The composition and features of the hydropneumatic suspension type Hydractive
Content
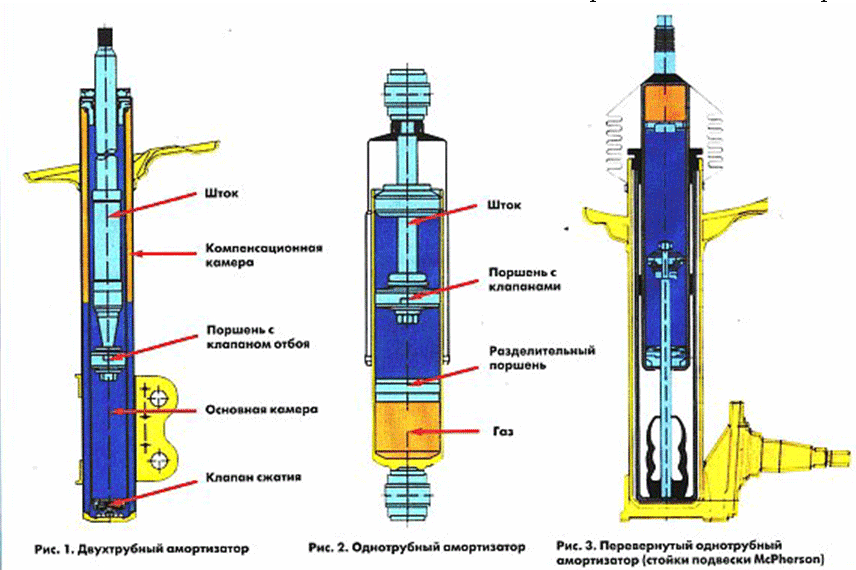
Hydropneumatic suspensions occupy a special place among the designs of the undercarriage of vehicles. This is a rather complex system, where the elastic element is nitrogen compressed to a pressure of over 50 atmospheres, limited by the metal body of the working spheres and hydraulic fluid through an elastic membrane. The pressure is transferred to the sphere by a hydraulic cylinder, the piston of which is connected to the suspension arm. Damping functions are performed by valves of variable section, located between the piston and the liquid in the sphere.

The advent of Hydractive suspension
On passenger cars, this type has been used since 1954, after its introduction on Citroën cars. At first, the development went from the installation of hydropneumatics only on the rear axle of the Traction Avant model, then the mechanisms of the entire chassis, including steering, transmission and brakes, were integrated into it. Later, with the development of the direction, the degree of integration was reduced, limited to suspension elements.
Stages of development
The functions of the system changed, the designers were constantly in search. There are three generations of the system, although there were many variants depending on the specific car model.
First appearance
The appearance of the system was formed quite quickly, which is due to the simplicity and logic of its concept. Some features were later removed and some added, but the structure changed little:
- to adjust the stiffness of the suspension, additional pneumohydraulic spheres were used, one for each axle;
- the activation of the Auto increased comfort mode was carried out by the decision of the electronic unit that controls the valves on the axles;
- in hard sport mode, the valves were closed, each wheel was left with only the amount of compressed nitrogen that was in the area of \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbthe corresponding independent suspension.
In appearance, a rather primitive regulation solution provided an amazing smooth ride and fast switching modes. Suspension height could be controlled by pumping additional fluid through hydraulic lines. At constant pressure, this added or decreased ground clearance.
What has changed in the second generation
Another sphere has been added to keep pressure in the rear suspension when the engine is off. The stiffness control algorithms have changed, and with them the names of the modes. The fundamental difference between them almost disappeared, the threshold values for valve actuation based on sensor signals simply changed. It became possible to quickly respond to rolls and tilts of the body.
Hydractive 3
There are already a lot more changes here:
- a more modern synthetic liquid such as LDS is used instead of the early "mineral water" LHM;
- there was an automatic switching of modes according to the height of the body, at high speeds it lowered, and when determining a bad road, it increased the clearance;
- the stiffness of the suspension began to be adjusted automatically;
- common components with power steering and brake system are excluded from the equipment;
- the names of manually selected modes have changed again.

An even more supplemented and improved version received the designation Hydractive 3+.
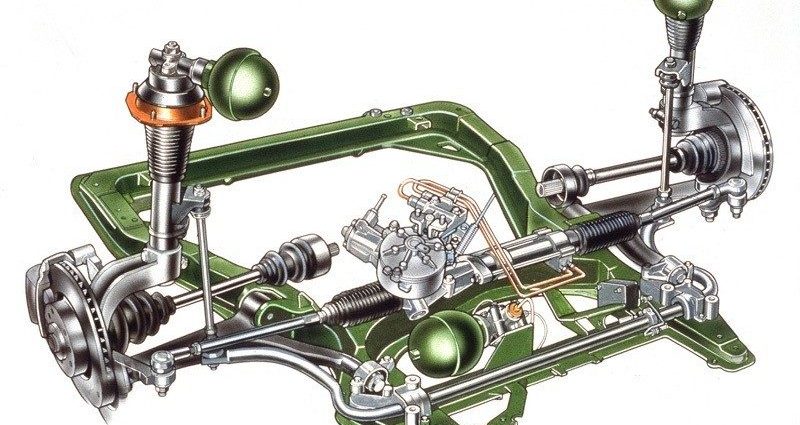
Suspension components and their function
The system is formed by the following basic units:
- working elements for each wheel - hydropneumatic spheres with separation of nitrogen and liquid by an elastic diaphragm;
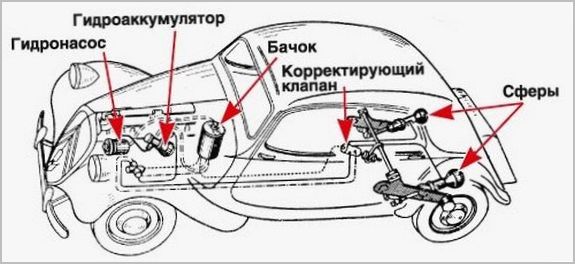
- mechanical, engine-driven, or later electric pump with pressure accumulator;
- additional tanks for various purposes that control the stiffness of the suspension;
- control mechanisms in the form of hydraulic valves with electric drive;
- high and low pressure pipelines distributed throughout the vehicle;
- control electronic unit with sensors and interface to other systems.
The pistons of the hydraulic cylinders of each wheel were connected to the usual mechanical guide vanes of independent suspensions, including the MacPherson type, but without shock absorbers and springs. Their role was performed by throttling hydraulic valves in the over-piston space and compressed gas in the spheres.
Suspension work
The force from the moving wheel through the guide apparatus, rod and piston is transferred to the liquid in the working wheel spheres. Due to its incompressibility, the oil operates under the same pressure throughout the system, provided that the control valves are open. The gas in the spheres, on the contrary, is compressed, reducing the volume and increasing the pressure. Thus, an increase in the effort of resistance to the piston stroke in the hydraulic cylinder is achieved, and hence counteracting the compression of the suspension.
Thanks to pipelines, pressure can be transmitted to any point in the system, and therefore it can be regulated on all wheels. The possibility of counteracting body pecks, rolls, changes in ground clearance depending on the vehicle load is implemented.

The properties of compressed gas, which are fundamentally different from the qualities of the metal used in springs, and even more so from multi-leaf springs experiencing internal friction, have become the most useful for improving smooth running. The accuracy of the suspension response in dynamic mode is provided by a built-in damper in the form of adjustable throttle holes, through which fluid flows from the piston to the membrane inside the sphere.
The working fluid for the system was also changed twice. The first, red LHS, was developed as an alternative to conventional brake fluid, but retained some of its shortcomings, in particular, the ability to saturate with moisture. The resulting corrosion reduced the durability of the active suspension. Then it was replaced with a green mineral oil of the LHM type, which eliminates this drawback. But its base, developed on the basis of oils for automatic transmissions, had its own problems in the form of rapid aging. The latest versions are filled with orange LDS synthetics, which best meet the requirements of the hydropneumatic elements of the system. Liquids are incompatible and non-interchangeable, the membranes in the spheres are designed strictly for their type.
The production technology of the most important element of hydraulic suspension - nitrogen-filled spheres, provides an almost unlimited service life of diaphragm seals. But the inevitable nitrogen leaks over long periods of time lead to their excessive deformation and rupture. Initially, pumping of spheres in operation was envisaged, then filling valves were abolished. But the fundamental possibility of adding gas is still available.
A ruptured membrane stops the normal operation of the serviced wheel, but for safety reasons, a safety mode is provided in its ride height area.
Advantages of hydropneumatics
This type of suspension has long been not limited to use on Citroen cars. Many premium models from different manufacturers are equipped with them, where special requirements are placed on the precise operation of the undercarriage. This gives the machines special qualities that are almost unattainable by other means:
- a combination of comfort, smoothness and excellent handling;
- working out tasks on all types of road surfaces;
- electronic control of suspension functions in all modes, from parking to fast movement on motorways;
- automatic adaptation and manual control;
- high reliability in the latest versions, comparable to more traditional types of suspensions.
The only disadvantage is the high complexity, which greatly affects the price of the car. This is not so noticeable in the premium class, but practically excludes the use in budget segments.