a specialist. Hydraulic compensators are also demanding on the quality of the oil and the operation of the entire lubrication system. If you are using low quality oil, then this can directly affect their performance.
Possible malfunctions and their causes
The resulting knock indicates a malfunction in the gas distribution mechanism. If there are hydraulic expansion joints, the reason may be:
- Malfunction of the hydraulic pushers themselves - failure of the plunger pair or jamming of the plungers, jamming of the ball valve, natural wear;
- Low oil pressure in the system;
- Oil passages clogged in the cylinder head;
- Air in the lubrication system.
It can be quite difficult for the average driver to find a faulty lash adjuster. To do this, you can, for example, use a car stethoscope. It is enough to listen to each hydraulic lifter to identify the damaged one by its characteristic knock.
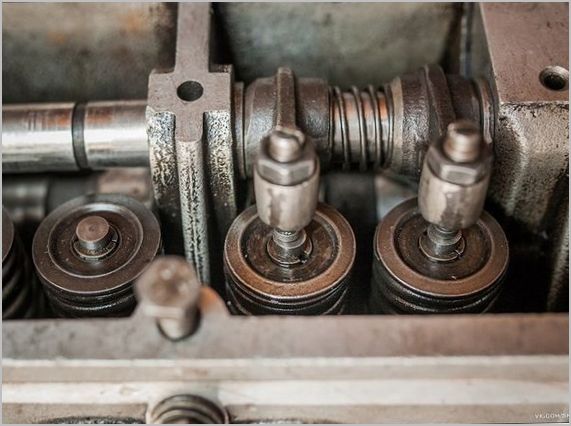

In addition, you can check the operation of the compensators, you can, if possible, remove them from the engine. They should not shrink when filled. Some types can be disassembled and the degree of wear of internal parts can be determined.
Poor quality oil leads to clogged oil passages. This can be corrected by changing the oil itself, the oil filter and cleaning the hydraulic lifters themselves. Can be washed with special fluids, acetone or high-octane gasoline. As for the oil, if the problem is in it, then after changing it, this should help eliminate the knock.
Experts recommend replacing not individual compensators, but all at once. This must be done after 150-200 thousand kilometers. At this distance, they wear out naturally.
When replacing hydraulic compensators, some nuances should be considered:
- The new hydraulic tappets are already filled with oil. This oil does not need to be removed. Oil is mixed in the lubrication system and air does not enter the system;
- After washing or disassembly, “empty” compensators (without oil) must not be installed. This is how air can get into the system;
- After installing new hydraulic compensators, it is recommended to rotate the crankshaft several times. This is necessary so that the plunger pairs come into working condition and the pressure increases;
- After replacing the compensators, it is recommended to change the oil and filter.
To keep hydraulic expansion joints from causing as few problems as possible during operation, use a high quality engine oil recommended in the vehicle's owner's manual. It is also necessary to follow the rules for changing the oil and filters. If these recommendations are followed, the hydraulic lifters will last a long time.

